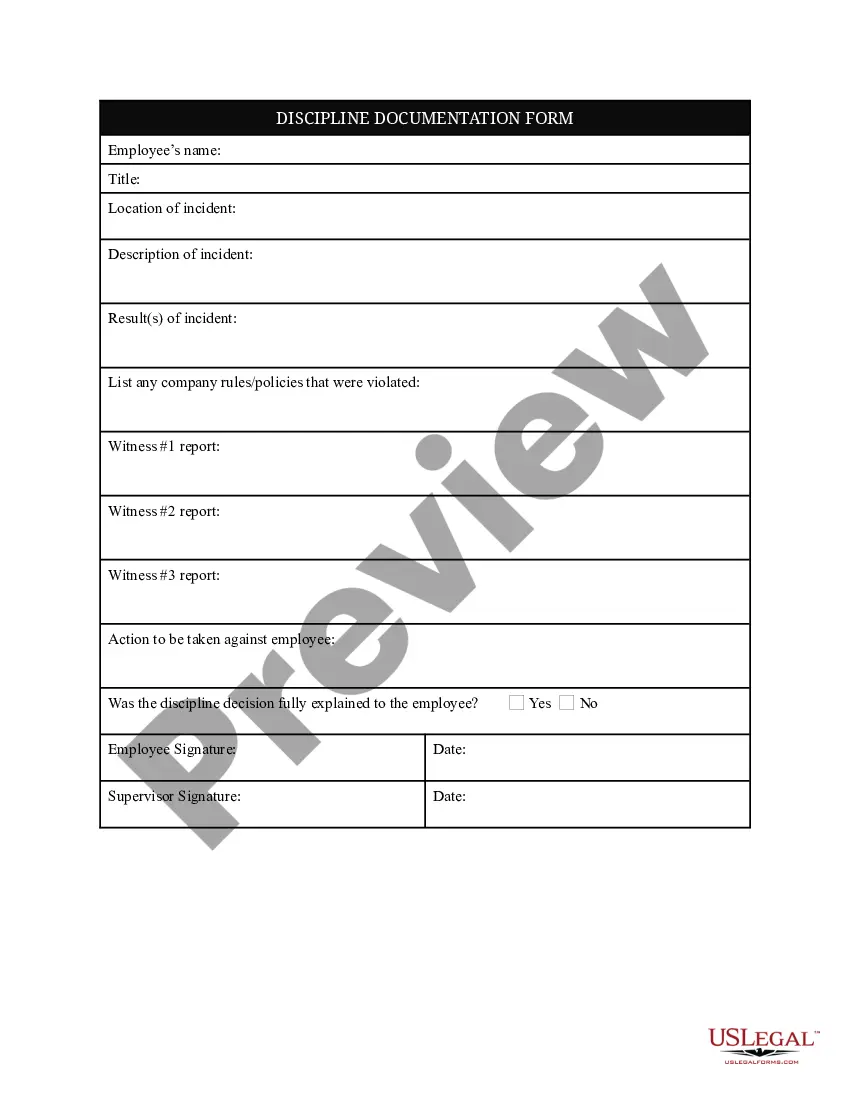
Agreement Receivable Statement With Balance Sheet In Wake
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
The amount that is receivable will be recorded as a debit to the assets. These entries balance each other out.
What Are the Types of Receivables? Generally, receivables are divided into three types: trade accounts receivable, notes receivable, and other accounts receivable. Accounts Receivable: Accounts receivable usually occur because of credit sales. It arises as a result of buying goods or services on credit.
Short-term bills receivable- Bills due within one year from the balance sheet date are classified as current assets in the balance sheet. Long-term bills receivable- Bills due after one year from the balance sheet date are classified as non-current assets in the balance sheet.
To report accounts receivable effectively on the balance sheet: Break down accounts receivable into categories, such as “trade accounts receivable” and “other receivables.” Clearly indicate the aging of accounts receivable to show how much is current, 30, 60, or 90+ days overdue.
An account receivable is recorded as a debit in the assets section of a balance sheet. It is typically a short-term asset—short-term because normally it's going to be realized within a year.”
The payee should record the interest earned and remove the note from its Notes Receivable account. Thus, the payee of the note should debit Accounts Receivable for the maturity value of the note and credit Notes Receivable for the note's face value and Interest Revenue for the interest.
The journal entry to record the conversion of A/R to a note receivable would be to debit note receivable and credit accounts receivable. The entry reclassifies the amount on the balance sheet on the date of the conversion. There is no impact to the income statement.
Notes receivable are recorded as an asset account for the amount owed by the note “maker,” also known as the debtor. Key aspects like time frame, formal documentation and interest differentiate notes receivable from accounts receivable.
The principal part of a note receivable is reported as a current asset if due within one year of the balance sheet date; otherwise, it's reported as a noncurrent asset under notes receivable. Interest is recorded as a current asset if it is due within one year of the balance sheet date.