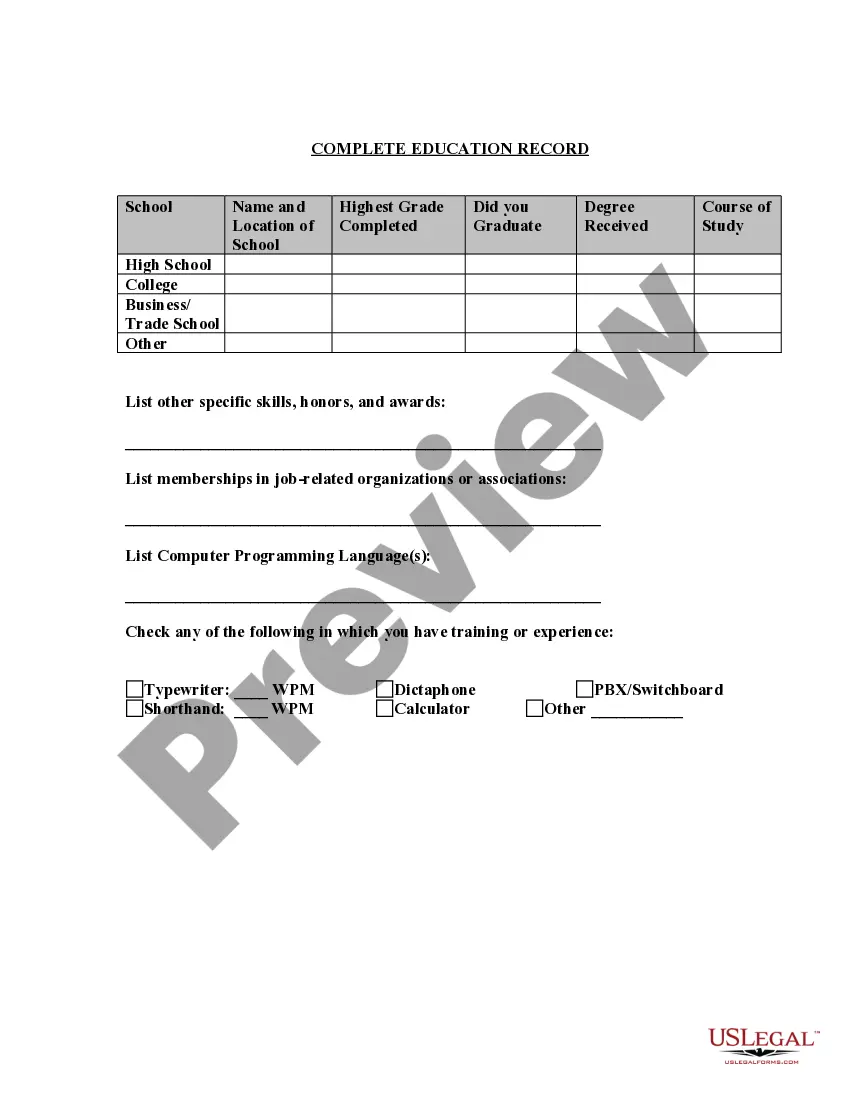
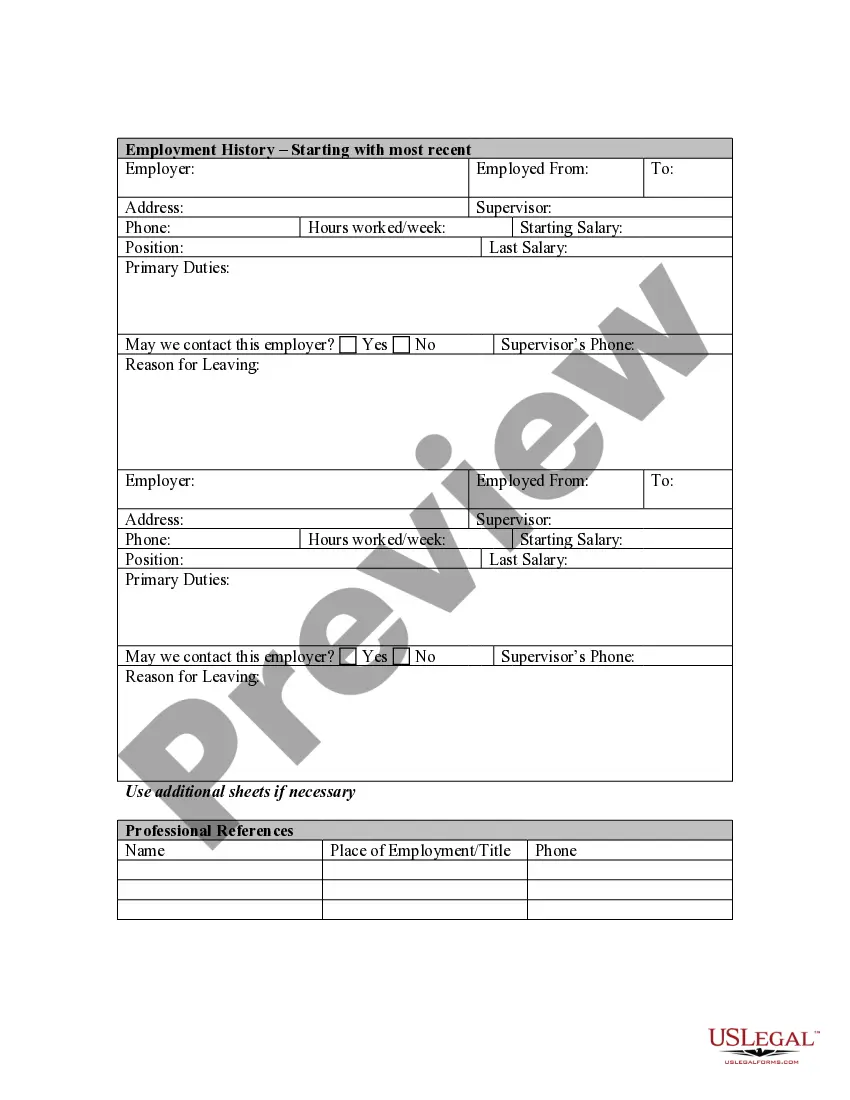
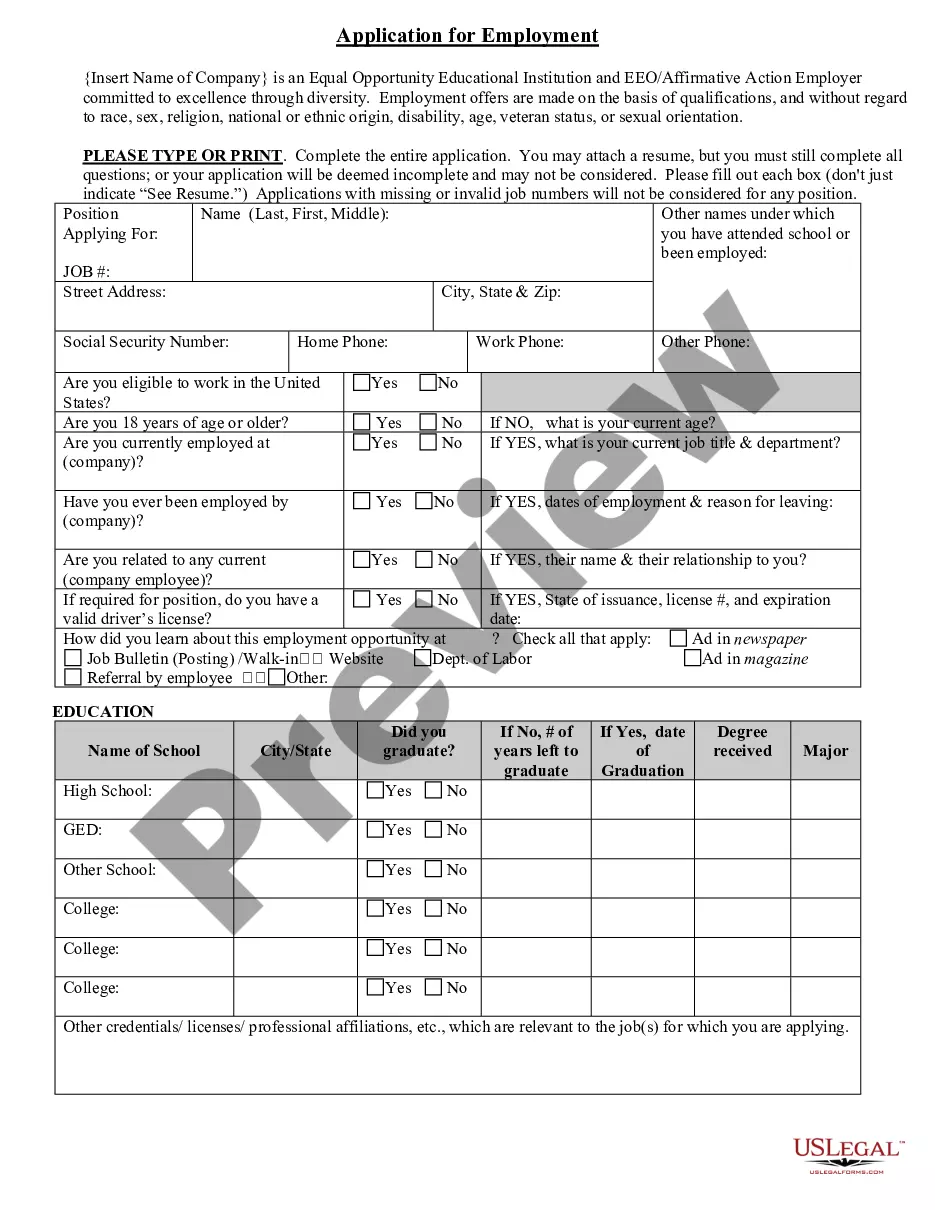
Minnesota Application for Work or Employment - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, or Nonexempt Position
Description
How to fill out Application For Work Or Employment - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, Or Nonexempt Position?
