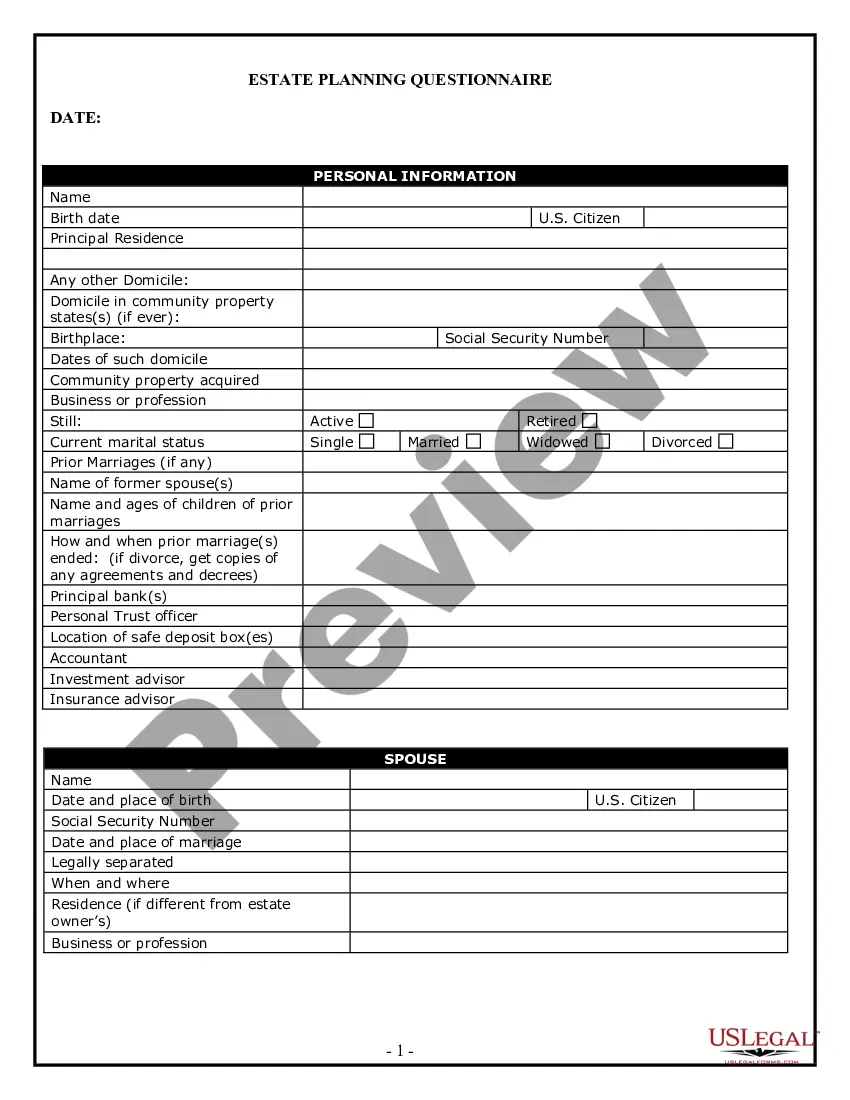
This is a multi-state form covering the subject matter of the title.
Pregnancy Discrimination At Work Examples In Queens
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Proving pregnancy discrimination requires more than a victim's claim. There must be evidence that the employer acted against the individual exclusively based on their pregnancy. That evidence must be clear, inarguable, and documented.
If you're experiencing severe pregnancy-related symptoms that impact your ability to work, you have the right to request reasonable accommodations from your employer. This could include adjustments to your work schedule, duties, or work location, such as remote work.
Highlights refusing to hire, failing to promote, demoting, or firing pregnant workers after learning they are pregnant; discharging workers who take medical leave for pregnancy-related conditions (such as a miscarriage);
You absolutely can sue for being terminated for the sole purpose of being pregnant. There is a process to bring in the lawsuit against your employer, and I would strongly obtain an attorney right away.
Pregnancy has been a protected class for a while in the United States. The PWFA went into effect on June 27, 2023. On April 15, 2024 the EEOC issued its final regulation to carry out the law. So, no. US employers are not allowed to deny employment if you are pregnant IF YOUR EMPLOYER HAS MORE THAN 15 EMPLOYEES.
After 26 weeks: There should be no extended work hours, with a 40-hour week being the maximum for the employee/patient. No travel further than 50 miles is allowed. Lifting is restricted to no more than 20 pounds. No climbing on ladders or stools is allowed.
Balancing work and pregnancy requires both setting boundaries and being flexible. Prioritize tasks, learn to say 'no' when necessary, and disconnect from work during personal time to reduce stress and prevent burnout. At the same time, be adaptable to the unique needs of your pregnancy.
A woman who is having a normal, healthy pregnancy can work right up until the start of labour. However, you can choose to stop working whenever suits you. Some women choose to stop several weeks before their due date but others will be at work even in early labour.
Proving pregnancy discrimination requires more than a victim's claim. There must be evidence that the employer acted against the individual exclusively based on their pregnancy. That evidence must be clear, inarguable, and documented.
Violations have involved a variety of fact patterns, including: refusing to hire, failing to promote, demoting, or firing pregnant workers after learning they are pregnant; discharging workers who take medical leave for pregnancy-related conditions (such as a miscarriage);