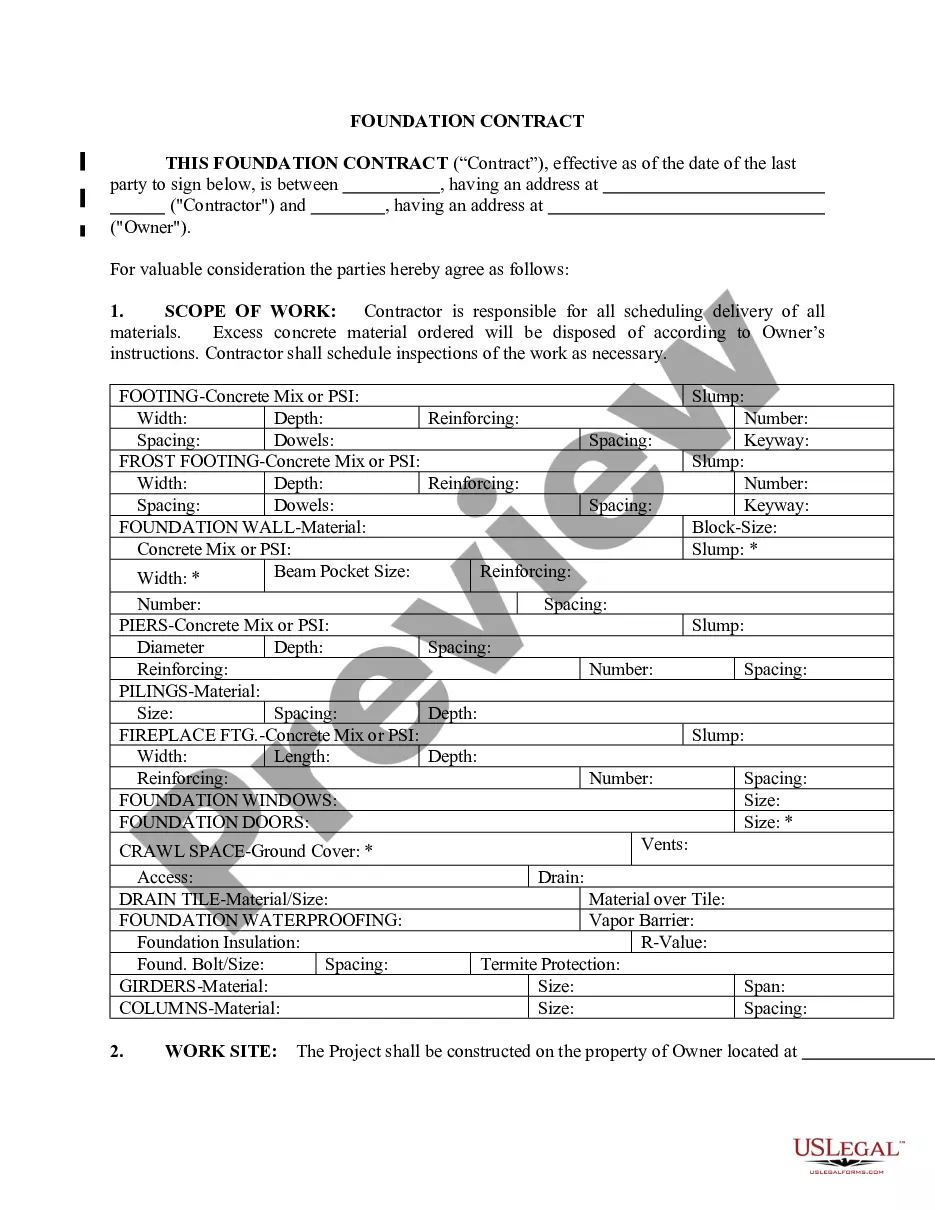
Declaratory Judgment Act With Hasan Minhaj In Suffolk
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
A declaratory judgment is typically requested when a party is threatened with a lawsuit but the lawsuit has not yet been filed; or when a party or parties believe that their rights under law and/or contract might conflict; or as part of a counterclaim to prevent further lawsuits from the same plaintiff (for example, ...
Similarly, the Declaratory Judgment Act, 28 U.S.C. § 2201, is not an independent source of federal jurisdiction. The purpose of that Act is merely to provide an additional remedy, once jurisdiction is found to exist on another ground.
The benefit of a declaratory judgment is that it prevents lawsuits that are likely to be unsuccessful, which saves the courts, and ultimately taxpayers, resources and time. A policyholder that receives an unfavorable declaratory judgment is unlikely to file a lawsuit, as the suit is much more likely to be dismissed.
Declaratory relief allows a party who is not certain of his rights to prevent the accrual of avoidable damages and to obtain an adjudication before the parties bring a coercive lawsuit.
To bring a claim for declaratory judgment in a situation where a patent dispute may exist or develop, the claimant must establish that an actual controversy exists. If there is a substantial controversy of sufficient immediacy and reality, the court will generally proceed with the declaratory-judgment action.
A declaratory judgment plaintiff does not need to allege actual infringement. It is sufficient, for standing purposes, to show that a party “has engaged in a course of conduct evidencing a definite intent and apparent ability to commence use of the mark.” See Starter Corp. v. Converse, Inc., 84 F.
A declaratory judgment is a ruling of the court to clarify something (usually a contract provision) that is in dispute. A summary judgment is a ruling that a case or portion of a case must be dismissed because there are no triable issues of material fact in dispute.
Declaratory judgments have the same effect and force as final judgments and are legally binding.
Declaratory judgments can provide legal certainty to each party in a matter when this could resolve or assist in a disagreement. Often an early resolution of legal rights will resolve some or all of the other issues in a matter.
Declaratory judgments have the same effect and force as final judgments and are legally binding.