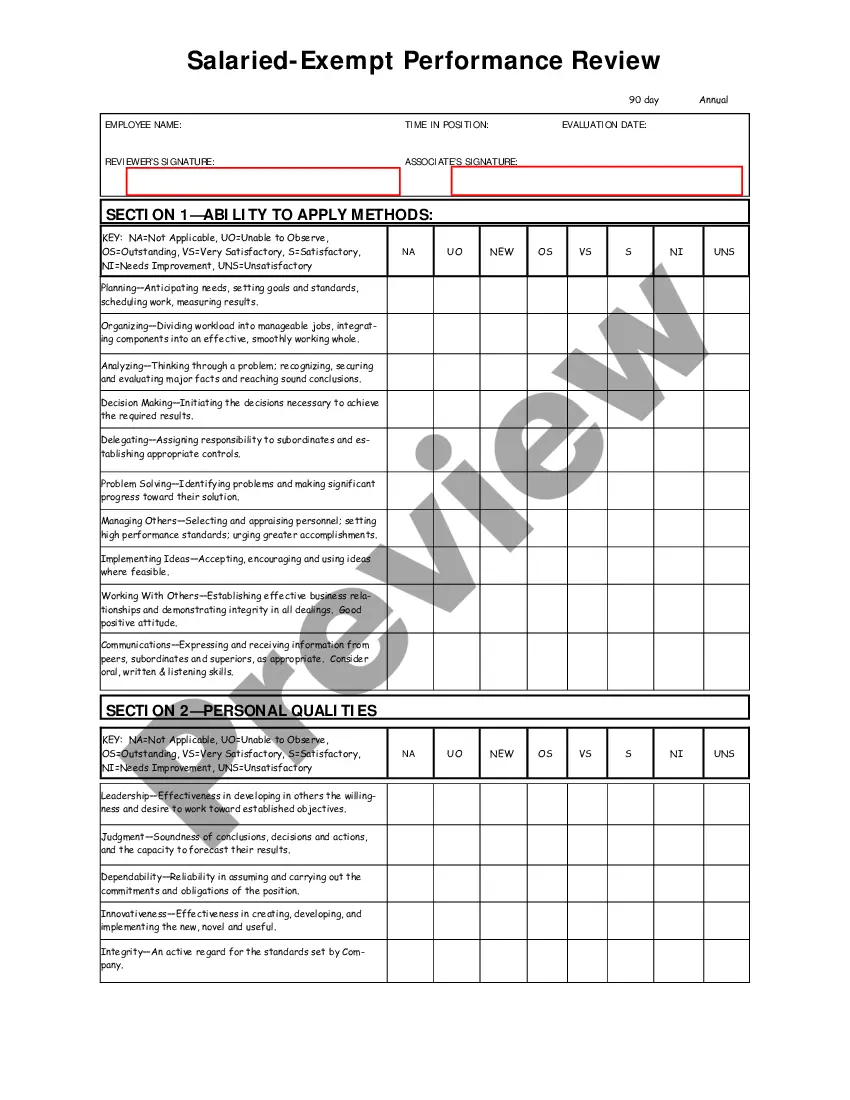
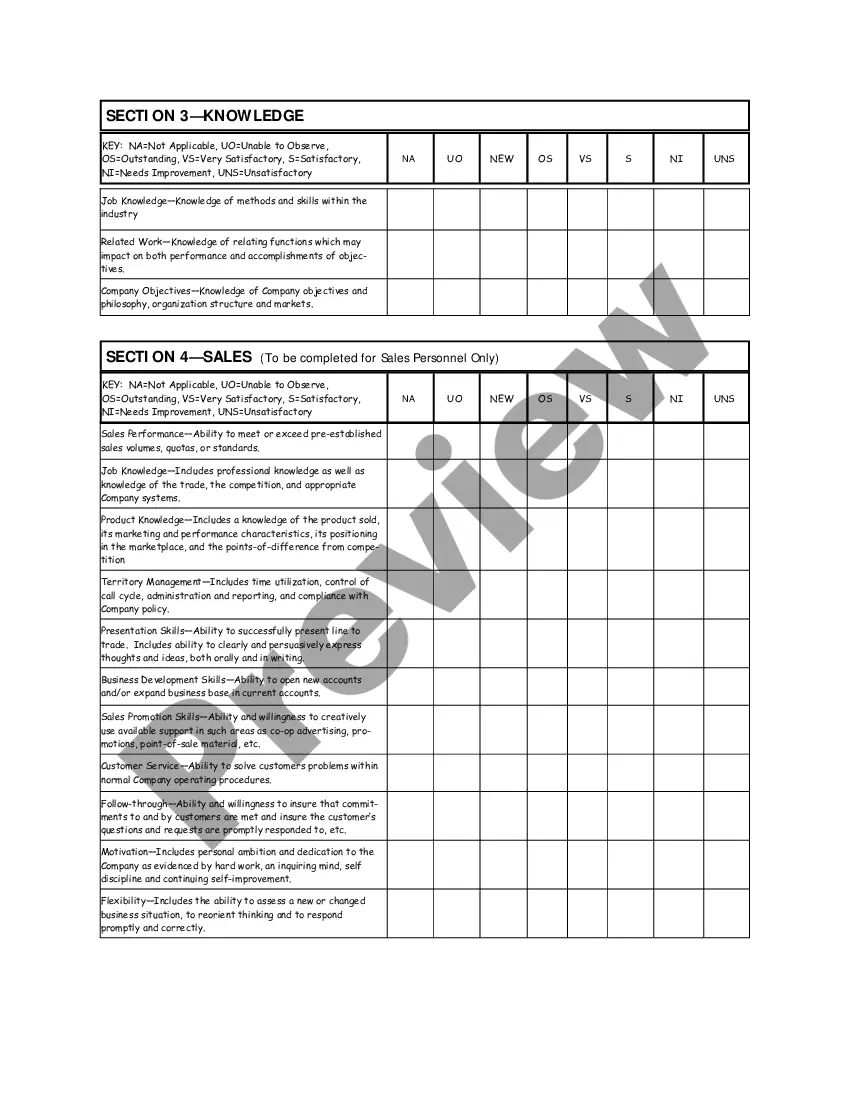
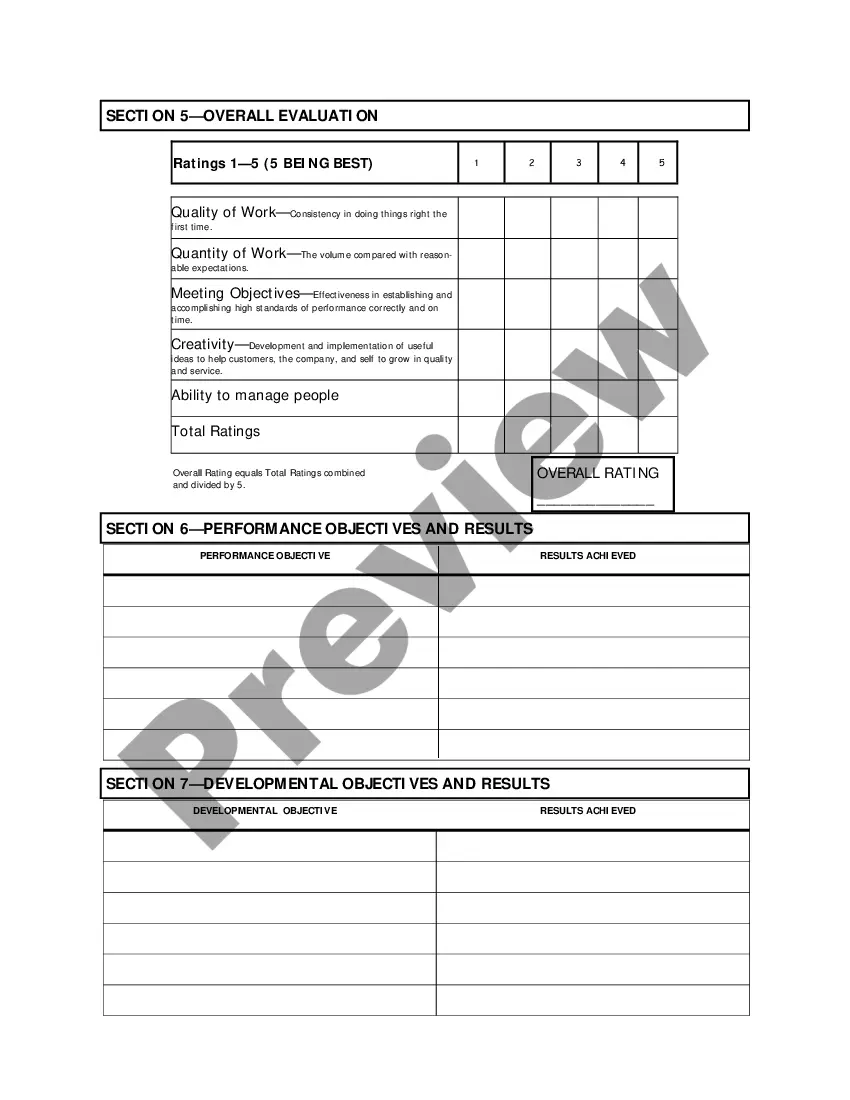
Oregon Salary - Exempt Employee Review and Evaluation Form
Description
How to fill out Salary - Exempt Employee Review And Evaluation Form?
