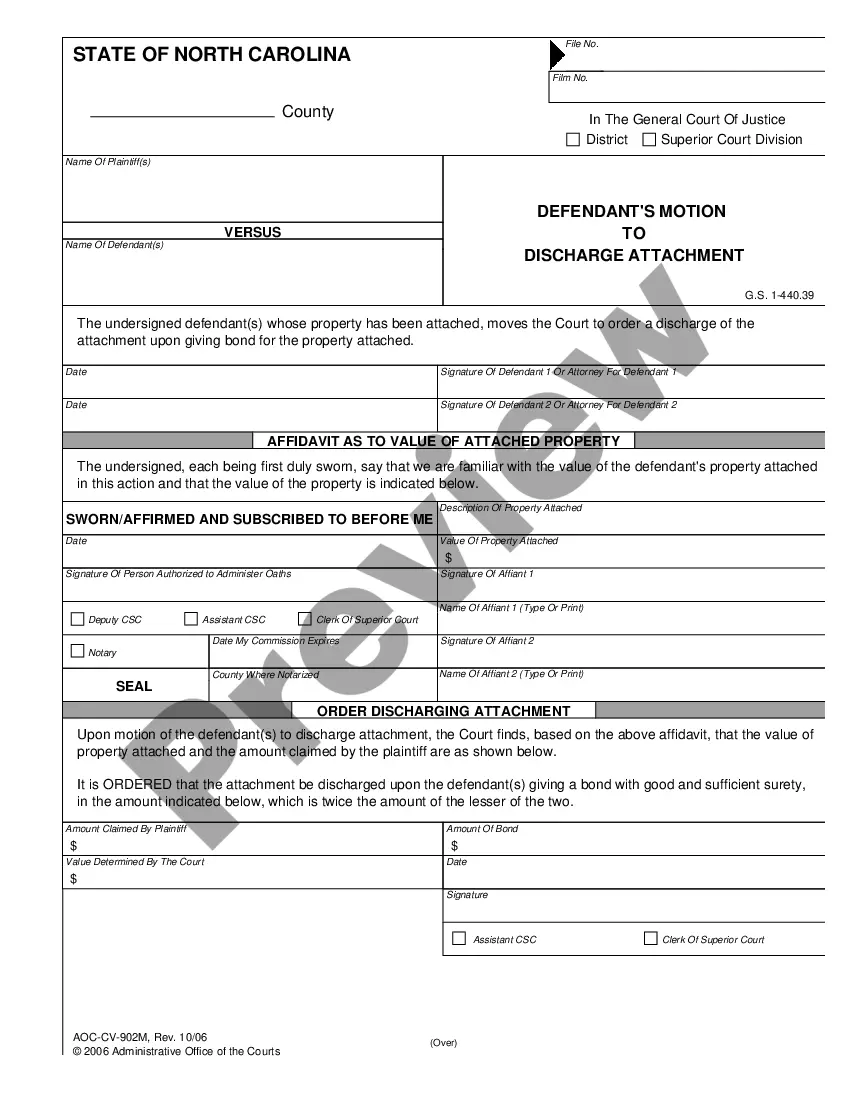
Maine Declination of Right to Appointment and Nomination of Personal Representative
Description
How to fill out Maine Declination Of Right To Appointment And Nomination Of Personal Representative?
Among numerous no-cost and fee-based templates accessible online, you can’t be confident about their precision and dependability.
For instance, who created them or if they possess enough expertise to cater to your needs.
Always remain calm and utilize US Legal Forms!
Click Buy Now to initiate the purchase process or search for another sample utilizing the Search field present in the header.
- Locate Maine Declination of Right to Appointment and Nomination of Personal Representative templates crafted by expert legal professionals and escape the pricey and lengthy procedure of seeking an attorney and subsequently having to compensate them to draft a document for you that you can effortlessly find on your own.
- If you already possess a membership, Log In to your account and locate the Download button beside the form you’re searching for.
- You will also have access to all your previously obtained samples in the My documents section.
- If you’re using our platform for the very first time, adhere to the guidelines below to obtain your Maine Declination of Right to Appointment and Nomination of Personal Representative swiftly.
- Ensure the file you discover is applicable in your state.
- Review the document by perusing the information using the Preview function.
Form popularity
FAQ
The following equation can be used to calculate the declination angle: 03b4=221223.45°Acos(360/365A(d+10)) where the d is the number of days since the start of the year The declination angle equals zero at the equinoxes (March 22 and September 22), positive during the summer in northern hemisphere and negative during winter
The following equation can be used to calculate the declination angle: 03b4=221223.45°Acos(360/365A(d+10)) where the d is the number of days since the start of the year The declination angle equals zero at the equinoxes (March 22 and September 22), positive during the summer in northern hemisphere and negative during winter
Magnetic declination is the difference between true north (the axis around which the earth rotates) and magnetic north (the direction the needle of a compass will point). It is usually printed on the map to the left of the scale bar at the bottom of a USGS 7.5' quadrangle.
Magnetic north is the direction towards the north magnetic pole, which is a wandering point where the Earth's magnetic field goes vertically down into the planet. The north magnetic pole is currently about 400km south of the north geographic pole, but can move to about 1,000km away.
Whenever you transfer a magnetic bearing taken in the field to your map, you add the magnetic declination to get the true bearing. (Note that a west declination is, in essence, subtracted because you are adding a negative number.)
The angle between grid north and true north is called the convergence angle. To obtain the true declination it is necessary to add or subtract the convergence angle to the Grid Declination.
Multiply it by -23.44, the tilt of the Earth's axis in degrees. The result is the solar declination in degrees for that day of the year. From the example, the cosine of 53.2603 is 0.5982; multiply it by -23.44 to get -14.02 degrees.
Multiply it by -23.44, the tilt of the Earth's axis in degrees. The result is the solar declination in degrees for that day of the year. From the example, the cosine of 53.2603 is 0.5982; multiply it by -23.44 to get -14.02 degrees.