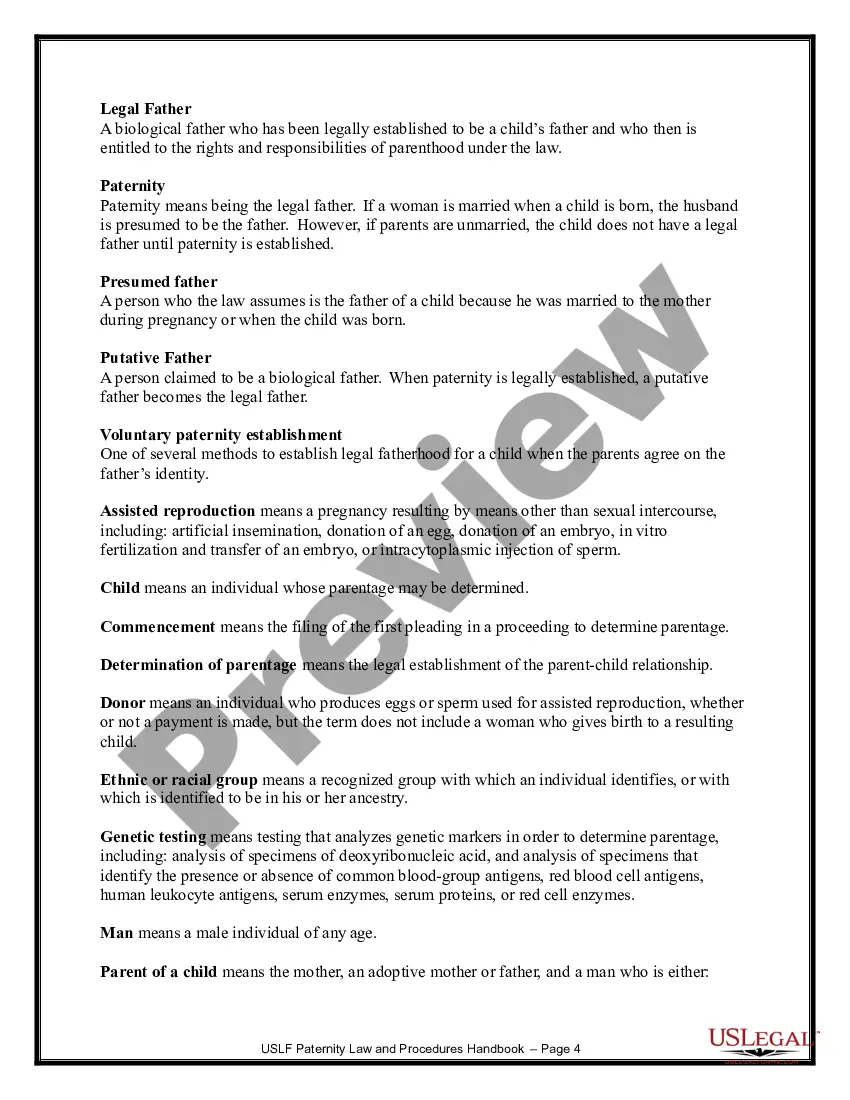
Across the United States each year, a large percentage of children are born to unmarried parents. State law requires the father to support the child financially, but sometimes the father is hesitant to officially acknowledge paternity of the child. This Paternity Laws and Procedures Handbook provides state-specific paternity resources for establishing paternity, and discusses the relevant law and procedures in a general, and easily understood manner. A law summary of the paternity laws in your state is provided. Voluntary paternity establishment and paternity establishment through court action are discussed, as is the genetic testing that the court may order to confirm paternity in doubtful cases. Reading this Handbook will allow you to go forward in the paternity establishment process with the confidence of knowing what to expect at each turn, and provide you with the points of contact in your state for the people and resources that can help you and your child succeed.
Alabama Paternity Law and Procedure Handbook
Description
Get your form ready online
Our built-in tools help you complete, sign, share, and store your documents in one place.
Make edits, fill in missing information, and update formatting in US Legal Forms—just like you would in MS Word.
Download a copy, print it, send it by email, or mail it via USPS—whatever works best for your next step.
Sign and collect signatures with our SignNow integration. Send to multiple recipients, set reminders, and more. Go Premium to unlock E-Sign.
If this form requires notarization, complete it online through a secure video call—no need to meet a notary in person or wait for an appointment.
We protect your documents and personal data by following strict security and privacy standards.
Make edits, fill in missing information, and update formatting in US Legal Forms—just like you would in MS Word.

