California Weekly Time Sheet for Multiple Pay Rate
What is this form?
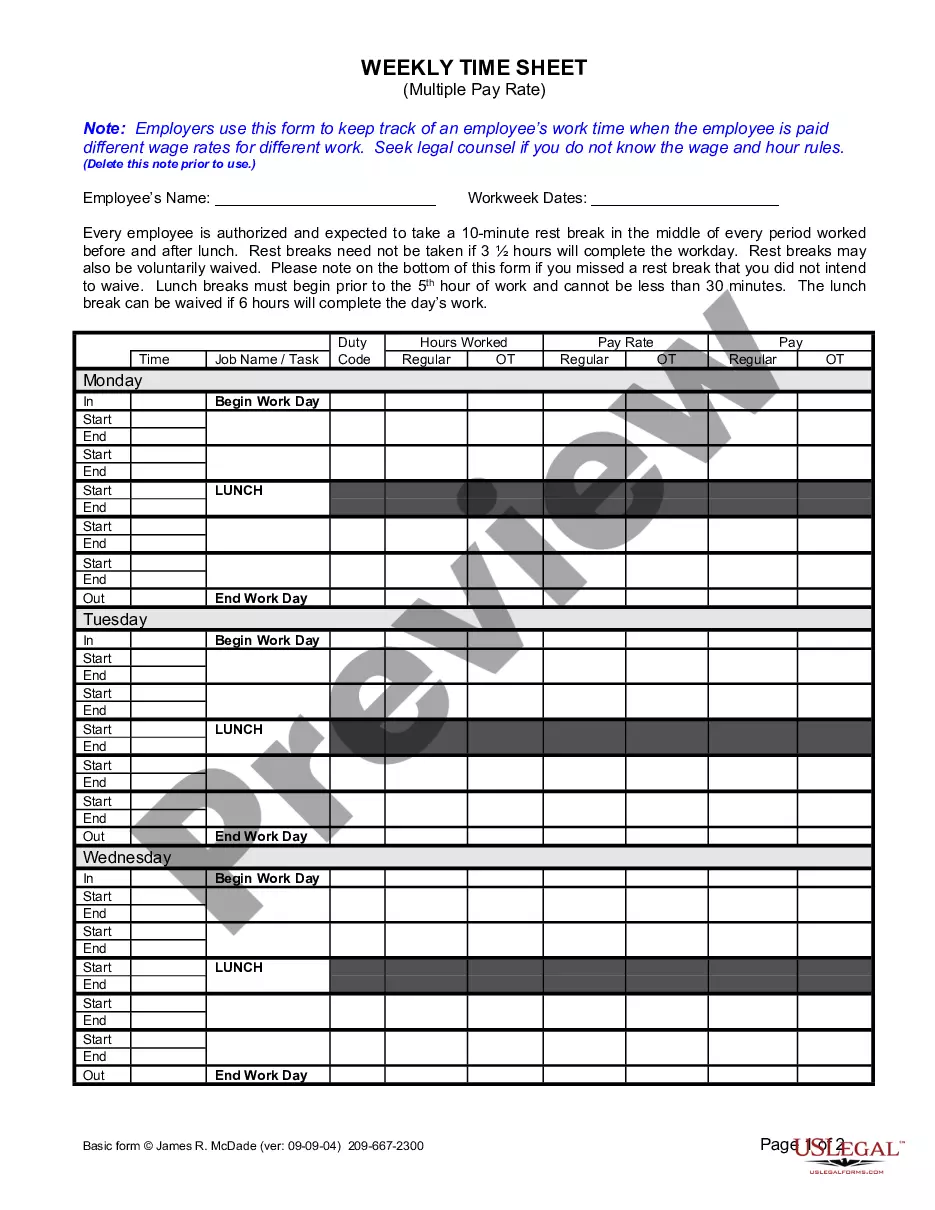
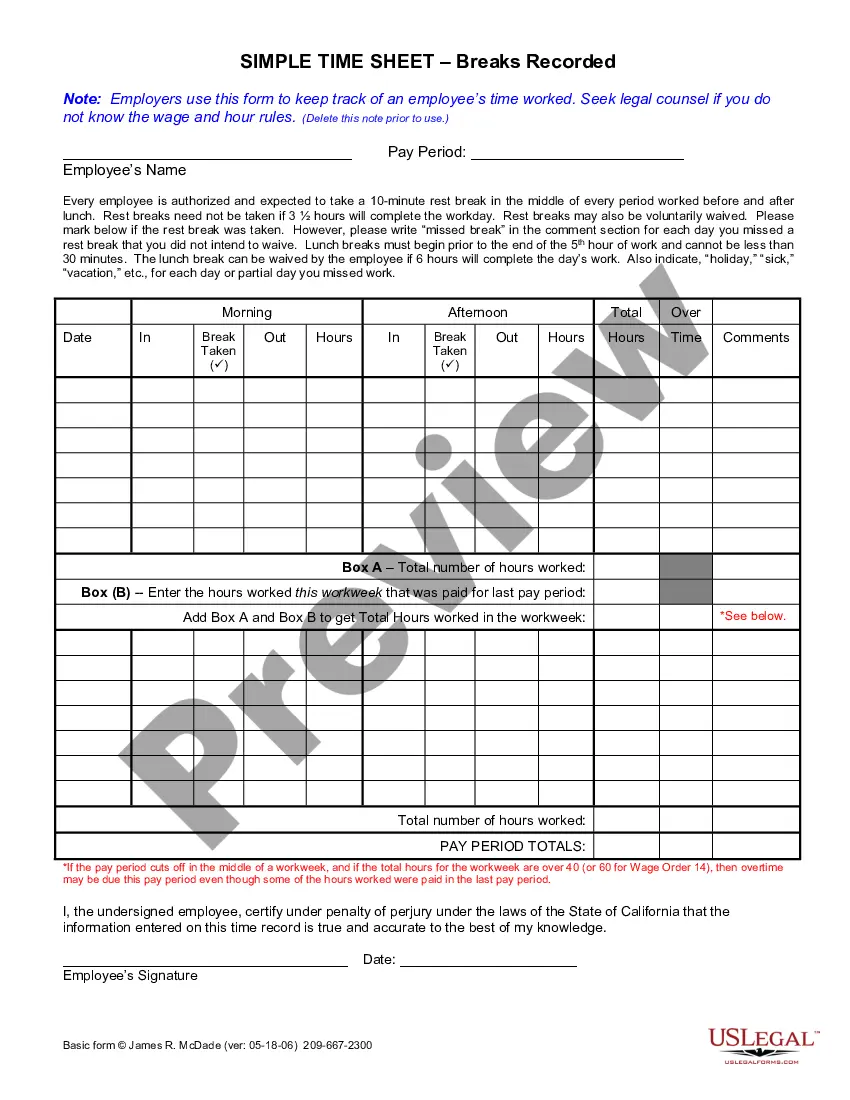
The Weekly Time Sheet for Multiple Pay Rate is a legal document used by employers to accurately track the work hours of employees who are compensated at different wage rates for various tasks. This form helps ensure compliance