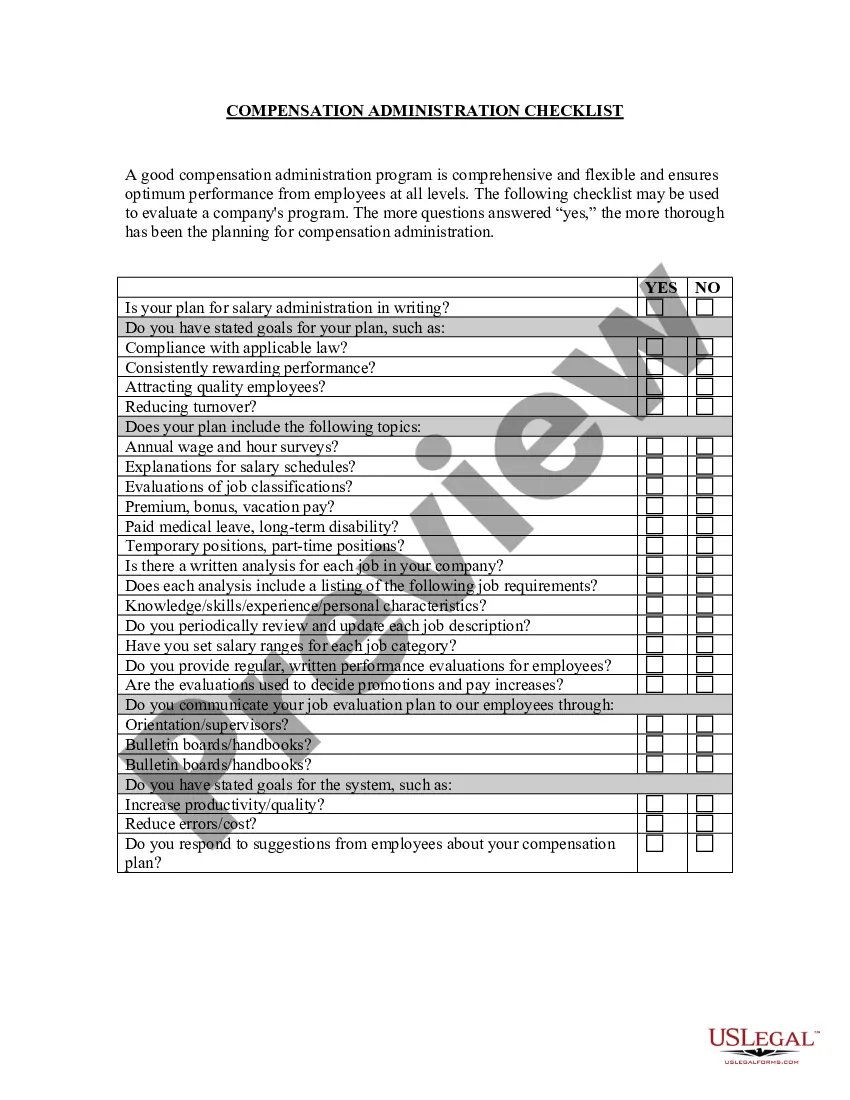
Washington Equal Pay Checklist
Description
How to fill out Equal Pay Checklist?
You can invest hours online trying to locate the authentic document template that satisfies the state and federal requirements you are looking for.
US Legal Forms offers numerous legitimate forms that have been vetted by experts.
You can download or print the Washington Equal Pay Checklist from our service.
To acquire another copy of your form, use the Search box to find the template that meets your needs and requirements. Once you have found the template you want, click Purchase now to proceed. Select the pricing plan you prefer, enter your details, and register for an account on US Legal Forms. Complete the transaction. You can use your Visa, Mastercard, or PayPal account to pay for the legitimate document. Choose the format of your document and download it to your device. Make adjustments to the document as needed. You can fill out, edit, sign, and print the Washington Equal Pay Checklist. Purchase and print numerous document layouts through the US Legal Forms website, which offers the largest collection of legitimate forms. Utilize professional and state-specific templates to address your business or personal needs.
- If you already have a US Legal Forms account, you can Log In and tap the Acquire button.
- Then, you can fill out, edit, print, or sign the Washington Equal Pay Checklist.
- Every legitimate document template you purchase is yours forever.
- To obtain another version of the retrieved form, navigate to the My documents section and click the respective button.
- If this is your first time using the US Legal Forms website, follow the simple instructions below.
- First, ensure that you have selected the correct document template for your desired state/area.
- Review the form details to confirm you have chosen the correct template.
Form popularity
FAQ
In Washington, employers must provide final paychecks to departing employees promptly. Generally, the final paycheck is due at the end of the last working day, or within three days if an employee is terminated. Compliance with these rules is essential for businesses and is included in the Washington Equal Pay Checklist. Using tools like US Legal Forms can help employers navigate these regulations effectively.
The Wage Payment Act in Washington state regulates how employers pay their workers, ensuring timely and complete compensation. This legislation is crucial for maintaining accountability and fairness in wage distribution. Understanding this law is part of the Washington Equal Pay Checklist, which helps employers adhere to ethical pay standards. By following this act, businesses can foster a respectful and responsible workplace culture.
In Washington state, employers cannot ask candidates about their salary history. This law supports fair pay practices and aligns with the Washington Equal Pay Checklist. Instead, employers should focus on a candidate's qualifications and the value they bring to the position. By doing so, organizations can promote equity and transparency in their hiring processes.
To conduct a payroll audit, start by reviewing your employee compensation records. Cross-check the pay rates against your established salary structure and evaluate if they align with your company’s pay policy. Utilize the Washington Equal Pay Checklist to ensure compliance with equal pay laws, and identify any discrepancies. If needed, consider using USLegalForms platform for resources and templates to streamline the audit process.
The Equal Pay Act requires that men and women in the same workplace be given equal pay for equal work. The jobs need not be identical, but they must be substantially equal. Job content (not job titles) determines whether jobs are substantially equal.
The Equal Pay Act (EPA) protects both men and women. All forms of compensation are covered, including salary, overtime pay, bonuses, life insurance, vacation and holiday pay, cleaning or gasoline allowances, hotel accommodations, reimbursement for travel expenses, and benefits.
Equal pay for equal work is the concept of labour rights that individuals in the same workplace be given equal pay. It is most commonly used in the context of sexual discrimination, in relation to the gender pay gap.
The Equal Pay Act requires that men and women in the same workplace be given equal pay for equal work. The jobs need not be identical, but they must be substantially equal. Job content (not job titles) determines whether jobs are substantially equal.
There are ways you can find out if you are being paid equally, including:asking your colleagues;conducting an equal pay questionnaire;checking job ads;researching job evaluation studies.
The EPA's four affirmative defenses allow unequal pay for equal work when the wages are set "pursuant to (i) a seniority system; (ii) a merit system; (iii) a system which measures earnings by quantity or quality of production; or (iv)any other factor other than sex."