Maryland First and Final Accounting
Description
Get your form ready online
Our built-in tools help you complete, sign, share, and store your documents in one place.
Make edits, fill in missing information, and update formatting in US Legal Forms—just like you would in MS Word.
Download a copy, print it, send it by email, or mail it via USPS—whatever works best for your next step.
Sign and collect signatures with our SignNow integration. Send to multiple recipients, set reminders, and more. Go Premium to unlock E-Sign.
If this form requires notarization, complete it online through a secure video call—no need to meet a notary in person or wait for an appointment.
We protect your documents and personal data by following strict security and privacy standards.
Make edits, fill in missing information, and update formatting in US Legal Forms—just like you would in MS Word.

Download a copy, print it, send it by email, or mail it via USPS—whatever works best for your next step.

Sign and collect signatures with our SignNow integration. Send to multiple recipients, set reminders, and more. Go Premium to unlock E-Sign.
If this form requires notarization, complete it online through a secure video call—no need to meet a notary in person or wait for an appointment.
We protect your documents and personal data by following strict security and privacy standards.
Looking for another form?
Key Concepts & Definitions
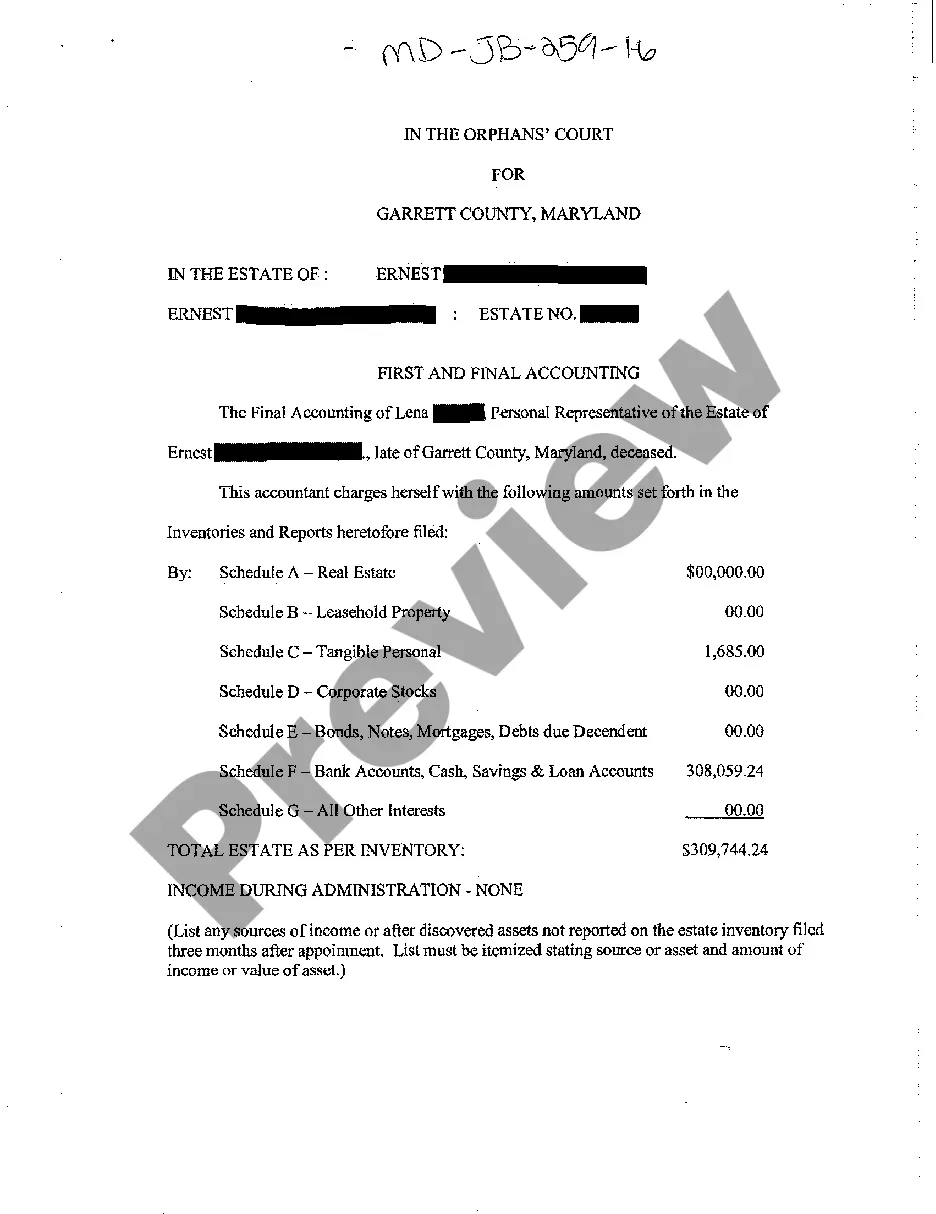
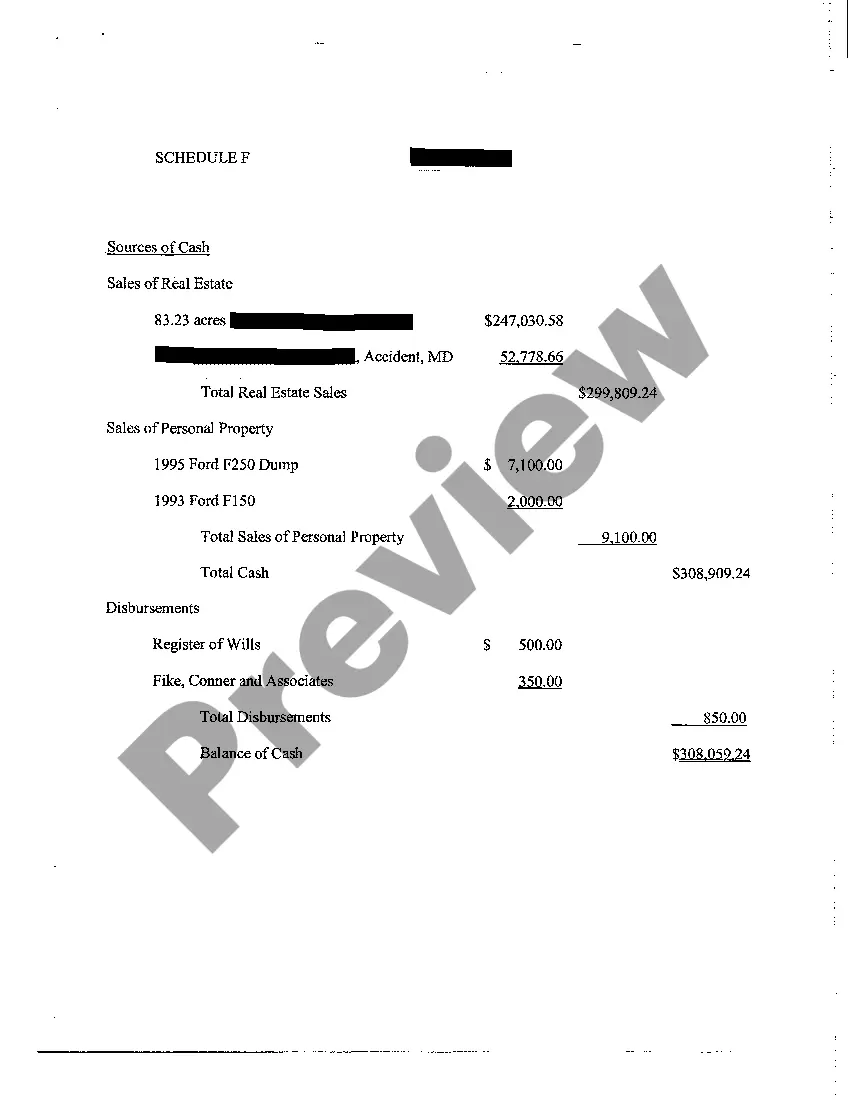
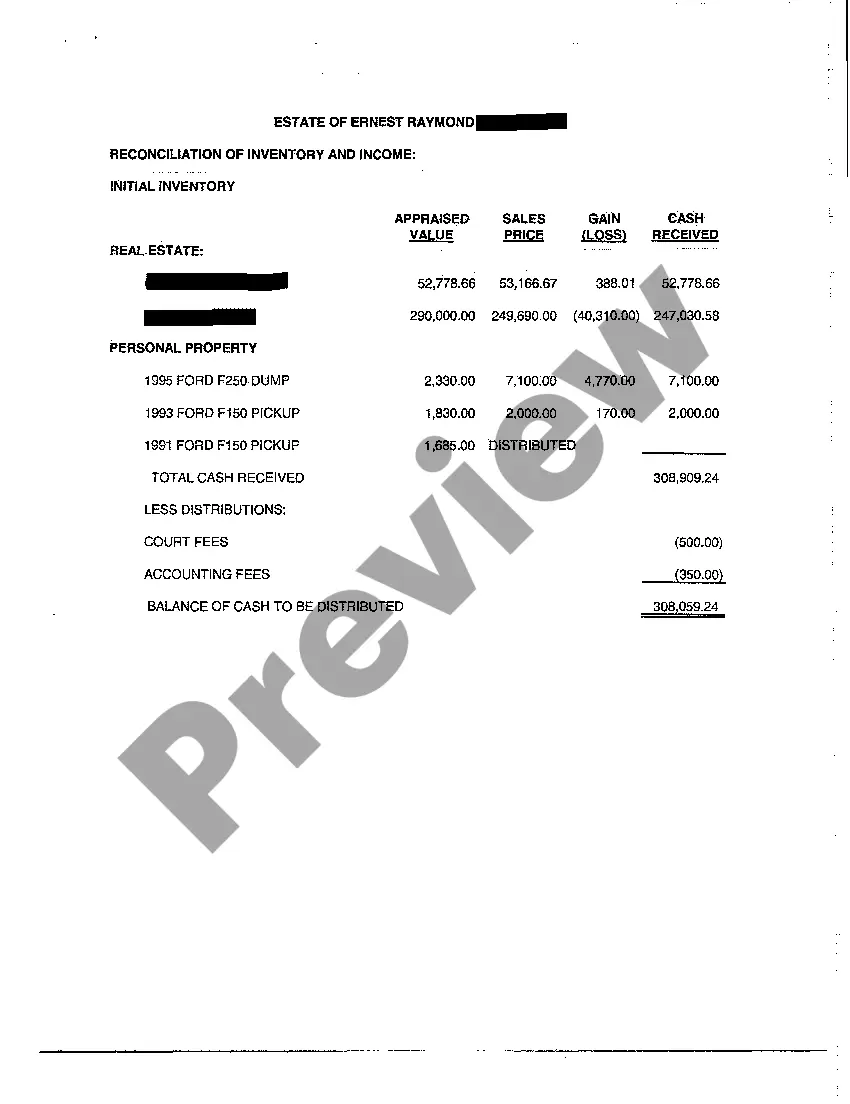
A16 First and Final Accounting refers to a specific form used in the probate process in the United States, which details all financial transactions and closing statements of an estate. This document is essential for providing transparency to beneficiaries and the court regarding how an estate has been managed.
Step-by-Step Guide
- Gathering Financial Details: Collect all financial statements, receipts, and related documents of the estate.
- Filling Out the A16 Form: Accurately fill out the A16 form, including all assets, liabilities, income, and expenditures.
- Submission for Review: Submit the completed form to the probate court for review.
- Distribution of Assets: Once approved, distribute the remaining assets according to the will or state law.
Risk Analysis
- Inaccuracies in Financial Reporting: Incorrect or incomplete entries can lead to legal complications or delays.
- Beneficiary Disputes: Discrepancies in the reported figures can cause disagreements among beneficiaries, potentially leading to litigation.
- Legal Compliance: Failure to adhere to state and federal laws can result in fines or additional legal scrutiny.