with wage and hour laws by detailing hours worked at different pay rates, which is essential for proper payroll processing. Unlike regular time sheets, it accommodates multiple pay rates within a single reporting period, making it a valuable tool for organizations with diverse job roles.
When to use this form
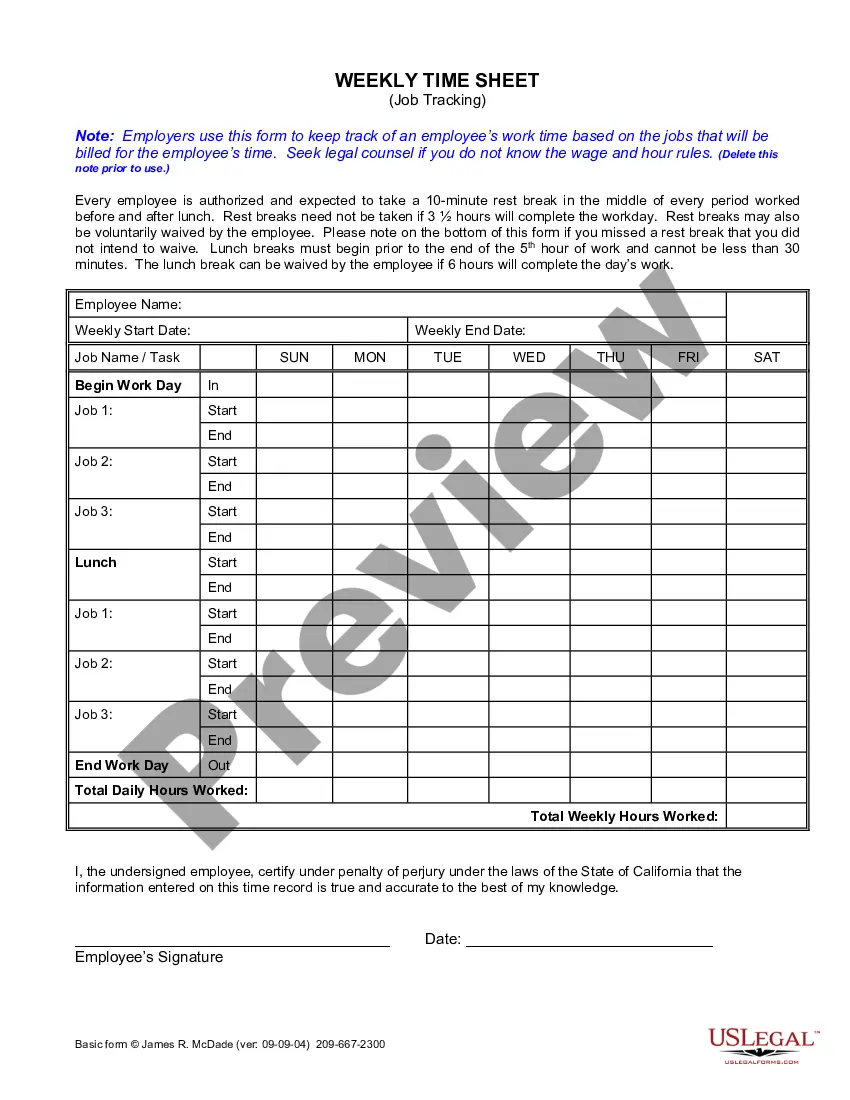
