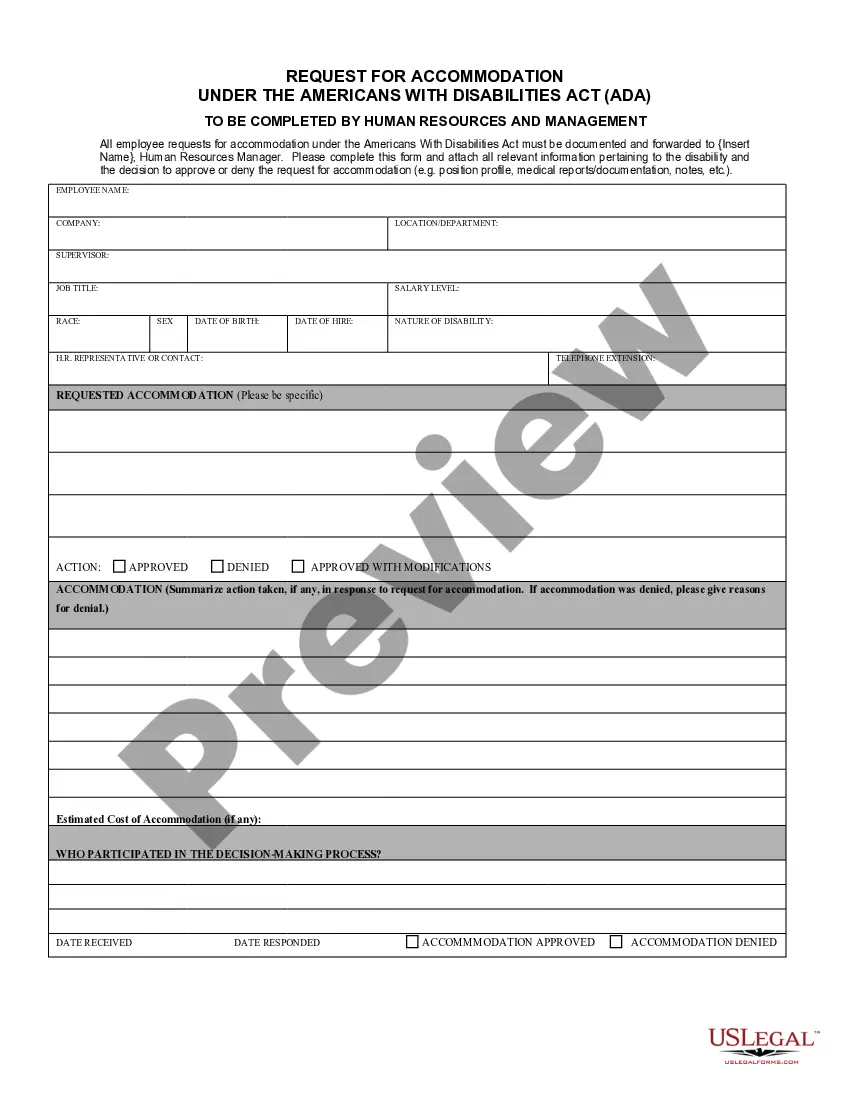
Maryland Request for Accommodation under the ADA
Description
How to fill out Request For Accommodation Under The ADA?
US Legal Forms - one of the most extensive collections of legal documents in the United States - offers a variety of legal template formats that you can download or create.
By utilizing the website, you can access thousands of forms for both business and personal purposes, organized by categories, states, or keywords. You can obtain the latest versions of documents like the Maryland Request for Accommodation under the ADA within moments.
If you already possess a subscription, Log In and download the Maryland Request for Accommodation under the ADA from your US Legal Forms catalog. The Download button will appear on every form you view. You can access all previously saved forms in the My documents section of your account.
Process the purchase. Use your credit card or PayPal account to finalize the transaction.
Select the format and download the document onto your device. Make changes. Complete, edit, print, and sign the saved Maryland Request for Accommodation under the ADA. Each template you added to your account has no expiration date and belongs to you indefinitely. Therefore, if you wish to download or print another copy, simply navigate to the My documents section and click on the form you need. Access the Maryland Request for Accommodation under the ADA with US Legal Forms, one of the most extensive collections of legal document formats. Utilize thousands of professional and state-specific templates that meet your business or personal needs.
- If you are using US Legal Forms for the first time, follow these simple steps to get started.
- Ensure you have chosen the appropriate form for your city/state.
- Click the Review button to examine the form's content.
- Read the form details to confirm that you have selected the right document.
- If the form does not suit your requirements, utilize the Search box at the top of the page to find the suitable one.
- If you are content with the form, confirm your choice by clicking the Buy now button.
- Then, choose the pricing plan you prefer and provide your details to register for an account.
Form popularity
FAQ
An individual meets the Americans with Disabilities with Act definition act of disability that would qualify them for reasonable accommodations if they have a physical or mental impairment that substantially limits one or more major life activities (sometimes referred to in the regulations as an actual disability)
Under Title I of the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), a reasonable accommodation is a modification or adjustment to a job, the work environment, or the way things are usually done during the hiring process.
Examples of accommodations that may be deemed unreasonable include the following: Eliminating a primary job responsibility. Lowering production standards applied to other employees. Providing more paid leave to an employee with a disability than provided to other employees.
A reasonable accommodation is any change to the application or hiring process, to the job, to the way the job is done, or the work environment that allows a person with a disability who is qualified for the job to perform the essential functions of that job and enjoy equal employment opportunities.
A violation can occur when job postings discourage individuals with disabilities from applying, exclude them, or deny a qualified individual employment because of their disability. It is an ADA violation for any employer to demote, terminate, harass, or fail to provide reasonable accommodations to disabled employees.
REASONABLE ACCOMMODATION RELATED TO THE BENEFITS AND PRIVILEGES OF EMPLOYMENT. The ADA requires employers to provide reasonable accommodations so that employees with disabilities can enjoy the "benefits and privileges of employment" equal to those enjoyed by similarly-situated employees without disabilities.
4. What accommodations are not considered reasonable? Reasonable accommodation does not include removing essential job functions, creating new jobs, and providing personal need items such as eye glasses and mobility aids.
Wheelchair use:Installing a ramp to make a workplace wheelchair-accessible.Modifying a restroom so a worker with disabilities can use it.Changing the layout of cubicles to provide enough room for a wheelchair to pass.Providing a raised or adjustable desk so that a wheelchair can be used in place of a chair.
Examples of reasonable accommodations include making existing facilities accessible; job restructuring; part-time or modified work schedules; acquiring or modifying equipment; changing tests, training materials, or policies; providing qualified readers or interpreters; and reassignment to a vacant position.
For example, a request for reasonable accommodation is a right under Title I and therefore a protected activity. A protected activity can also include opposing a practice the individual thinks is unlawful discrimination under Title I.