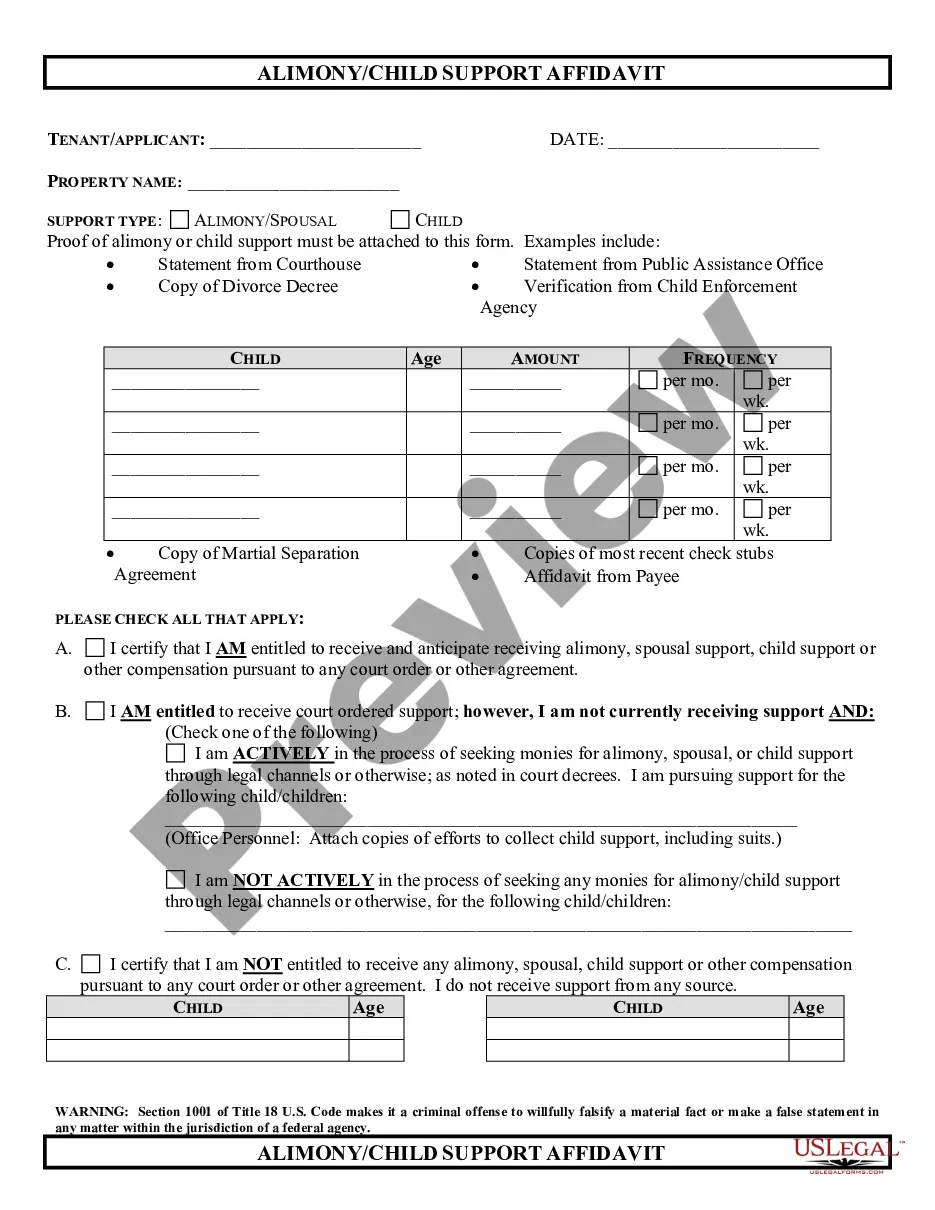
This package is only for parties with no children and with property and debts. It is also only for parties who have agreed to all of the terms of the divorce and who will execute a property settlement agreement. This package includes (1)Information about Divorce, (2) Forms List, (3) Forms Explanations, (4) Instructions and Steps, (5) Checklist, (6) Forms and (7) Access to divorce law summary for your State. The forms include the required petition or complaint, waiver, separation agreement, financial reporting statements, judgment and other forms to complete your divorce.
Hawaii No-Fault Agreed Uncontested Divorce Package for Dissolution of Marriage for Persons with No Children with or without Property and Debts
Description
How to fill out Hawaii No-Fault Agreed Uncontested Divorce Package For Dissolution Of Marriage For Persons With No Children With Or Without Property And Debts?
Access the largest collection of sanctioned forms.
US Legal Forms is a service where you can discover any specific state document in just a few clicks, such as the Hawaii No-Fault Agreed Uncontested Divorce Package for the Termination of Marriage for Individuals without Children with or without Assets and Liabilities samples.
There is no need to waste hours searching for a court-acceptable template. Our expert professionals guarantee that you will receive the latest templates consistently.