Download a copy, print it, send it by email, or mail it via USPS—whatever works best for your next step.

Sign and collect signatures with our SignNow integration. Send to multiple recipients, set reminders, and more. Go Premium to unlock E-Sign.
If this form requires notarization, complete it online through a secure video call—no need to meet a notary in person or wait for an appointment.
We protect your documents and personal data by following strict security and privacy standards.
Looking for another form?
How to fill out Alabama Paternity Law And Procedure Handbook?
Utilize US Legal Forms to obtain a printable Alabama Paternity Law and Procedure Handbook.
Our court-acknowledged forms are created and routinely refreshed by experienced attorneys.
Ours is the most comprehensive Forms collection available online and provides economical and precise templates for individuals, legal practitioners, and small to medium businesses.
Examine the form by reading the description and utilizing the Preview feature. Press Buy Now if it’s the template you seek. Create your account and pay through PayPal or credit card. Download the template to your device and feel free to reuse it multiple times. Use the Search field to find another document template. US Legal Forms provides a vast array of legal and tax templates and packages for business and personal requirements, including the Alabama Paternity Law and Procedure Handbook. Over three million users have successfully utilized our service. Select your subscription plan and access high-quality forms in just a few clicks.
- The documents are organized into state-specific categories.
- Many of them can be previewed prior to downloading.
- To access samples, users must have a subscription and Log In to their account.
- Click Download beside any form you require and locate it in My documents.
- For users without a subscription, follow these instructions to easily locate and download the Alabama Paternity Law and Procedure Handbook.
- Confirm that you possess the correct template for the needed state.
Form popularity
FAQ
To file a motion for a paternity test in Alabama, you need to prepare and submit the appropriate forms to the court. This process usually includes detailing why the test is necessary and providing any additional evidence. The Alabama Paternity Law and Procedure Handbook can guide you through the specifics and help ensure everything is properly filed.
A DNA test may be required for child support in Alabama if the alleged father disputes his paternity. Courts use DNA testing to confirm biological relationships, which can directly influence child support decisions. Refer to the Alabama Paternity Law and Procedure Handbook for essential information on how to navigate this process.
A paternity test is not always required for child support in Alabama, but it is often necessary if there is a question of the father's identity. Establishing paternity can streamline the child support process significantly. The Alabama Paternity Law and Procedure Handbook offers insights into when and how these tests should be pursued.
In Alabama, signing a birth certificate can establish paternity if both parents are in agreement. This acknowledgment carries legal weight, but it may not be sufficient in disputes over child support or custody. For comprehensive guidance, refer to the Alabama Paternity Law and Procedure Handbook to understand the legal ramifications.
To add a father's name to a birth certificate in Alabama, both parents generally need to sign an acknowledgment of paternity. If there is a disagreement about paternity, a court order may be necessary. The Alabama Paternity Law and Procedure Handbook provides detailed procedures and forms to assist you in this process.
Rule 32 in Alabama refers to the child support guidelines established by the state. These guidelines help determine the amount of child support owed, based on the income of both parents and the needs of the child. Familiarizing yourself with the Alabama Paternity Law and Procedure Handbook can provide clarity on how these calculations work and what factors are considered.
In Alabama, a mother can refuse a paternity test; however, this refusal may affect the legal proceedings related to paternity. The Alabama Paternity Law and Procedure Handbook outlines the implications of such a decision. It's important to consider how this refusal can impact child support, custody, and visitation rights.
Paternity laws in Alabama outline the process for establishing a legal father-child relationship. These laws cover aspects like genetic testing, signing paternity affidavits, and the rights of both parents. The Alabama Paternity Law and Procedure Handbook serves as a critical tool, providing clarity on these laws and helping individuals navigate the complexities of paternity. With this handbook, you can receive step-by-step guidance to ensure compliance and protection of parental rights.
Yes, in Alabama, signing the birth certificate does establish paternity, but it may not be sufficient in every situation. While it provides legal recognition, there are additional steps a father may need to take for full legal rights. For comprehensive information and clarification, consult the Alabama Paternity Law and Procedure Handbook, which offers detailed guidance on signing birth certificates and subsequent legal processes. This resource ensures that fathers understand their responsibilities and rights right from the start.
Fathers of children born out of wedlock in Alabama have specific rights, including the right to establish paternity, seek custody, and request visitation. It is crucial for fathers to document their relationship and involvement in the child’s life. The Alabama Paternity Law and Procedure Handbook can be an invaluable resource for understanding these rights and ensuring that they are protected throughout the legal process. Fathers should be proactive in asserting these rights to foster meaningful relationships with their children.