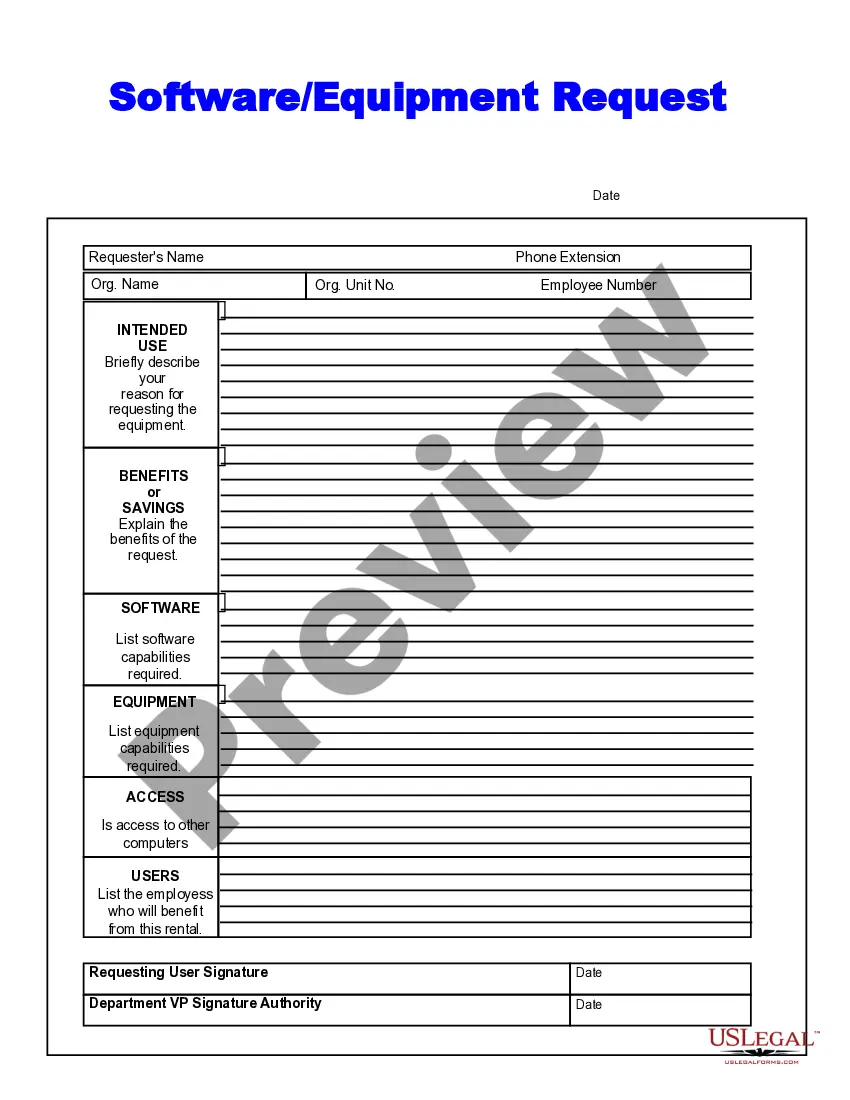
14th Amendment For Debt Ceiling In Cuyahoga
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
14th Amendment - Citizenship Rights, Equal Protection, Apportionment, Civil War Debt | Constitution Center.
The Fourteenth Amendment to the Constitution of the United States granted citizenship and equal civil and legal rights to anyone born in the United States or who became a citizen of the country. This included African Americans and slaves who had been freed after the American Civil War.
No State shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges or immunities of citizens of the United States; nor shall any State deprive any person of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law; nor deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the laws.
Congress has always acted when called upon to raise the debt limit. Since 1960, Congress has acted 78 separate times to permanently raise, temporarily extend, or revise the definition of the debt limit – 49 times under Republican presidents and 29 times under Democratic presidents.
On July 28, 1868, the final state necessary for ratification of the amendment agreed to it. Many white Ohioans initially approved of the Fourteenth Amendment. Members of the Union Party, a group of Ohio's Republican Party and pro-war Democrats, strongly supported the amendment.
Why was the Fourteenth Amendment controversial in women's rights circles? This is because, for the first time, the proposed Amendment added the word "male" into the US Constitution.
Section 5 grants Congress the power to enforce the Amendment by "appropriate legislation." After adopting the Fourteenth Amendment, Congress passed legislation that criminalized insurrection. Today, this law is codified in 18 U.S. Code § 2383.
The Fourteenth Amendment's Due Process Clause provides that no state may deprive any person of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law.
A major provision of the 14th Amendment was to grant citizenship to “All persons born or naturalized in the United States,” thereby granting citizenship to formerly enslaved people.
A major provision of the 14th Amendment was to grant citizenship to “All persons born or naturalized in the United States,” thereby granting citizenship to formerly enslaved people.