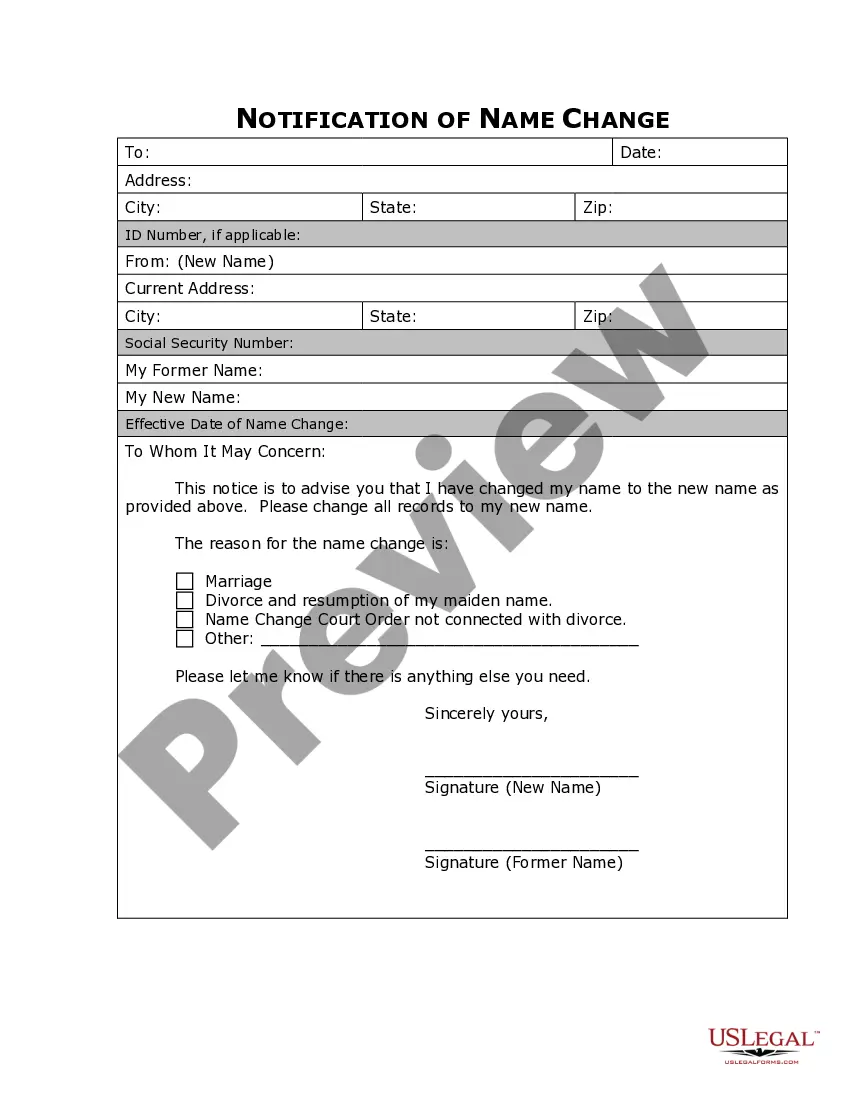
Underwriting Commission For Securities
Description
How to fill out Underwriting Agreement Of Ameriquest Mortgage Securities, Inc.?
Locating a reliable source for obtaining the latest and pertinent legal templates is a significant part of dealing with bureaucracy. Selecting the appropriate legal documents requires accuracy and meticulousness, which is why it is crucial to acquire samples of Underwriting Commission For Securities exclusively from trustworthy sources, such as US Legal Forms. An unsuitable template will squander your time and hinder the matter at hand. With US Legal Forms, you have minimal concerns.
You can access and verify all the information about the document’s application and relevance for your circumstances and in your state or county.
After you have the form saved on your device, you can edit it using the editor or print it to complete it manually. Remove the hassle associated with your legal paperwork. Browse the extensive US Legal Forms catalog to discover legal templates, assess their relevance to your situation, and download them instantly.
- Utilize the library navigation or search feature to find your sample.
- Examine the form’s details to ensure it meets the requirements of your state and area.
- Check the form preview, if available, to confirm the template is indeed the one you are looking for.
- Continue the search and find the appropriate document if the Underwriting Commission For Securities does not suit your requirements.
- When you are confident about the form’s relevance, download it.
- If you are a registered user, click Log in to verify and access your chosen forms in My documents.
- If you don't have an account yet, click Buy now to acquire the template.
- Select the pricing plan that meets your needs.
- Proceed to register to complete your purchase.
- Finalize your transaction by choosing a payment method (credit card or PayPal).
- Select the document format for downloading Underwriting Commission For Securities.
Form popularity
FAQ
Example of Underwriting Fees Scenario: Amanda is applying for a mortgage loan of $300,000 to buy a house. The bank charges an underwriting fee of 1% of the loan amount. Calculation: Underwriting Fee = 1% of $300,000.
An issuer can, for example, sell a bond to the underwriter at $90 per bond. The underwriter then positions the problem at $100, thereby enabling it to make a profit of $10. The profit that is made is rightly called as Underwriting Commission.
It may be given at a lower rate if possible. As per SEBI Guidelines also, the rate of underwriting commission must not exceed @ 2.5% of the issue price. Therefore, the Underwriting commission on shares as per SEBI guidelines is up to 2.5%.
Underwriting Commission The consideration payable to the underwriters for. underwriting the issue of shares or debentures of a company is called underwriting. commission. Such a commission is paid at a specified rate on the issue price of the.
In the securities market, underwriting involves determining the risk and price of a particular security. It is a process seen most commonly during initial public offerings, wherein investment banks first buy or underwrite the securities of the issuing entity and then sell them in the market.