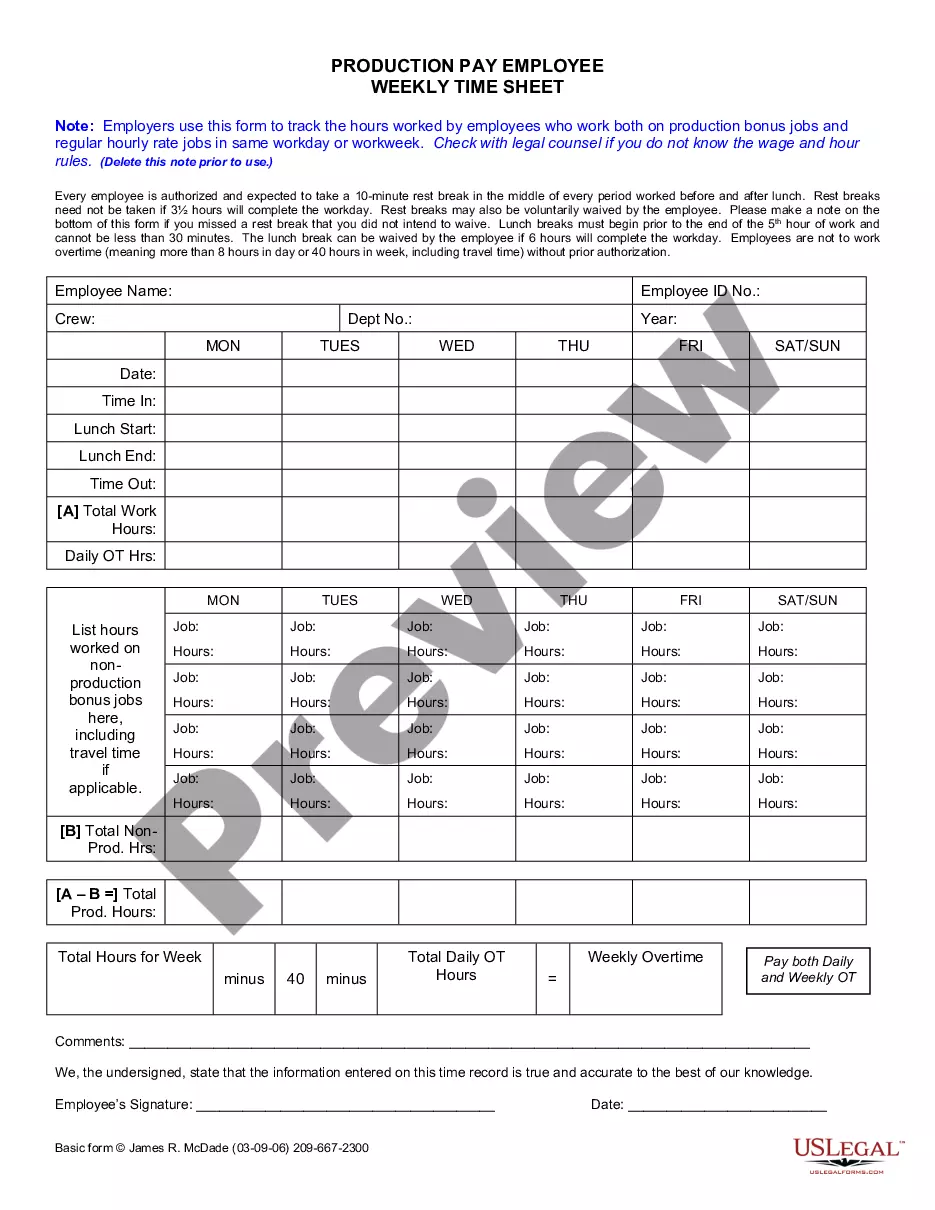
This form should be used whenever an employee works at multiple pay rates during the same week. It is particularly applicable for companies with varied job assignments, such as construction, healthcare, or any industry where task-specific pay is common. It is also beneficial for accurately documenting overtime hours worked when different rates apply.
