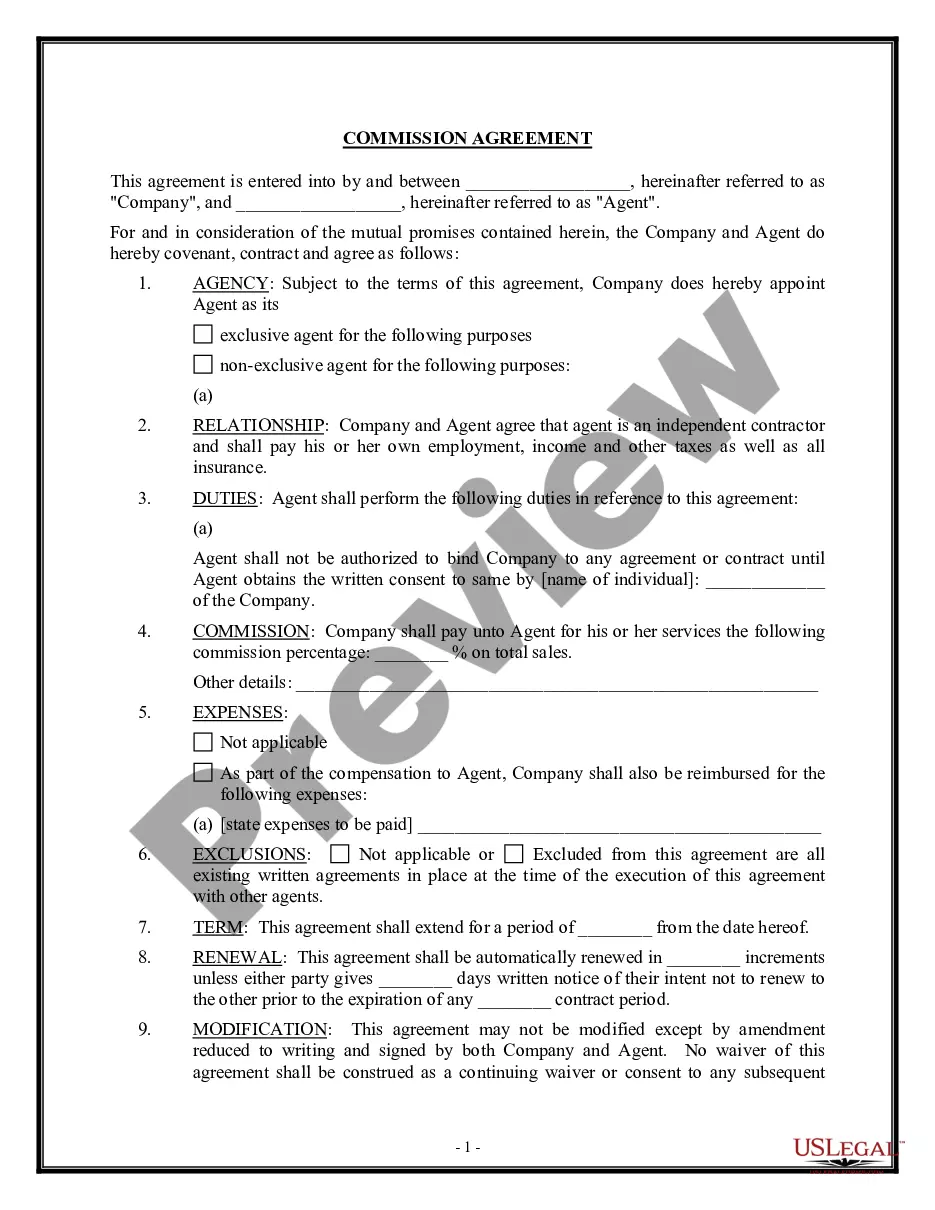
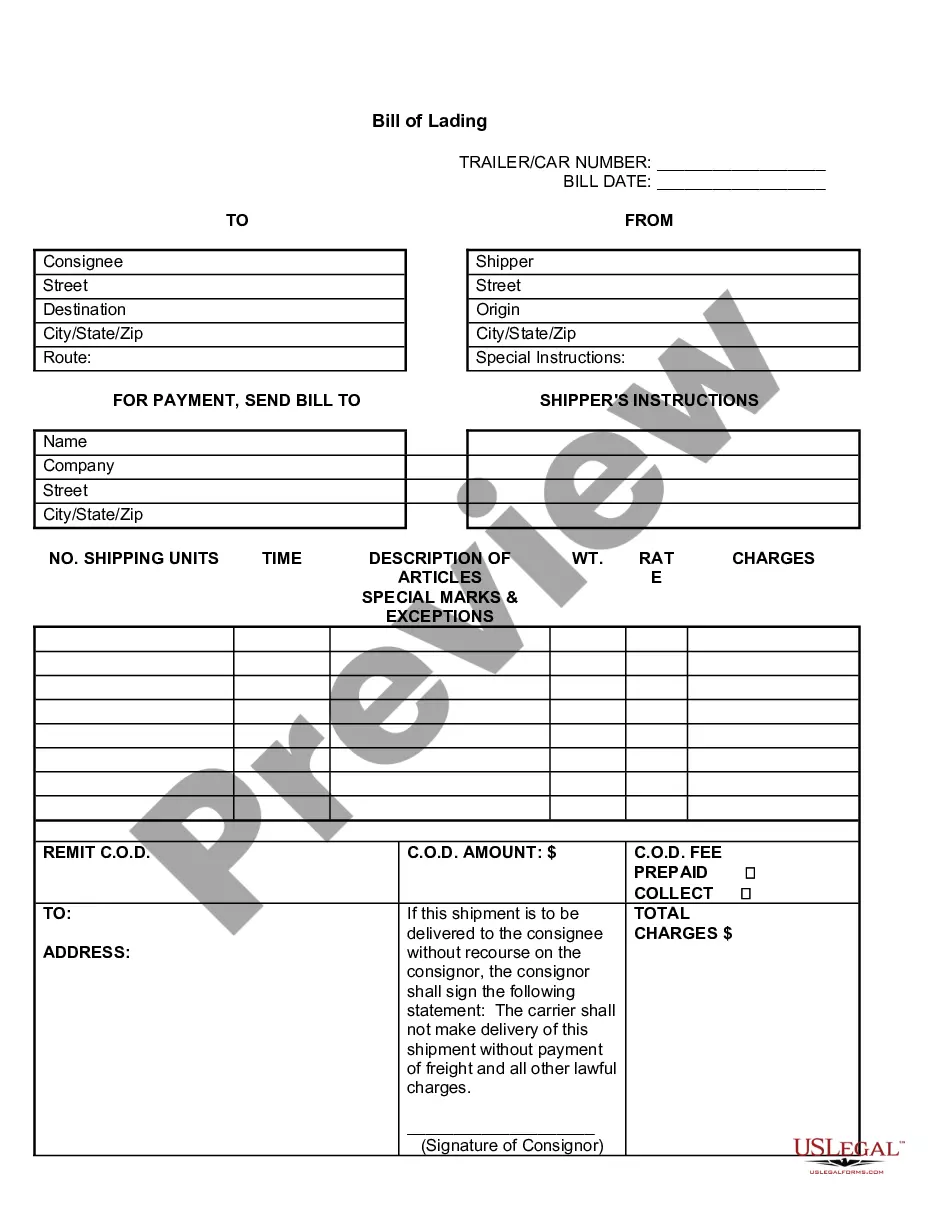
When applying for government grants there are a number of things to remember so the proposal is not rejected. Make sure they are on forms, and make sure that they comply with the stated guidelines. To ensure your proposal gets full consideration:
" Make sure the projects fit the guidelines and intent.
" Special categories of costs to reflect the areas that funding can cover. In some cases, only actual costs are allowed.
" Keep accurate records of expenditures and receipts.
" Submit the required number of application copies.
" Submit the application on time.
" Consider payment procedures, schedules, and partial payment schedules.
" Evaluation reports are often essential to final funding.
" Check on copyrights and credits.
" Make sure you know the funding organization requires credit.
" Check where copyright of materials is necessary and whose responsibility it is to get it.
" Note the decision date, so you can follow up if necessary.