After selecting a pricing plan, create an account. Make payment via credit card or PayPal. Download the document to your computer by clicking on the Download button. That’s it! You are required to submit the Hawaii No-Fault Agreed Uncontested Divorce Package for the Termination of Marriage for Individuals without Children with or without Assets and Liabilities template and review it. To ensure everything is accurate, contact your local legal advisor for assistance. Register and conveniently browse through approximately 85,000 useful forms.
- To utilize the document library, choose a subscription and create an account.
- If you have already set it up, simply Log In and press the Download button.
- The Hawaii No-Fault Agreed Uncontested Divorce Package for the Termination of Marriage for Individuals without Children with or without Assets and Liabilities template will instantly be saved in the My documents section (a section for every document you save on US Legal Forms).
- To establish a new account, follow the brief guidelines below.
- If you need to use a state-specific template, ensure you specify the correct state.
- If available, examine the description to understand all the details of the document.
- Utilize the Preview option if it’s offered to review the document's content.
- If everything appears to be correct, click on the Buy Now button.
Form popularity
FAQ
When you use the Hawaii No-Fault Agreed Uncontested Divorce Package for Dissolution of Marriage for Persons with No Children with or without Property and Debts, you may not need to go to court. This package simplifies the process significantly, often allowing you to finalize everything without a court appearance. However, you may want to check specific local requirements to ensure that you complete all necessary steps. By choosing this package, you work towards a smoother, more straightforward path to divorce.
The primary alternative to a no-fault divorce is a fault-based divorce, where one spouse blames the other for the breakdown of the marriage. However, choosing a no-fault divorce, such as the Hawaii No-Fault Agreed Uncontested Divorce Package for Dissolution of Marriage for Persons with No Children with or without Property and Debts, often proves less stressful and more amicable. This method allows both parties to avoid prolonged conflict, focusing on a respectful separation instead. When you consider this option, you can achieve a fair outcome more peacefully.
The quickest divorce in Hawaii often occurs through the Hawaii No-Fault Agreed Uncontested Divorce Package for Dissolution of Marriage for Persons with No Children with or without Property and Debts. If both parties agree on the terms, you can finalize the divorce in as little as a few weeks. This package simplifies the procedure, helping you avoid unnecessary delays. Thus, prompt resolution becomes achievable without complications.
The timeline for an uncontested divorce in Hawaii typically ranges from a few weeks to several months. When you use the Hawaii No-Fault Agreed Uncontested Divorce Package for Dissolution of Marriage for Persons with No Children with or without Property and Debts, you can expedite the process. Once you file the necessary paperwork, the court usually processes it quickly if all documents are in order. Therefore, you can look forward to a smoother and faster resolution.
fault divorce in Hawaii means that neither spouse needs to prove blame in the dissolution of the marriage. Couples simply state that the marriage is irretrievably broken, which simplifies the proceedings. The Hawaii NoFault Agreed Uncontested Divorce Package for Dissolution of Marriage for Persons with No Children with or without Property and Debts offers a structured way to navigate this process effectively, ensuring all aspects are covered efficiently.
While no-fault divorce allows for a more amicable process, some may feel it's too simplistic and may not address underlying issues. Additionally, assets may be evenly divided, which can lead to dissatisfaction for one party. However, the Hawaii No-Fault Agreed Uncontested Divorce Package for Dissolution of Marriage for Persons with No Children with or without Property and Debts encourages open communication, helping mitigate these concerns.
The duration of an uncontested divorce in Hawaii can vary, but it typically takes around 1 to 3 months, depending on the court’s processing time. By utilizing the Hawaii No-Fault Agreed Uncontested Divorce Package for Dissolution of Marriage for Persons with No Children with or without Property and Debts, you can expedite the paperwork and streamline the overall process. This package provides clear instructions, which can further reduce delays.
fault divorce simplifies the process by allowing couples to separate without proving wrongdoing. This can foster a more cooperative environment, which is crucial when negotiating terms. By choosing the Hawaii NoFault Agreed Uncontested Divorce Package for Dissolution of Marriage for Persons with No Children with or without Property and Debts, you can benefit from a quicker and less stressful resolution.
In Hawaii, adultery does not directly affect the outcome of a no-fault divorce. Since the state recognizes no-fault grounds, the focus remains on the dissolution terms rather than accusations of infidelity. Utilizing the Hawaii No-Fault Agreed Uncontested Divorce Package allows couples to proceed with their divorce straightforwardly, without the need to delve into personal matters.
In a Hawaii divorce, the distribution of the house depends on various factors, including whether it's classified as marital or separate property. When using the Hawaii No-Fault Agreed Uncontested Divorce Package for Dissolution of Marriage for Persons with No Children with or without Property and Debts, both parties can negotiate the division of assets amicably. This approach can lead to a more satisfactory arrangement for both parties.