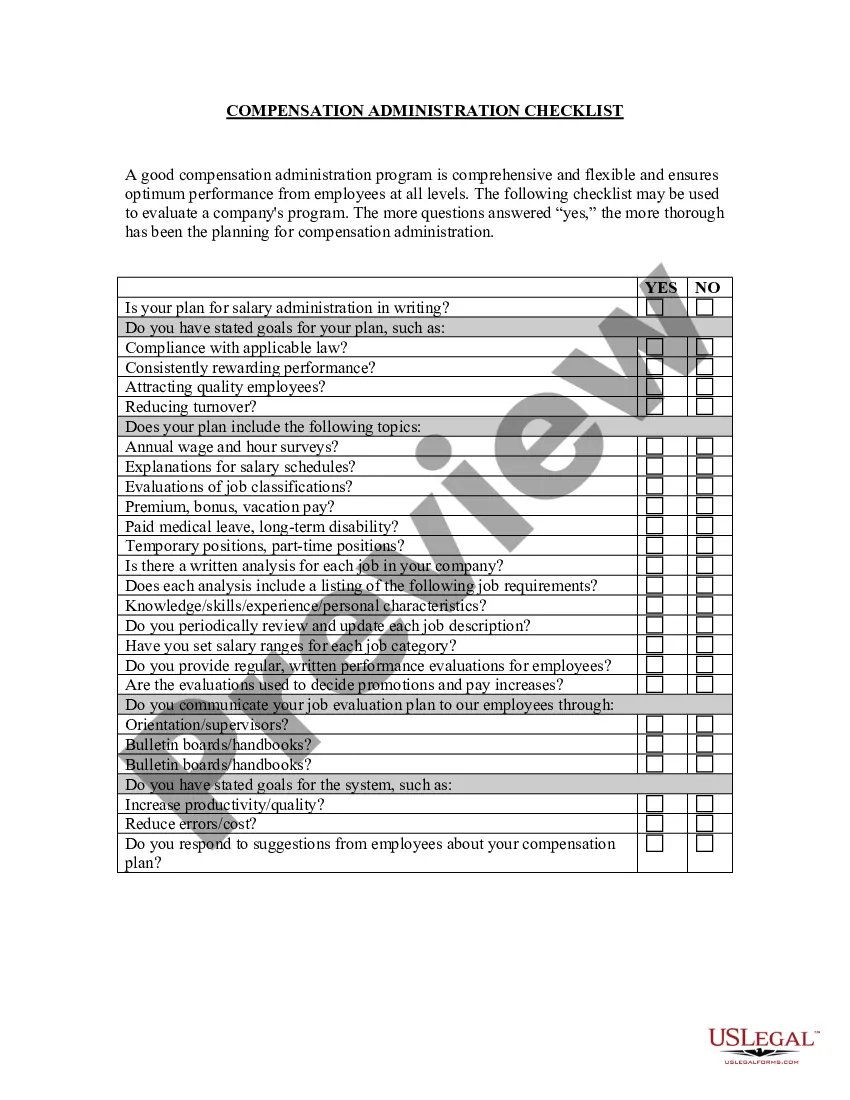
Guam Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist
Description
How to fill out Equal Pay - Administration And Enforcement Checklist?
Finding the appropriate legitimate document design can be a challenge.
Certainly, there are numerous templates available online, but how can you locate the authentic form you need.
Utilize the US Legal Forms website. The service offers thousands of templates, including the Guam Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist, for both business and personal purposes.
You can preview the document using the Preview button and review the description to confirm it is the right one for you.
- All documents are reviewed by professionals and meet both state and federal requirements.
- If you are already registered, Log In to your account and click the Download button to obtain the Guam Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist.
- Use your account to search through the legitimate documents you have previously purchased.
- Visit the My documents section in your account and download another copy of the document you require.
- If you are a new user of US Legal Forms, here are some simple steps to follow.
- First, make sure you have chosen the correct document for your city/state.
Form popularity
FAQ
The Fair Chances Hiring Act in Guam aims to provide individuals with criminal records a fair opportunity in the hiring process. It restricts employers from inquiring about prior convictions until later stages of the hiring process, thus allowing candidates to demonstrate their qualifications first. This approach promotes inclusivity in the workforce, which is essential to building a diverse community. Utilize the Guam Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist to understand related compliance aspects.
Public Law 35-5 in Guam addresses various employment practices, focusing heavily on non-discriminatory practices in the workplace. It highlights the need for equal pay regardless of gender or other factors, promoting fairness for all workers. Understanding this law can assist employers and employees alike in upholding their rights and responsibilities. To help navigate these legal frameworks, consult the Guam Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist.
As of now, the minimum salary in Guam is set at $10.50 per hour, which ensures workers receive fair compensation for their efforts. This law applies to most employees, affirming the importance of equitable payment practices. For a comprehensive understanding of wage regulations, the Guam Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist serves as a valuable resource. It helps ensure compliance with local wage laws.
The final paycheck law in Guam mandates that employees receive their final wages upon termination of their employment. This includes all earned wages, overtime pay, and any accrued vacation time. Employers must process these payments without unnecessary delay, ensuring that employees can move forward promptly. For clarity on compliance, consider referring to the Guam Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist.
The Equal Pay Act of 1963 is a U.S. law that prohibits employers from paying different wages to men and women who work under similar conditions and whose jobs require the same level of skill, effort, and responsibility. It is part of the amended Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938.
There are several elements that must be met in compensation discrimination complaints under the Equal Pay Act. The jobs being compared must require substantially equal skill, effort, and responsibility and be performed under similar working conditions within the same establishment.
Enforced by the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC), the law applies to employers with 20 or more employees and to federal government, interstate agencies, employment agencies and labor unions.
On January 29, 2009, President Barack Obama signed into law the Lilly Ledbetter Fair Pay Act. The Act requires employers to redouble their efforts to ensure that their pay practices are non-discriminatory and to make certain that they keep the records needed to prove the fairness of pay decisions.
Payroll records is a blanket term that applies to all documentation associated with paying employees, from hiring documents and direct deposit authorization forms to paystubs. This includes anything that documents total hours worked, their pay rate, tax deductions, employee benefits, etc.
A pay stub, also known as a check stub, is the part of a paycheck or a separate document that lists details about the employee's pay. It itemizes the wages earned for the pay period and year-to-date payroll information. The check stub also shows taxes and other deductions taken out of an employee's earnings.