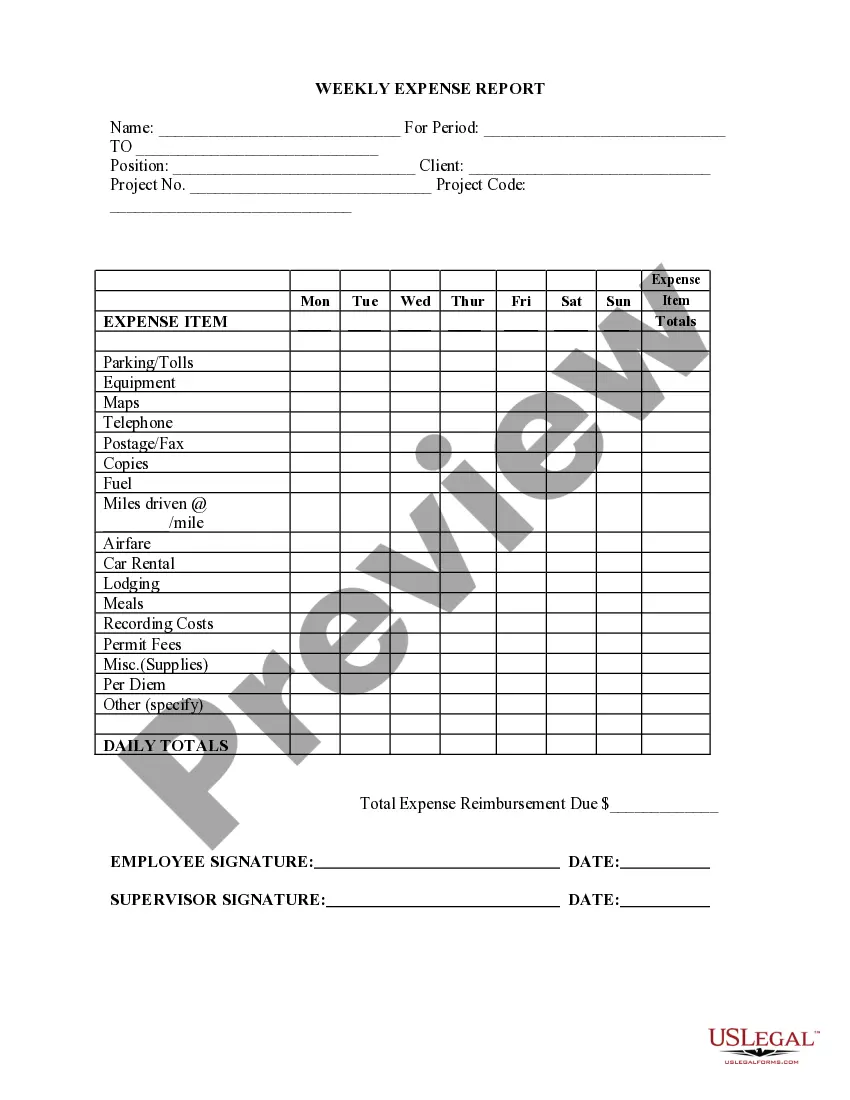
Oklahoma Employee Time Report (Nonexempt)
Description
How to fill out Employee Time Report (Nonexempt)?
You can spend countless hours online looking for the legal document template that fulfills the federal and state requirements you seek.
US Legal Forms offers thousands of legal forms that have been reviewed by professionals.
You have the option to download or print the Oklahoma Employee Time Report (Nonexempt) from our platform.
First, make sure you have selected the correct document template for your chosen state/region. Review the form description to confirm you have selected the right form. If available, use the Review button to examine the document template as well. If you need to find another version of the form, use the Search field to locate the template that suits your needs and criteria. Once you have found the template you wish to acquire, click Purchase now to proceed. Select the pricing plan you'd like, enter your details, and register for your account on US Legal Forms. Complete the transaction. You may use your credit card or PayPal account to pay for the legal form. Choose the format of the document and download it to your device. Make modifications to your document if needed. You can fill out, edit, sign, and print the Oklahoma Employee Time Report (Nonexempt). Download and print thousands of document templates using the US Legal Forms website, which provides the largest collection of legal forms. Utilize professional and state-specific templates to address your business or personal needs.
- If you already possess a US Legal Forms account, you can sign in and click the Download button.
- Next, you can fill out, modify, print, or sign the Oklahoma Employee Time Report (Nonexempt).
- Every legal document template you buy is yours permanently.
- To obtain another copy of a purchased form, visit the My documents section and click the appropriate button.
- If you are using the US Legal Forms website for the first time, follow the simple instructions outlined below.
Form popularity
FAQ
Salary level test. Employees who are paid less than $23,600 per year ($455 per week) are nonexempt. (Employees who earn more than $100,000 per year are almost certainly exempt.)
With few exceptions, to be exempt an employee must (a) be paid at least $23,600 per year ($455 per week), and (b) be paid on a salary basis, and also (c) perform exempt job duties. These requirements are outlined in the FLSA Regulations (promulgated by the U.S. Department of Labor).
Examples of non-exempt employees include contractors, freelancers, interns, servers, retail associates and similar jobs. Even if non-exempt employees earn more than the federal minimum wage, they still take direction from supervisors and do not have administrative or executive positions.
If you are a non-exempt employee, your employer must pay you at least the federal minimum wage (currently $7.25 per hour in Texas and under federal law) and must pay you overtime pay at a rate of at least one and a half times your hourly pay rate for all hours worked over 40 in each workweek.
Employees who do not meet the requirements to be classified as exempt from the Minimum Wage Act are considered nonexempt. Nonexempt employees may be paid on a salary, hourly or other basis. Employees who do not qualify for an exemption but are paid on a salary basis are considered salaried nonexempt.
Then consider yourself lucky: Neither federal nor state law makes this a legal requirement. In Oklahoma, no law gives employees the right to time off to eat lunch (or another meal) or the right to take short breaks during the work day. Employees must be paid for shorter breaks they are allowed to take during the day.
"Non-exempt" means an employee who is covered by the minimum wage and overtime provisions of FLSA or is granted special non-exempt status.
Meals and BreaksOklahoma does not have any laws requiring an employer to provide a meal period or breaks to employees sixteen (16) years of age or older, thus the federal rule applies. OK Dept. of Labor Wage Law FAQ The federal rule does not require an employer to provide either a meal (lunch) period or breaks.
Nonexempt: An individual who is not exempt from the overtime provisions of the FLSA and is therefore entitled to overtime pay for all hours worked beyond 40 in a workweek (as well as any state overtime provisions). Nonexempt employees may be paid on a salary, hourly or other basis.
Under Oklahoma law, employees under the age of 16 may not work more than 5 consecutive hours without a 30-minute rest period and must be permitted a 1-hour cumulative rest period for each 8 consecutive hours worked (OK Stat.