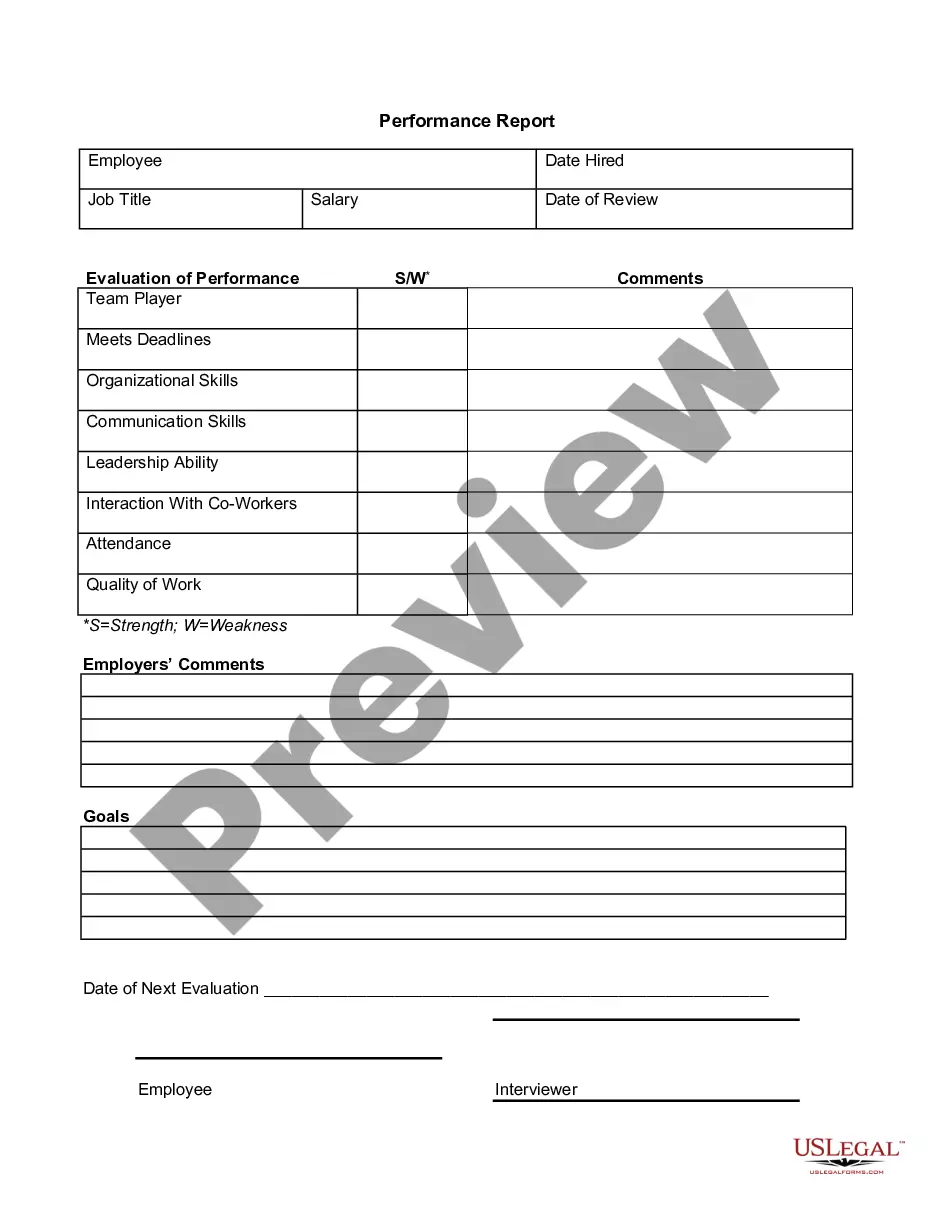
Completion Report Meaning In Travis
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Travis CI is a hosted continuous integration service used to build and test software projects hosted on GitHub, Bitbucket, GitLab, Perforce, Apache Subversion and Assembla.
Yml file is where the instructions for the site and the site navigation live. yml was originally short for Yet Another Markup Language (yaml) and now stands for YAML Ain't Markup Language . The yml file is simply a text file (use File > New file > Text File in RStudio).
Travis CI is a cloud-based continuous integration (CI) platform that automates the process of testing and deploying code changes. By seamlessly integrating with popular version control systems like GitHub and Bitbucket, Travis CI ensures that every code change is automatically tested and ready for deployment.
Travis CI is a Continuous Integration / Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) platform that enables developers to quickly and easily build, test and deploy code. The easy-of-use and flexibility offered by Travis CI is core to software development as part of a modern DevOps toolchain.
Travis CI is a Continuous Integration / Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) platform that enables developers to quickly and easily build, test and deploy code. The easy-of-use and flexibility offered by Travis CI is core to software development as part of a modern DevOps toolchain.
Travis CI is a CI/CD (Continuous Integration and Deployment) tool that helps development teams release code rapidly and automate the build, test, and deployment of their applications. Using Travis CI, engineers can automate their entire testing suite for new commits, reducing the potential for human error.
As a continuous integration platform, Travis CI supports your development process by automatically building and testing code changes, providing immediate feedback on the success of the change. Travis CI can also automate other parts of your development process by managing deployments and notifications.
Travis. yml , which is a YAML format text file, to the root directory of the repository. This file specifies the programming language used, the desired building and testing environment (including dependencies which must be installed before the software can be built and tested), and various other parameters.
Key differences. There are many differences between Travis and Azure Pipelines, including: Travis builds have stages, jobs and phases, while Azure Pipelines has steps that can be arranged and executed in an arbitrary order or grouping that you choose.
Usage-based plan w/o subscription charges you at the end of each month for the number of users who triggered the builds during this month. With every build started, Travis CI keeps track of how many unique users triggered a build within a current billing period.