Workplace Discrimination In India In Allegheny
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
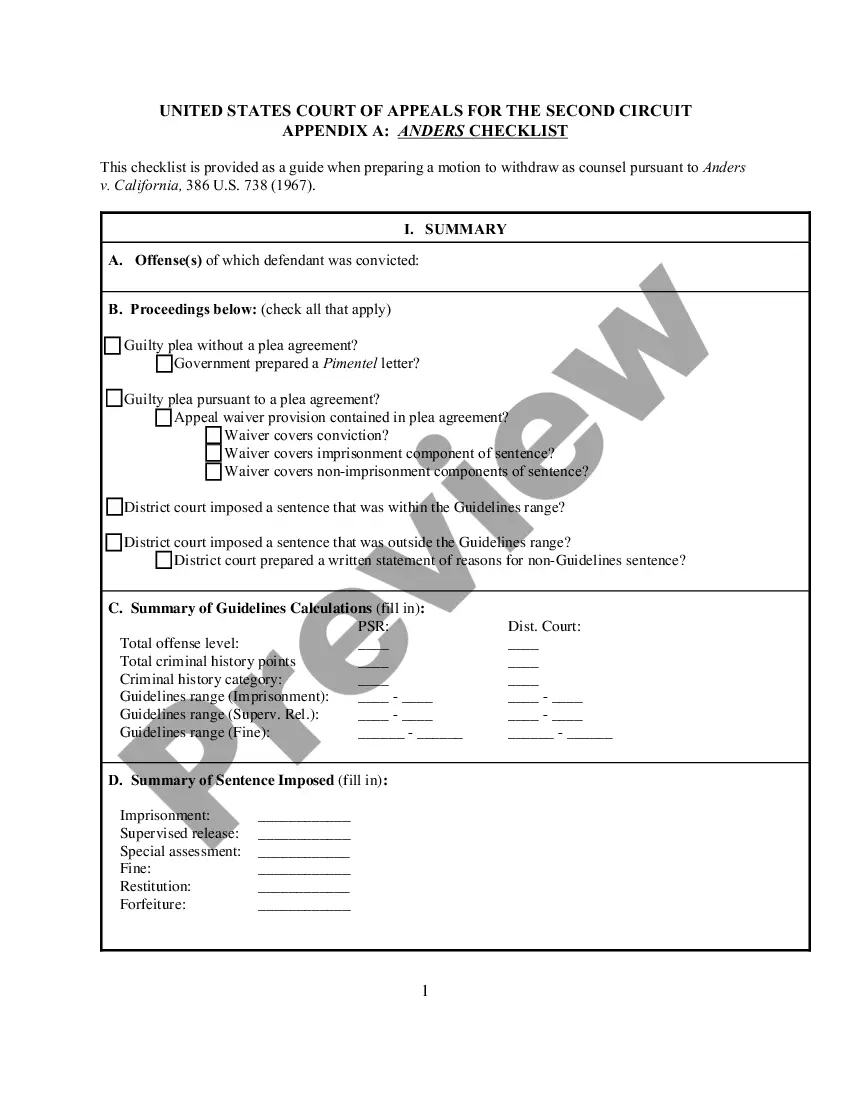
shall be punishable with imprisonment for a term of not less than one month and not more than six months and also with fine which shall be not less than one hundred rupees and not more than five hundred rupees.
Closer home, in India, discrimination is based on the gender, religious and caste location of individuals.
There are very few laws protecting employees and candidates against geographical discrimination. A person's location or origin is not a protected class like race or religion. From an ethical standpoint, employers and managers should endeavor to treat employees the same no matter their location or geographical origin.
If you feel you have experienced illegal discrimination, you can file a complaint or report a bias incident to the Pennsylvania Human Relations Commission (PHRC). Email the PHRC or call your regional office.
Report discrimination to a local Fair Employment Practices Agency (FEPA). If the discrimination breaks both a state and federal law, the FEPA will also send your complaint to the EEOC. Use the EEOC's directory of field offices to find the FEPA near you.
The answer depends on your claims and willingness to pursue litigation. If your claims are strong and you are invested in the litigation process, it can be very “worth it” to feel you are standing up for accountability, getting compensation for your injuries, and incentivizing the company to change its ways.
Filing a Claim for Employment Discrimination Before you may file a lawsuit against your employer in court, you must first file a complaint of discrimination with either the EEOC or PHRC. You must file the complaint with either agency within 180 days of the adverse employment action.
The following would be considered illegal discrimination if there is evidence that the decision was made based on a protected characteristic: Sexual Harassment. Refusal to Provide Services. Unfair Lending Practices. Misrepresenting the Availability of Housing. Refusal to Allow “Reasonable Modifications” Refusing Rental.