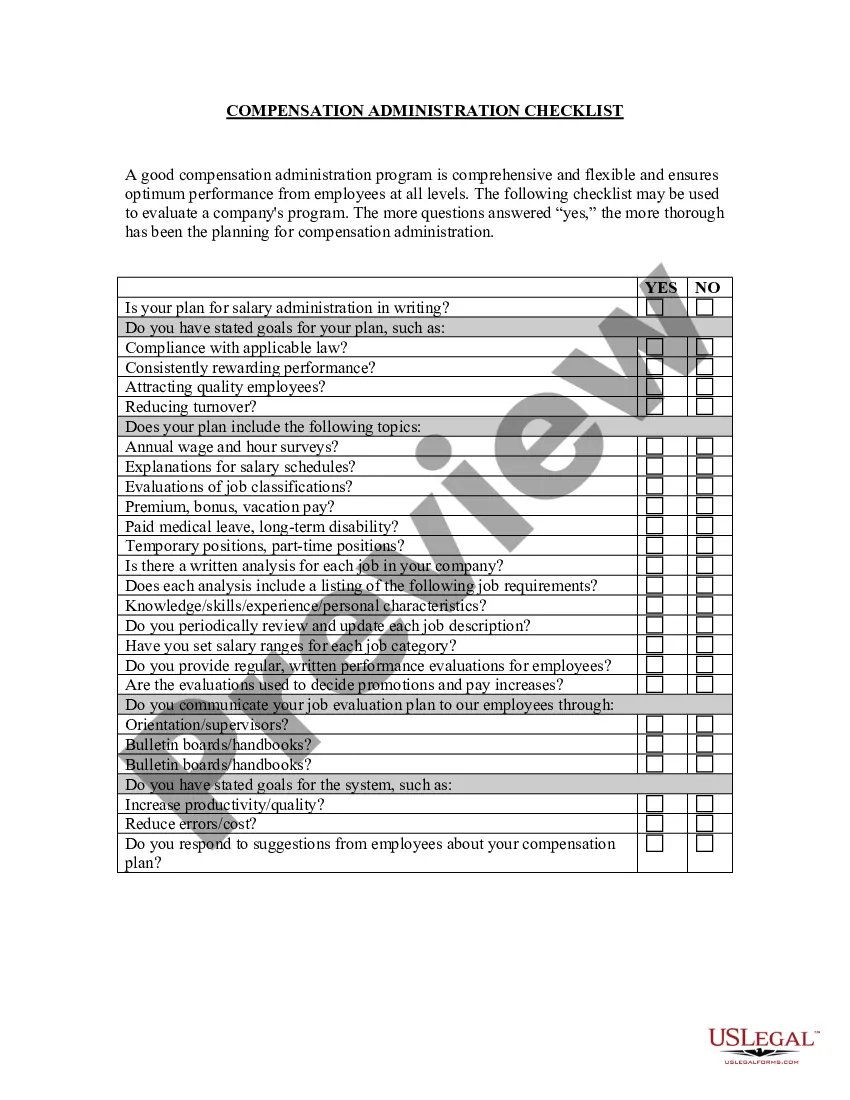
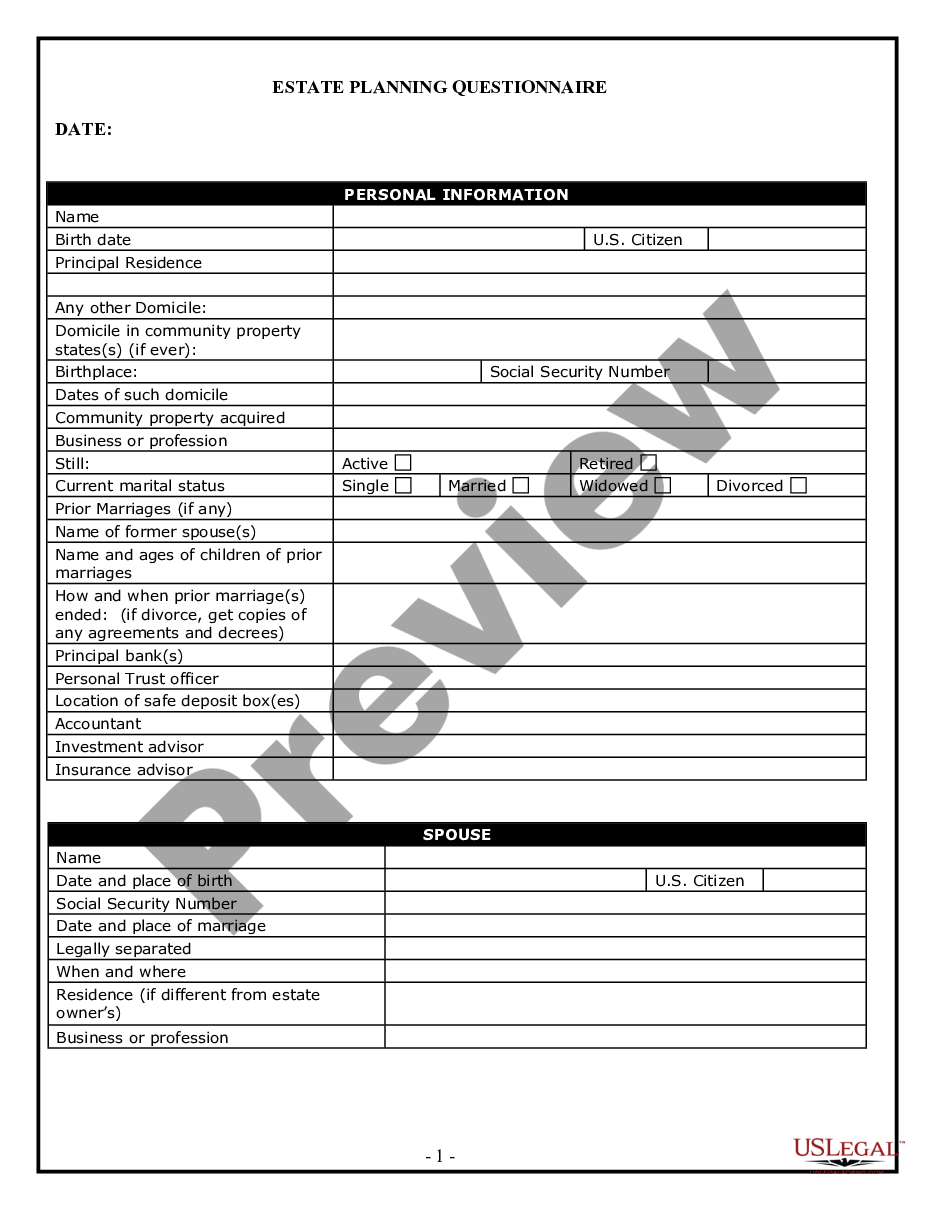
Washington Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist
Description
How to fill out Equal Pay - Administration And Enforcement Checklist?
You can spend time online searching for the legal document template that fulfills the state and federal requirements you require.
US Legal Forms offers a vast array of legal forms that are evaluated by experts.
You can conveniently download or print the Washington Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist from my support.
To find another version of the document, use the Search section to locate the template that meets your needs and requirements.
- If you already have a US Legal Forms account, you can sign in and click on the Acquire button.
- Then, you can complete, modify, print, or sign the Washington Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist.
- Every legal document template you receive is yours permanently.
- To obtain another copy of the purchased document, visit the My documents tab and click on the corresponding button.
- If you are using the US Legal Forms website for the first time, follow the simple instructions below.
- First, ensure you have selected the correct document template for the county/town of your choice.
- Review the document description to confirm you have chosen the right form.
Form popularity
FAQ
Moonlighting, or working a second job outside of your primary employment, is generally legal in Washington state. However, it is crucial to review your primary employer's policies and any contracts you may have signed. Employers may prohibit outside employment under certain conditions, particularly if it could conflict with their business interests. For guidance on navigating employment contracts and the Washington Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist, consider using resources from US Legal Forms.
Yes, in Washington state, employees have the right to request access to their personnel file. Employers must provide this file upon request within a reasonable timeframe. Understanding your rights related to personnel files is vital, and guidance on such matters can be found in the Washington Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist.
