Maryland’s Legislative Process is a multi-step process through which bills are introduced, debated, and voted on in order to become state laws. The process begins with the introduction of a bill either in the House of Delegates or the Senate. Once a bill is introduced, it is referred to the appropriate committee for review. The committee then holds hearings and debates the bill, and votes on whether to report the bill favorably. The bill is then sent to the full chamber for a vote. If it passes, it is sent to the other chamber, where the process is repeated. Once the bill passes through both chambers, the bill is sent to the Governor for signature. After the Governor signs the bill, it becomes a law. There are two types of Maryland Legislative Process: Regular Session and Special Session. Regular Session is held annually and begins in January, while Special Session is held at the Governor’s discretion and can be called during any period of recess.
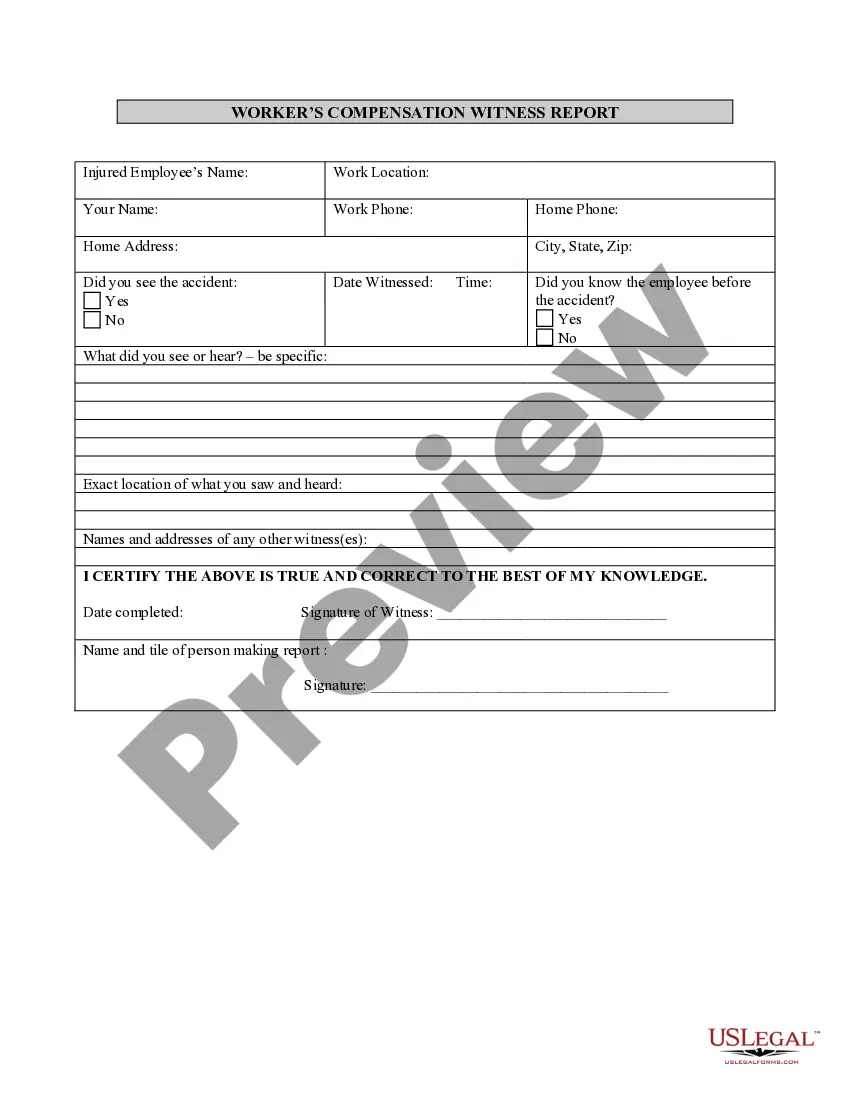
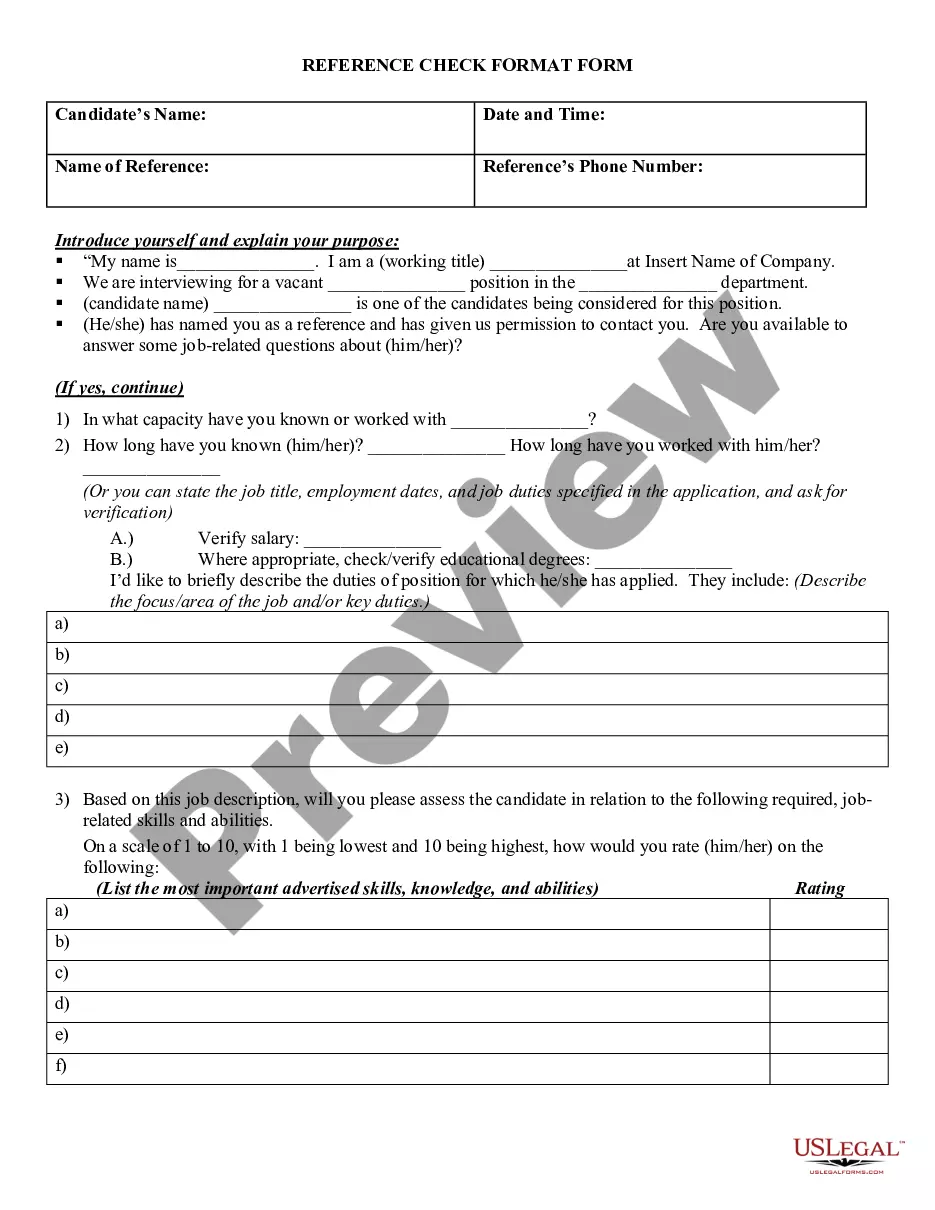
Maryland The Legislative Process
Description
Get your form ready online
Our built-in tools help you complete, sign, share, and store your documents in one place.
Make edits, fill in missing information, and update formatting in US Legal Forms—just like you would in MS Word.
Download a copy, print it, send it by email, or mail it via USPS—whatever works best for your next step.
Sign and collect signatures with our SignNow integration. Send to multiple recipients, set reminders, and more. Go Premium to unlock E-Sign.
If this form requires notarization, complete it online through a secure video call—no need to meet a notary in person or wait for an appointment.
We protect your documents and personal data by following strict security and privacy standards.
Make edits, fill in missing information, and update formatting in US Legal Forms—just like you would in MS Word.

Download a copy, print it, send it by email, or mail it via USPS—whatever works best for your next step.

Sign and collect signatures with our SignNow integration. Send to multiple recipients, set reminders, and more. Go Premium to unlock E-Sign.
If this form requires notarization, complete it online through a secure video call—no need to meet a notary in person or wait for an appointment.
We protect your documents and personal data by following strict security and privacy standards.
Looking for another form?
How to fill out Maryland The Legislative Process?
US Legal Forms is the easiest and most lucrative method to find suitable legal templates.
It’s the largest online collection of business and personal legal documents crafted and verified by attorneys.
Here, you can discover printable and fillable templates that adhere to federal and local regulations - just like your Maryland The Legislative Process.
Review the form details or preview the document to confirm you’ve located the one that fits your needs, or search for another one using the search feature above.
