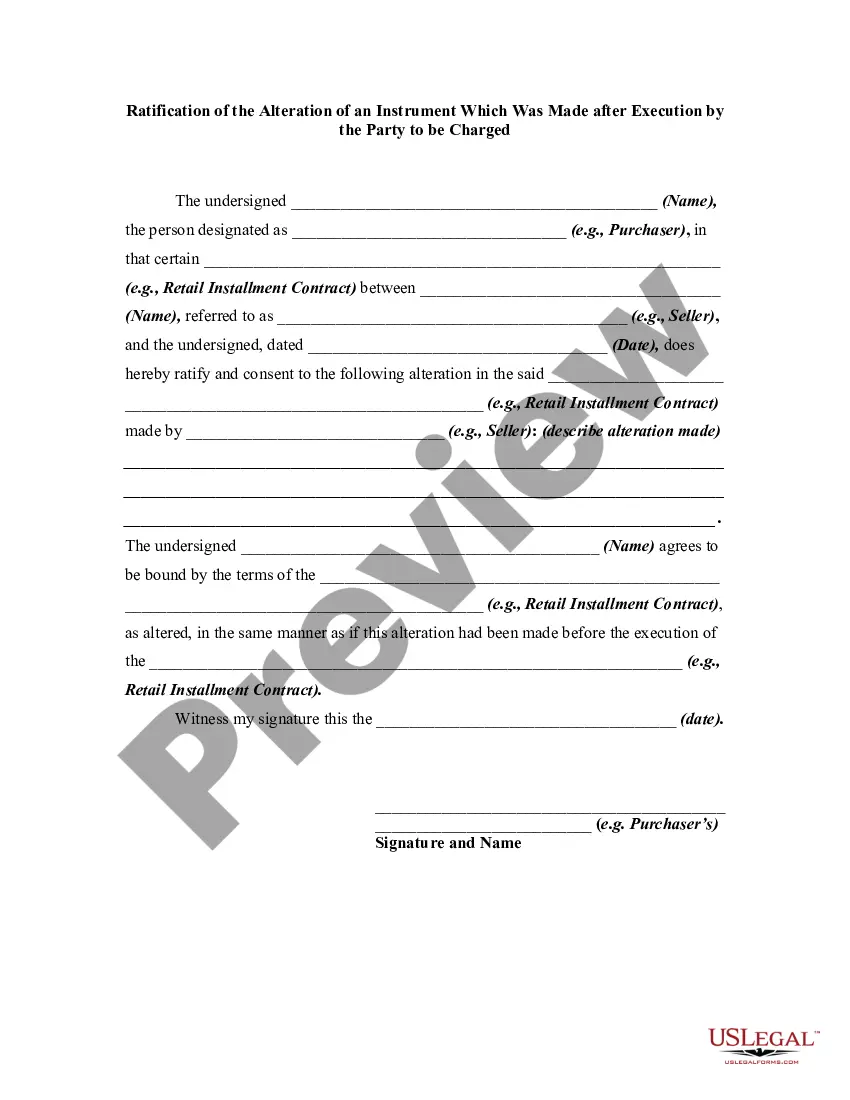
An alteration of a written instrument is a change in language of the instrument that is made by one of the parties to the instrument who is entitled to make the change. Any material alteration of a written instrument, after its execution, made by the owner or holder of the instrument, without the consent of the party to be charged, renders the instrument void as to the nonconsenting party. The party to be charged refers to that party or parties against whom enforcement of a contract or instrument is sought.
If a party consents to the alteration, the instrument will not be rendered invalid as to that party.
Georgia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged
Description
How to fill out Ratification Of The Alteration Of An Instrument Which Was Made After Execution By The Party To Be Charged?
If you need to fill out, acquire, or print legal document templates, utilize US Legal Forms, the largest selection of legal forms available online.
Utilize the site's simple and user-friendly search to find the documents you require. Numerous templates for business and personal purposes are organized by categories and jurisdictions, or keywords.
Utilize US Legal Forms to acquire the Georgia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged in just a few clicks.
