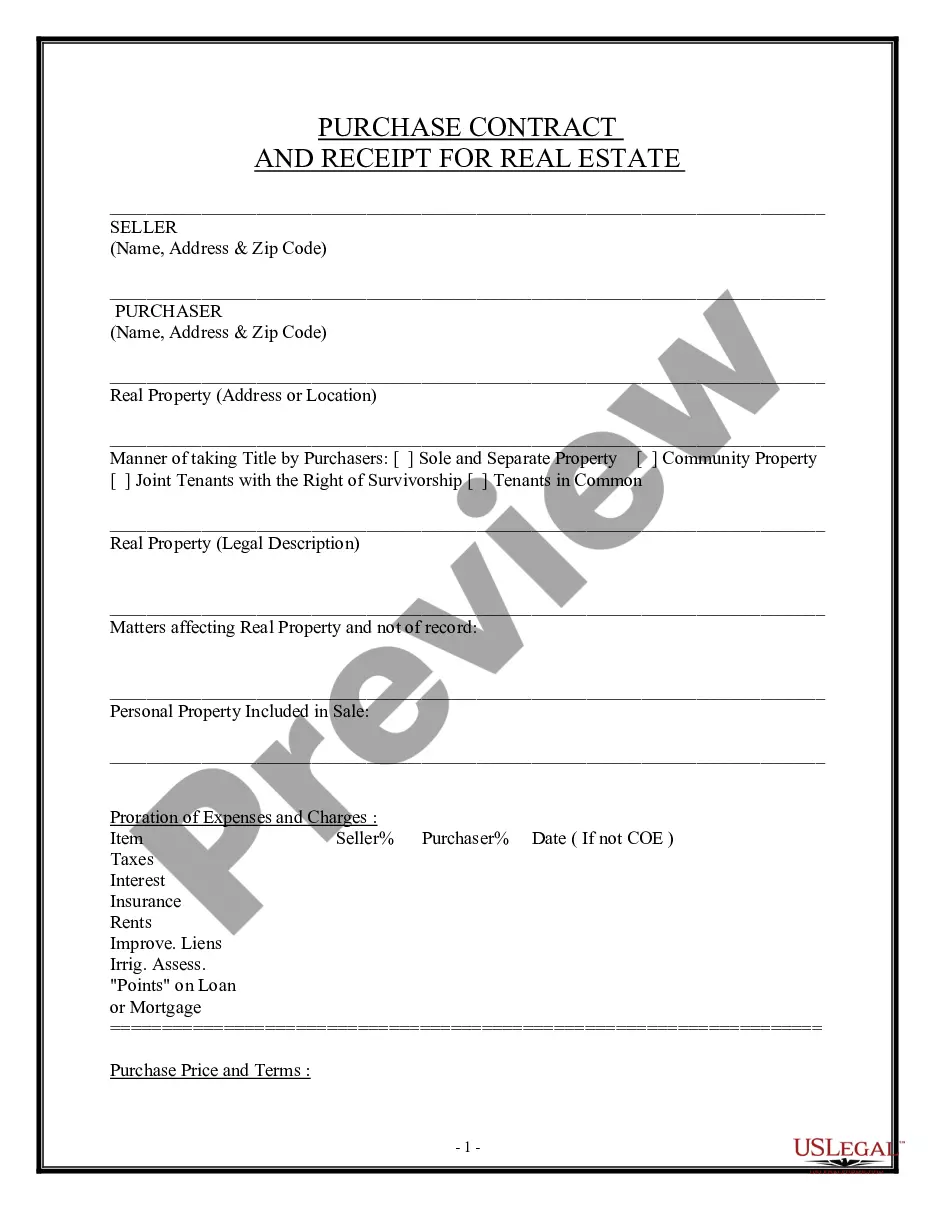
Georgia Purchase Contract and Receipt - Residential
Description
How to fill out Purchase Contract And Receipt - Residential?
US Legal Forms - one of the largest collections of legal documents in the United States - offers a variety of legal form templates that you can download or create.
By using the website, you can access thousands of forms for business and personal needs, organized by category, state, or keywords. You can find the latest forms like the Georgia Purchase Agreement and Receipt - Residential in just a few minutes.
If you already have a subscription, Log In to download the Georgia Purchase Agreement and Receipt - Residential from the US Legal Forms library. The Get button will appear on every form you view. You will have access to all previously downloaded forms within the My documents section of your account.
Process the payment. Use your credit card or PayPal account to complete the transaction.
Choose the format and download the form to your device. Make changes. Fill out, edit, sign, and print the downloaded Georgia Purchase Agreement and Receipt - Residential. Each template you add to your account has no expiration date and is yours permanently. So, if you want to download or print another copy, simply go to the My documents section and click on the form you need. Access the Georgia Purchase Agreement and Receipt - Residential with US Legal Forms, one of the most extensive libraries of legal document templates. Utilize thousands of professional and state-specific templates that satisfy your business or personal requirements and needs.
- If you want to use US Legal Forms for the first time, here are some simple instructions to help you get started.
- Ensure you have selected the correct form for your area/state.
- Click the Preview button to review the form’s content.
- Read the form description to confirm that you have chosen the right one.
- If the form does not meet your needs, use the Search box at the top of the page to find the appropriate one.
- Once satisfied with the form, confirm your choice by clicking the Get now button.
- Then, select the pricing plan you prefer and provide your details to register for an account.
Form popularity
FAQ
The four fundamental rules of contract law include mutual consent, consideration, capacity, and legality. Mutual consent refers to the agreement between parties, often indicated by an offer and acceptance. Consideration involves each party providing something of value in the contract. Additionally, all parties must have the legal capacity to enter a contract, and the contract must pertain to legal activities.
Despite having a home purchase agreement, earnest money, and contingencies in place, both buyers and sellers can back out of purchasing or selling a home.
A purchase and sale agreement, also known as a purchase and sale contract, P&S agreement, or PSA, is a legally-binding document that establishes the terms and conditions related to a real estate transaction. It defines what requirements the buyer must meet as well as purchase price, limitations, and contingencies.
Also known as a sales contract or a purchase contract, a purchase agreement is a legal document that establishes the parameters of the sale of goods between a buyer and a seller.
Among the terms typically included in the agreement are the purchase price, the closing date, the amount of earnest money that the buyer must submit as a deposit, and the list of items that are and are not included in the sale.
A Georgia residential purchase and sale agreement is a contract that legally binds two parties (seller and buyer) together for the purpose of transferring ownership of residential property.
If any of the contingencies in your contract aren't met, you can back out of buying a house after signing a contract with no repercussions. Alternatively, you may choose to have the seller remedy the situation (if possible) or renegotiate the contract.
The Purchase & Sale Agreement (P&S) is a legally binding contract that dictates how the sale of a home will proceed. It comes after the Offer to Purchase, and supersedes that earlier document once it's signed. The P&S is more substantial than the offer and can seem pretty complicated, so I'm going to break it down.
3) If the Buyer and Seller aren't able to reach an agreement and the Buyer isn't able to bring the additional funds to closing, then as the Buyer, you can get out of the real estate contract as long as you terminate the Purchase & Sales Agreement prior to the end of the Appraisal Contingency Period.
Can a home seller back out after a sale? Yes, a home seller can back out of a real estate contract, but only in instances in which they're willing to compensate the buyer for their trouble, or they sold to a buyer who is also experiencing buyer's remorse.