If you need to obtain extensive, download, or print legal document templates, utilize US Legal Forms, the most significant collection of legal forms available online.
Take advantage of the site’s straightforward and user-friendly search feature to locate the documents you require.
Various templates for business and personal purposes are organized by categories and states, or keywords.
Step 4. After you have found the form you need, click the Purchase now button. Select your preferred pricing plan and enter your details to register for an account.
Step 5. Complete the transaction. You can use your credit card or PayPal account to finalize the payment.
- Utilize US Legal Forms to locate the Minnesota Application for Employment or Work - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, or Nonexempt Position with just a few clicks.
- If you are already a US Legal Forms customer, Log In to your account and click the Download button to retrieve the Minnesota Application for Employment or Work - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, or Nonexempt Position.
- You can also access forms you previously saved from the My documents section of your account.
- For first-time users of US Legal Forms, adhere to the guidelines below.
- Step 1. Confirm you have selected the form for your correct area/state.
- Step 2. Utilize the Review feature to examine the form’s content. Don’t forget to read the description.
- Step 3. If you are dissatisfied with the form, use the Search field at the top of the screen to find alternative versions of the legal form format.
Form popularity
FAQ
Exempt employees are mostly paid on a salary basis and not per hour. Unlike non-exempt employees, employers may decide whether to pay exempt employees for any extra work outside the official 40 working hours per week. As a business owner, this allows you flexibility in your payment and employee benefits policies.
The term exempt employee refers to a category of employees set out in the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). Exempt employees do not receive overtime pay, nor do they qualify for minimum wage. When an employee is exempt, it primarily means that they are exempt from receiving overtime pay.
The federal exempt salary amount was increased to $684 a week Jan. 1, 2020. Additionally, while federal law allows some additional partial-day salary deductions for missed work hours due to FMLA leave, illness or disability, Minnesota law does not allow these same salary deductions.
An exempt employee is not entitled overtime pay by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). These salaried employees receive the same amount of pay per pay period, even if they put in overtime hours. A nonexempt employee is eligible to be paid overtime for work in excess of 40 hours per week, per federal guidelines.
The Minnesota Fair Labor Standards Act contains exemptions for more than 20 types of workers, including: nonprofit volunteers; elected officials; police and firefighters; seasonal fair, carnival and ski facility workers (overtime exempt only);
An exempt employee is not entitled overtime pay by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). These salaried employees receive the same amount of pay per pay period, even if they put in overtime hours. A nonexempt employee is eligible to be paid overtime for work in excess of 40 hours per week, per federal guidelines.
An exempt employee is an employee who does not receive overtime pay or qualify for minimum wage. Exempt employees are paid a salary rather than by the hour, and their work is executive or professional in nature.
Key Takeaways. An exempt employee is an employee who does not receive overtime pay or qualify for minimum wage. Exempt employees are paid a salary rather than by the hour, and their work is executive or professional in nature.
What does non-exempt mean? If employees are non-exempt, it means they are entitled to minimum wage and overtime pay when they work more than 40 hours per week.
Nonexempt: An individual who is not exempt from the overtime provisions of the FLSA and is therefore entitled to overtime pay for all hours worked beyond 40 in a workweek (as well as any state overtime provisions). Nonexempt employees may be paid on a salary, hourly or other basis.