The 7-minute rule again highlights the requirement for employers to compensate employees for work correctly. If an employee works more than 7 minutes, they are entitled to pay for that duration. This rule is crucial for accurate payroll practices and is part of the guidelines in the Washington Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist, ensuring fair treatment.
In Washington, it is unlawful to ask job applicants about their salary history during the hiring process. This law supports equitable pay practices and aims to diminish wage disparities. The regulations related to salary history inquiries are detailed in the Washington Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist, making it vital for employers to adhere to them.
Washington state does not follow a 'use it or lose it' policy for vacation time. Instead, employers are required to pay out unused vacation days upon employment termination or if the employee requests it, as per the regulations. This is important to understand for proper employee rights, and the Washington Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist can help clarify these rules further.
The 7-minute rule in Washington state pertains to the payment for short increments of work time. If an employee works for more than 7 minutes, they must be compensated for that time. This rule ensures fair wages based on actual time worked and is included in the Washington Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist, providing clarity on compensation practices.
The 72-hour rule in Washington state refers to the requirement for employers to pay employees within a specified timeframe when they are terminated. Specifically, when an employee is laid off, they should receive their final paycheck within three business days. Understanding this rule is crucial for both employees and employers, and it’s addressed in the Washington Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist.
In Washington state, if you take your lunch break after working five hours, it may violate the meal break regulations. Employees are entitled to a meal break of at least 30 minutes if they work more than five hours in a shift. Failure to provide this break can lead to potential claims under the Washington Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist. You may wish to consult legal guidelines or resources for detailed compliance.