Have you been in a location where you require documents for either professional or personal needs almost on a daily basis.
There are numerous legal document templates available online, but finding forms you can trust is not straightforward.
US Legal Forms provides a vast array of template documents, including the Oregon Salary - Exempt Employee Review and Evaluation Form, designed to comply with state and federal regulations.
Choose the pricing plan you desire, fill in the necessary information to create your account, and purchase the order using your PayPal or credit card.
Select a convenient paper format and download your copy. Access all the document templates you have purchased in the My documents section. You can obtain another copy of the Oregon Salary - Exempt Employee Review and Evaluation Form at any time, if necessary. Just select the desired form to download or print the document template.
- If you are already familiar with the US Legal Forms website and have an account, simply Log In.
- Then, you can download the Oregon Salary - Exempt Employee Review and Evaluation Form template.
- If you do not have an account and want to start using US Legal Forms, follow these steps.
- Find the form you need and ensure it is for your specific city/region.
- Utilize the Preview button to view the document.
- Review the description to ensure you have selected the correct form.
- If the form is not what you are looking for, use the Search box to find the document that meets your needs and requirements.
- Once you find the correct form, click Buy now.
Form popularity
FAQ
As of 2023, the salary threshold for exempt employees in Oregon is annually set at 2.5 times the state minimum wage. This figure changes based on the minimum wage, so it's essential to stay updated. Utilizing the Oregon Salary - Exempt Employee Review and Evaluation Form can help employers evaluate and ensure compliance with these regulations seamlessly.
New employees in Oregon must complete various forms to begin their roles smoothly. Among these, the Oregon Salary - Exempt Employee Review and Evaluation Form is crucial for establishing a clear performance framework. Other important forms include the W-4 for tax withholding, an Oregon withholding form, and the I-9 for verifying employee eligibility. Obtaining all these documents ensures compliance and sets the stage for successful employment.
When starting a new job in Oregon, you'll need to complete various forms to ensure everything is in order. Key among them is the Oregon Salary - Exempt Employee Review and Evaluation Form, which helps set clear performance goals. Additionally, don’t forget to fill out the W-4 and I-9 forms, which are necessary to satisfy tax and employment verification requirements.
New hires in Oregon must complete several important documents. Firstly, they should fill out the Oregon Salary - Exempt Employee Review and Evaluation Form to establish performance expectations. They also need to submit tax forms, including the W-4, the Oregon withholding form, and the I-9 for employment eligibility to ensure they comply with both state and federal laws.
To hire an employee in Oregon, you need several essential forms to ensure compliance. First, gather the Oregon Salary - Exempt Employee Review and Evaluation Form to evaluate and document employee performance effectively. Additionally, ensure you have the appropriate tax withholding forms, such as the W-4 and the Oregon withholding form, as well as employee eligibility verification forms like the I-9.
Choose a quarterly report filing method:Oregon Payroll Reporting System (OPRS) electronic filing.Combined Payroll Tax Reports Form OQ.Interactive voice response system, call 503-378-3981. Use only to report quarters with no payroll or no hours worked.
These exemptions also apply in Texas. So if you're paid an annual salary and earning more than a certain amount set by law, you are considered "exempt" and not covered by the FLSA. This means exempt employees are not entitled to overtime pay for working more than 40 hours in a week.
Almost all Oregon employers are subject to the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), and the minimum salary to qualify for exemption under that law is $684 per week or $35,568 annually (allowing up to 10% of the salary basis threshold to be met with nondiscretionary bonuses/incentives, including commissions, paid at least
Definitions as they pertain to Oregon Employment Department Law. An employer is subject to unemployment insurance taxes when the employer pays wages of $1,000 or more in a calendar quarter, or employs one or more individuals in any part of 18 separate weeks during any calendar year.
Form 132 is filed with Form OQ on a quarterly basis. Oregon Combined Quarterly Report- Form OQUse this form to determine how much tax is due each quarter for state unemployment insurance, withholding, Tri-Met & Lane Transit excise taxes, and the Workers' Benefit Fund.