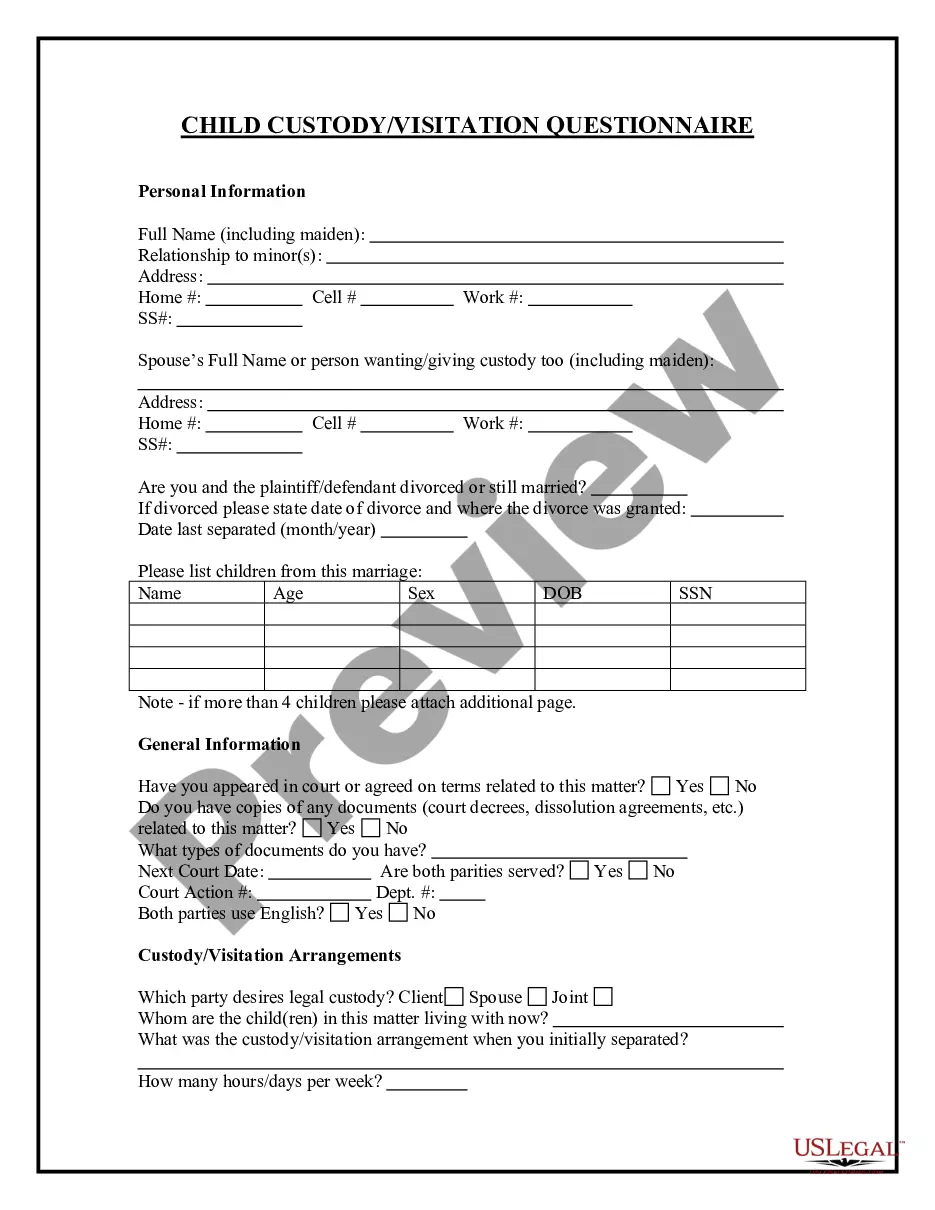
New Hampshire Jury Instruction - 1.9.1 Miscellaneous Issues Respondent Superior
Description
How to fill out Jury Instruction - 1.9.1 Miscellaneous Issues Respondent Superior?
If you want to full, obtain, or print lawful document layouts, use US Legal Forms, the greatest collection of lawful kinds, that can be found on-line. Use the site`s simple and easy convenient look for to get the papers you need. A variety of layouts for company and individual purposes are sorted by categories and says, or keywords and phrases. Use US Legal Forms to get the New Hampshire Jury Instruction - 1.9.1 Miscellaneous Issues Respondent Superior in just a number of mouse clicks.
In case you are currently a US Legal Forms buyer, log in for your accounts and click on the Down load button to have the New Hampshire Jury Instruction - 1.9.1 Miscellaneous Issues Respondent Superior. You can also access kinds you in the past acquired from the My Forms tab of your own accounts.
If you are using US Legal Forms for the first time, refer to the instructions listed below:
- Step 1. Ensure you have chosen the form for that appropriate metropolis/country.
- Step 2. Make use of the Review choice to look over the form`s content. Never neglect to learn the outline.
- Step 3. In case you are unsatisfied together with the kind, make use of the Look for industry at the top of the display to get other types of the lawful kind web template.
- Step 4. When you have found the form you need, go through the Purchase now button. Opt for the prices strategy you prefer and put your credentials to register for the accounts.
- Step 5. Approach the deal. You can utilize your credit card or PayPal accounts to perform the deal.
- Step 6. Choose the structure of the lawful kind and obtain it on your gadget.
- Step 7. Full, modify and print or indication the New Hampshire Jury Instruction - 1.9.1 Miscellaneous Issues Respondent Superior.
Every lawful document web template you get is your own property for a long time. You possess acces to each and every kind you acquired in your acccount. Select the My Forms section and decide on a kind to print or obtain yet again.
Compete and obtain, and print the New Hampshire Jury Instruction - 1.9.1 Miscellaneous Issues Respondent Superior with US Legal Forms. There are many professional and state-particular kinds you can use for the company or individual requires.
Form popularity
FAQ
CACI (Pronounced "Casey") is the name of the Judicial Council of California Civil Jury Instructions, the official civil jury instructions and verdict forms approved by the council on July 16, 2003.
CITE THIS PUBLICATION: Judicial Council of California Civil Jury Instructions (2023 edition) Cite these instructions: ?CACI No. _________.? Cite these verdict forms: ?CACI No. VF-_________.? This edition of CACI includes a number of additions and changes to the instructions, which were first published in 2003.
California Civil Jury Instruction 3113 addresses recklessness as a high probability that a person's conduct would cause harm, and he or she knowingly disregarded this risk.
The judge issues their jury instructions at the end of a trial, once the prosecution and defense have presented all of their evidence and arguments.
CACI Jury Instruction 3927 reads as follows: CACI 3927 - Aggravation of Pre-existing condition or disability: Plaintiff is not entitled to damages for any physical or emotional condition that he/she had before defendant's conduct occurred.
Types of Jury Instructions One is an ?official? plain-English set known as CACI (California Civil Jury Instructions). The other is BAJI (Book of Approved Jury Instructions). Either can be used. If there are no standard instructions that fit the case, ?special instructions? are drafted.