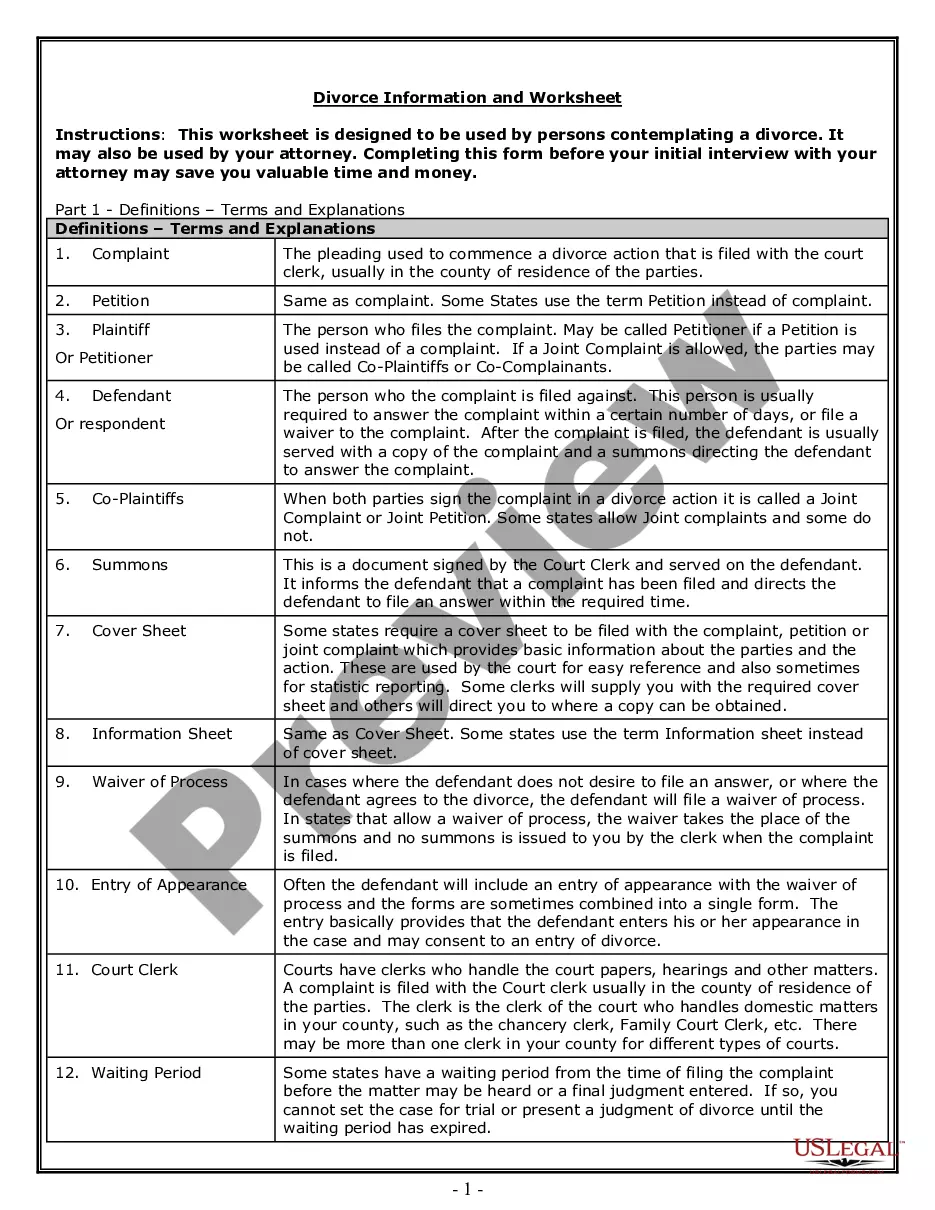
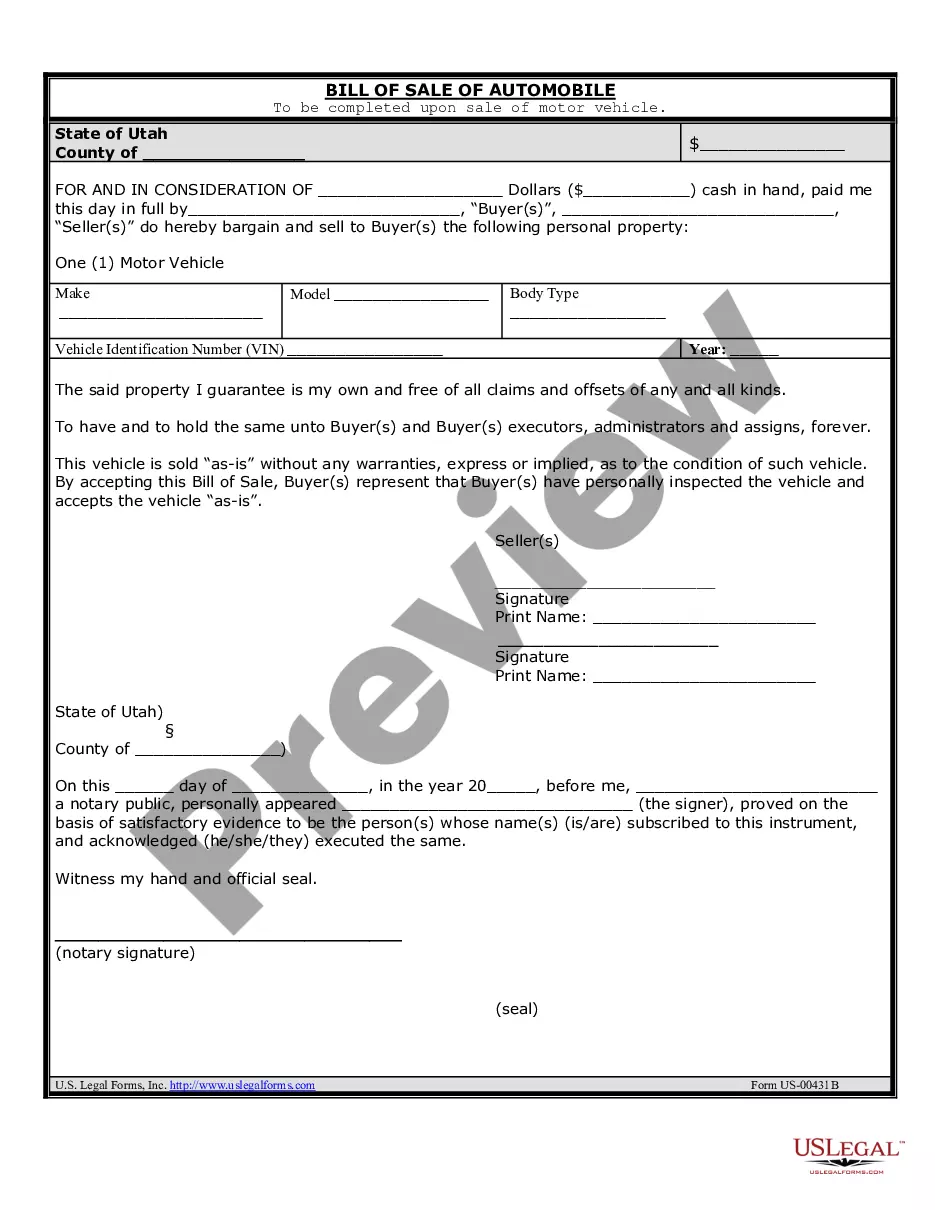
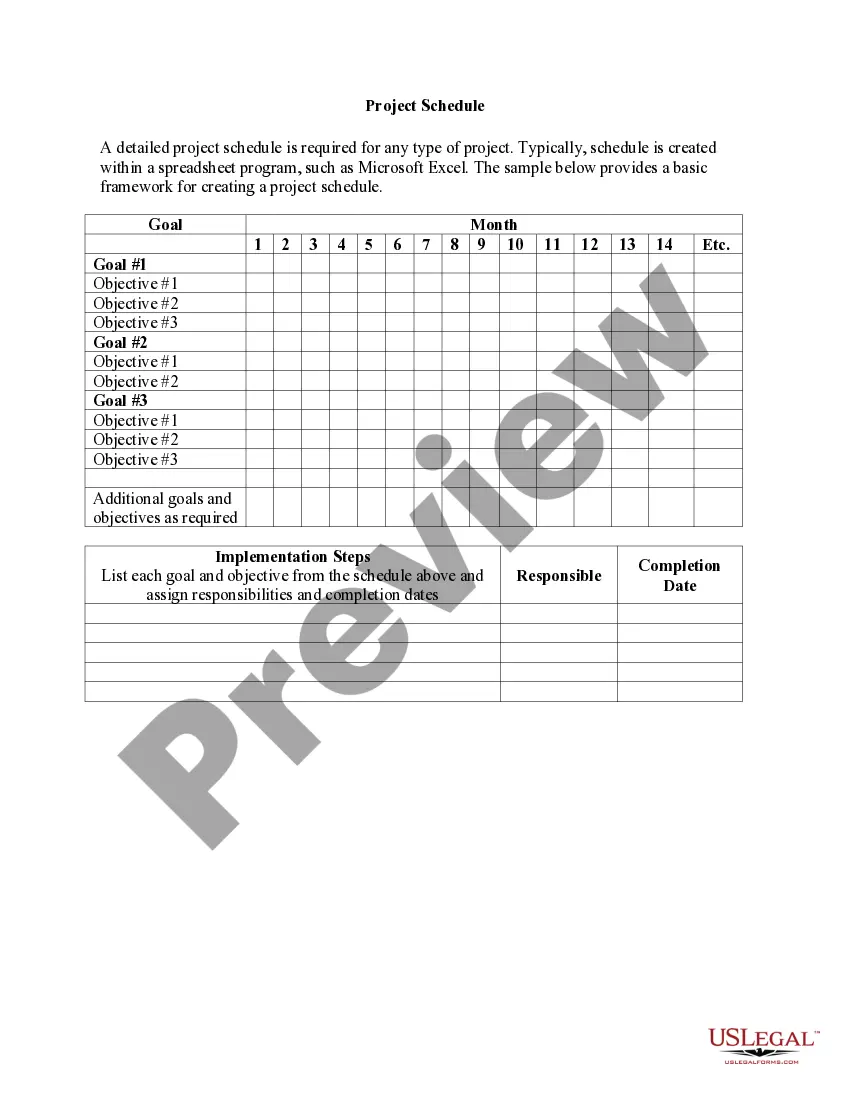
Action Limit Formula
Description
How to fill out Motion To Dismiss Action With Prejudice Of Plaintiff's Cause Of Action Barred By Statute Of Limitations?
Regardless of whether it's for commercial reasons or personal concerns, individuals inevitably face legal matters at some point in their lives.
Filling out legal documents demands meticulous focus, starting from selecting the right form template.
With an extensive catalog from US Legal Forms available, you no longer need to waste time searching for the correct template online. Use the library’s easy navigation to locate the right form for any scenario.
- Acquire the template you require by utilizing the search bar or browsing the catalog.
- Review the form's description to confirm it fits your circumstances, state, and county.
- Click on the form’s preview to inspect it.