Key Takeaways
- The importance of accuracy and thoroughness cannot be overstated in preparing an A16 First and Final Accounting.
- Understanding and compliance with legal requirements are crucial to the smooth execution of estate closure.
- Ensuring clear communication with all parties involved can preempt potential conflicts.
Common Mistakes & How to Avoid Them
- Omitting Transactions: Double-check all records before submission to avoid omissions.
- Estimation Rather Than Exact Reporting: Use actual figures and back them up with documentation.
- Delay in Submission: Follow a strict timetable to prevent delays and potential penalties.
How to fill out Maryland First And Final Accounting?
Greetings to the most extensive legal document repository, US Legal Forms. Here you can acquire any template such as Maryland First and Final Accounting forms and download them (as many as you desire). Create official paperwork in just a few hours, rather than days or even weeks, without the need to spend a fortune with a lawyer or attorney.
Obtain your state-specific template in just a few clicks and be confident that it was produced by our qualified attorneys.
If you’re already a subscribed client, simply Log In to your account and then click Download next to the Maryland First and Final Accounting form you require. Since US Legal Forms is internet-based, you’ll always have access to your saved formats, regardless of the device you’re utilizing. Review them in the My documents section.
Print the document and complete it with your/your business’s information. Once you’ve finalized the Maryland First and Final Accounting, send it to your attorney for confirmation. It’s an additional step but a crucial one to ensure you’re fully protected. Join US Legal Forms today and gain access to a plethora of reusable templates.
- If you haven't created an account yet, what are you waiting for? Follow our instructions below to get started.
- If this is a state-specific document, verify its legitimacy in the state where you reside.
- Check the description (if available) to determine if it’s the correct template.
- View more information with the Preview feature.
- If the template meets all your requirements, simply click Buy Now.
- To establish your account, choose a subscription plan.
- Utilize a credit card or PayPal account to sign up.
- Download the document in the format you prefer (Word or PDF).
Form popularity
FAQ
The first account of an estate in Maryland refers to the initial financial report submitted by the executor. This document outlines the opening assets, income generated, and initial expenses incurred during estate management. It serves as a foundation for subsequent reports, including the final account. By mastering the Maryland First and Final Accounting, executors can ensure a smooth transition between these reports.
Length of Probate Process in Maryland The administration of an estate often takes approximately one year. This includes marshaling all of the assets, valuing the assets as of the date of death and then making the distribution.
File the Will and Probate Petition. Secure Personal Property. Appraise and Insure Valuable Assets. Cancel Personal Accounts. Determine Cash Needs. Remove Estate Tax Lien. Determine Location of Assets and Secure "Date of Death Values" Submit Probate Inventory.
If a person owns assets in his or her individual name and dies without a Will, assets remaining after payment of administration expenses, debts and taxes (if any) are distributed to the person's heirs as provided under Maryland Intestacy Laws (the person is said to have died intestate).
Maryland is a reasonable compensation state for executor fees. Maryland executor compensation has a restriction, though. Maryland executor fees, by law, should not exceed certain amounts. Reasonable compensation is not to exceed 9% if less than $20,000; and $1,800 plus 3.6% of the excess over $20,000.
How to Close an Estate in Maryland Probate. Under Maryland law, Estates & Trusts, the final approval of the final account, as submitted to the register of wills, automatically closes the estate.
The Maryland statutes say that the maximum personal representative fee is 9 percent of the estate's value if the estate is worth $20,000 or less. That would equal $900 on a $10,000 estate. The fee is $1,800 for estates greater than $20,000, plus 3.6 percent of the estate's value over $20,000.
Maryland is a reasonable compensation state for executor fees. Maryland executor compensation has a restriction, though. Maryland executor fees, by law, should not exceed certain amounts. Reasonable compensation is not to exceed 9% if less than $20,000; and $1,800 plus 3.6% of the excess over $20,000.
Step 1, Determine whether You are the Personal Representative. Step 2, Petition to Probate the Estate. Step 3, Make an Inventory of the Estate. Step 4, Assess any projected Inheritance Taxes. Step 5, Consolidate the Estate and Manage Expenses.