Every legal document template you acquire is yours forever. You have access to every form you downloaded with your account. Go to the My documents section and select a form to print or download again.
Be proactive and download, and print the Georgia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged with US Legal Forms. There are numerous professional and state-specific forms you can utilize for your business or personal needs.
- If you are currently a US Legal Forms user, Log In to your account and click the Download button to obtain the Georgia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged.
- You can also access forms you previously downloaded in the My documents section of your account.
- If this is your first time using US Legal Forms, follow the steps below.
- Step 1. Ensure you have chosen the form for the appropriate area/state.
- Step 2. Use the Preview feature to review the form's details. Be sure to read the information.
- Step 3. If you are not satisfied with the form, utilize the Search area at the top of the screen to find other variations of the legal form template.
- Step 4. Once you have found the form you need, click the Purchase now button. Select the pricing plan you prefer and provide your credentials to register for an account.
- Step 5. Process the payment. You can use your Visa or MasterCard or PayPal account to complete the transaction.
- Step 6. Choose the format of the legal form and download it to your device.
- Step 7. Fill out, edit, and print or sign the Georgia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged.
Form popularity
FAQ
For a contract to be legally binding in Georgia, it must include offer, acceptance, consideration, and mutual consent. Each party must express their willingness to enter into an agreement and provide something of value. Additionally, all parties should have a clear understanding of the terms, reinforcing their commitment. This clarity becomes especially critical in matters involving the Georgia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged.
The primary statute governing contracts in Georgia is found in the Official Code of Georgia Annotated (O.C.G.A.) Title 13, which outlines the basic rules and regulations surrounding contractual obligations. Understanding this statute is crucial for anyone entering into contracts, as it sets the groundwork for enforceability and validity. Additionally, specific provisions may apply to unique situations, such as the Georgia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged.
In Georgia, a contract becomes legally binding when it meets several essential factors: offer, acceptance, consideration, and mutual intent to contract. Each party must agree to the terms and conditions, and both must provide something of value. Importantly, both parties must be aware and agree to the contract's implications, ensuring transparency. This underlines the importance of processes like the Georgia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged.
Several factors can void a contract in Georgia, including lack of capacity, illegality, misrepresentation, or coercion. If one of the parties lacks legal capacity, such as being a minor or mentally incapacitated, the contract may be deemed void. Additionally, if a contract's subject matter is illegal, it cannot be enforced. Understanding these factors is crucial when navigating legal agreements, including those related to the Georgia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged.
To establish a valid contract in Georgia, you must have an offer, acceptance, consideration, consent, and a lawful purpose. Each party must express an agreement to the terms, and both must agree to provide something of value, which is known as consideration. Additionally, the terms must be clear and not violate any laws. Understanding these requirements is essential for processes like the Georgia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged.
For a contract to be legal in Georgia, it must have several key elements: mutual consent, a lawful object, and consideration. Additionally, contracts should adhere to specific regulations concerning statutes like the Georgia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged. Ensuring these elements are present can help in creating enforceable contracts and prevent future disputes.
In Georgia, officers derive their authority to use force from O.C.G.A. § 16-3-21, which addresses justification for the use of force in defense of self or others. Understanding these statutes is vital for all parties involved. If you have questions surrounding these legal aspects, specifically regarding the Georgia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged, platforms like USLegalForms can provide essential guidance.
Yes, Georgia has various state statutes that govern a wide array of legal issues. These statutes provide the framework for handling matters, including contracts and ratifications. Familiarity with these statutes, particularly around topics like Georgia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged, helps individuals navigate legal challenges more effectively.
The statute of limitations for contracts in Georgia generally allows a party six years to file a claim. This period starts from the time the breach occurs. Considering aspects such as the Georgia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged can play a significant role in these timeframes. Taking prompt action can help ensure your rights are protected.
Ratification in contract law refers to the act of confirming or validating a previously unauthorized action or agreement. This can be especially relevant in scenarios involving the Georgia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged. It is essential that the party to be charged explicitly accepts the alterations to solidify the legal standing of the contract.