Who can use this document
- Employers who have employees with varied pay rates for different tasks.
- Payroll departments responsible for tracking work hours and processing payroll.
- Human resource professionals ensuring compliance with labor laws.
Steps to complete this form
- Enter the employee's name and the workweek dates at the top of the form.
- Record daily work hours in the designated sections, including start and end times.
- Indicate the job name or task performed for each segment of work.
- Fill out the corresponding pay rates for regular and overtime hours.
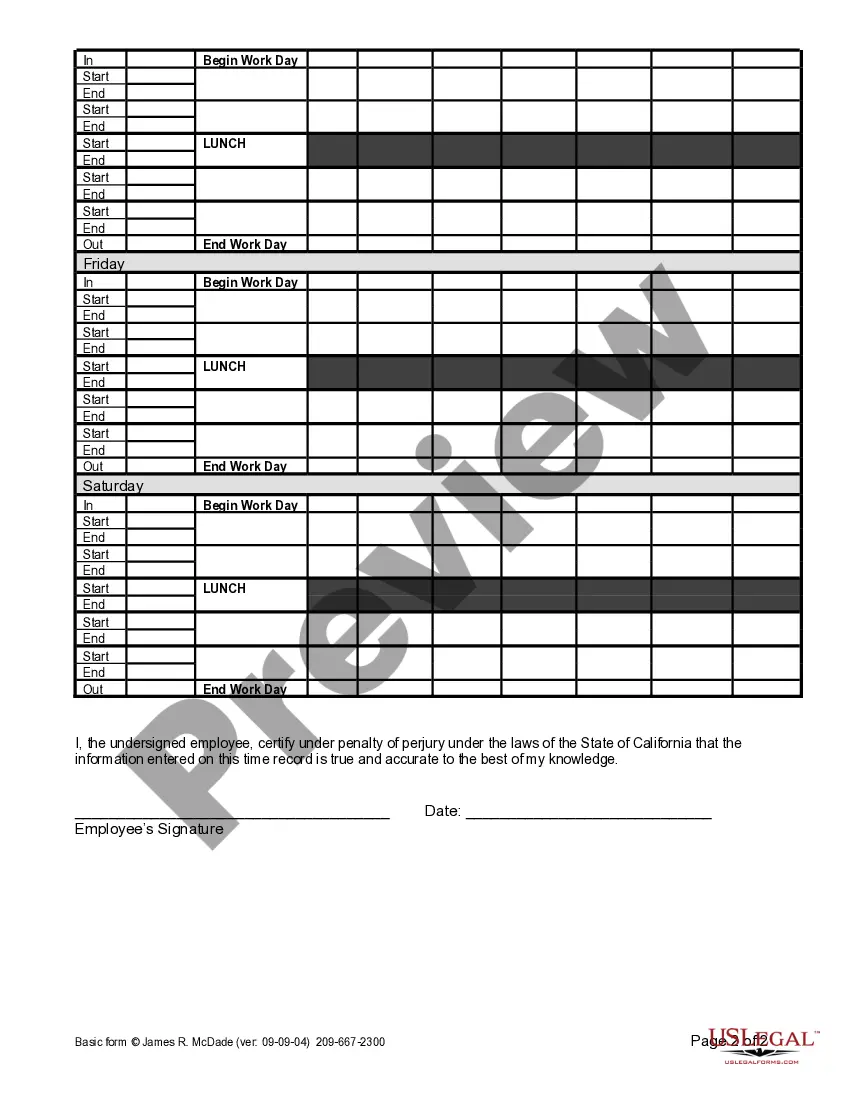
- Certify the accuracy of the information by signing and dating the form.