- If it's the wrong form, return to the search tool to find the Action Limit Formula example you need.
- Obtain the template if it is suitable for your requirements.
- If you possess a US Legal Forms account, click Log in to access previously saved documents in My documents.
- If you do not have an account yet, you can acquire the form by clicking Buy now.
- Select the appropriate pricing option.
- Complete the account registration form.
- Choose your payment method: either a credit card or a PayPal account.
- Select the document format you desire and download the Action Limit Formula.
- Once saved, you can complete the form using editing software or print it out and finish it by hand.
Form popularity
FAQ
Action limit: A predefined parameter value outside the alert limit. If exceeded, immediate formal action is to be triggered ing to a predetermined plan specifying the necessary investigative and corrective actions.
Alert Level Alert Level = Average +2 X Sigma. Ex: Average limit = 11.28. Standard Deviation (sigma) =4.16. = 11.28 + 2 X 4.16. =20. Action Level = Average + 3 X Sigma. Ex: Average limit = 11.28. Standard Deviation (sigma) =4.16. =11.28 +3 X 4.16. =24.
Alert Levels Calculation. 3) average + 3 SD. To calculate standard deviation (SD) (population), first calculate the difference between each rate and the average, and we square each value (x- µ)2. Next, to obtain the SD, calculate the average of these values and obtain the square root of that value.
Alert limit: A pre-determined parameter value slightly outside the usual tolerance band. As soon as it is exceeded, monitoring must be intensified ing to a predefined action plan.
The alert and action limits are statistically derived, and are used to define the typical operating range for the process. Once the limits are statistically established, it is necessary to define, in a standard operating procedure, the steps to take in case of out-of-alert or -action limits.