Notarization requirements for this form
This form does not typically require notarization to be legally valid. However, some jurisdictions or document types may still require it. US Legal Forms provides secure online notarization powered by Notarize, available 24/7 for added convenience.
Get your form ready online
Our built-in tools help you complete, sign, share, and store your documents in one place.
Make edits, fill in missing information, and update formatting in US Legal Forms—just like you would in MS Word.
Download a copy, print it, send it by email, or mail it via USPS—whatever works best for your next step.
Sign and collect signatures with our SignNow integration. Send to multiple recipients, set reminders, and more. Go Premium to unlock E-Sign.
If this form requires notarization, complete it online through a secure video call—no need to meet a notary in person or wait for an appointment.
We protect your documents and personal data by following strict security and privacy standards.
Make edits, fill in missing information, and update formatting in US Legal Forms—just like you would in MS Word.

Download a copy, print it, send it by email, or mail it via USPS—whatever works best for your next step.

Sign and collect signatures with our SignNow integration. Send to multiple recipients, set reminders, and more. Go Premium to unlock E-Sign.
If this form requires notarization, complete it online through a secure video call—no need to meet a notary in person or wait for an appointment.
We protect your documents and personal data by following strict security and privacy standards.
Common mistakes to avoid
- Failing to record all hours worked, leading to potential pay discrepancies.
- Not signing the form, which can invalidate the time record.
- Ignoring rest break policies, which may affect compliance with labor laws.
Advantages of online completion
- Convenient access to the form anytime, allowing for timely submissions.
- Editability for accurate and updated information before printing.
- Secure storage options for digital records, reducing paperwork clutter.
Looking for another form?
Form popularity
FAQ
In the cells which you want to calculate the payment for regular hours and overtime, enter the formula =F8I2 and formula =G8J2 separately, see screenshots: In the formula, F8 and G8 are the cells containing total regular hours and total overtime, I2 and J2 contain the payment per hour.
- Triple time which indicates that your regular rate multiplied by 3; - Triple time and a half which means your standard rate is multiplied by 3.5; - Or can be a quadruple time which is normal pay rate multiplied by 4, or even a customizable value by case (Other). Overtime hours worked and pay period (both optional).
For hourly, nonexempt employees, FLSA overtime is determined by multiplying the regular rate of pay by 1.5 and then multiplying the result by the number of overtime hours for the workweek. Let's say the employee makes $15 per hour and has 48 hours for the workweek.
Step 1: Data Entry. Step 2: Calculate hours worked. Step 3: Calculate Pay. Step 4: Drag down and finish. Create a basic timesheet as described in Part A, Step 2: Data Entry. Step 3: Calculate Hours worked. Create a basic timesheet as described in Part A.
Here's how you calculate time in a daily Excel timesheet template: Insert =sum(D8+F8) into the "Daily total" cell (marked as G8 in this timesheet example). As soon as employees type the hours in the "Morning hours" and "Afternoon hours" cells, this time automatically gets added to the "Daily total".
Determine the employee's base pay. Calculate the weighted average pay rate. Determine the weighted overtime total. Calculate the total earnings. 20 hours X $20 + 20 hours X $15 +10 hours X $10 = $800; $800/50 total hours = $16 per hour.
Tip: You can also add up times by using the AutoSum function to sum numbers. Select cell B4, and then on the Home tab, choose AutoSum. The formula will look like this: =SUM(B2:B3). Press Enter to get the same result, 16 hours and 15 minutes.
Type the formula "=a2b2" in cell C2. This formula multiplies the employee's hourly rate by the number hours the employee worked per week. Change the number format of the cell to currency.
Overtime pay is calculated: Hourly pay rate x 1.5 x overtime hours worked. Here is an example of total pay for an employee who worked 42 hours in a workweek: Regular pay rate x 40 hours = Regular pay, plus. Regular pay rate x 1.5 x 2 hours = Overtime pay, equals.