Click Buy now when you’re confident of its alignment with all the specifications, and select the subscription plan you prefer most.
- Obtaining your template requires only a few straightforward steps.
- Users with an existing account and an active subscription simply need to Log In to the site and download the form onto their device.
- Afterward, it can be located in their account under the My documents section.
- And here’s how you can acquire a properly prepared Maryland The Legislative Process if you are utilizing US Legal Forms for the first time.
Form popularity
FAQ
To gain legislative experience in Maryland, consider applying for internships or volunteer positions with your local elected officials or legislative committees. You can also participate in programs that offer mentorships for those interested in public policy. Furthermore, platforms like USLegalForms can assist you in accessing relevant legal documents to understand the legislative framework better and prepare you for your journey in public service.
You can get involved in the Maryland legislative process by attending local council meetings or legislative sessions. Engaging with your representatives through calls or emails is another effective way to voice your opinion on issues that matter to you. Additionally, joining local advocacy groups can provide you with opportunities to participate in campaigns and initiatives aimed at shaping legislation.
In Maryland, the local legislative process varies by county and city, but it generally includes the introduction of local bills by elected officials. These bills undergo a review and may be subject to public hearings to gather community feedback. After debates and amendments, the local council or governing body votes on the proposed legislation. Understanding this process is essential for residents who wish to influence local governance.
The legislative process in Maryland involves several steps that begin with the proposal of legislation. Once proposed, bills are reviewed and debated in committee before they reach the floor for a vote. If approved, the bills go to the opposite chamber for similar consideration. Finally, approved legislation is sent to the Governor for signing, which officially enacts the law.
The Life of a Law Step 1: Drafting the Idea. The first step can start with you.Step 2: Georgia General Assembly.Step 3: Georgia State Legislative Session.Step 4: Third Reading.Step 5: The Vote.Step 6: The Governor's Role.Step 7: The Bill Becomes a Law.
The work of Congress is initiated by the introduction of a proposal in one of four principal forms: the bill, the joint resolution, the concurrent resolution, and the simple resolution.
The legislative branch is made up of the House and Senate, known collectively as the Congress. Among other powers, the legislative branch makes all laws, declares war, regulates interstate and foreign commerce and controls taxing and spending policies.
MARYLAND'S LEGISLATURE The General Assembly has 188 members, with 47 senators and 141 delegates. One senator and three delegates are elected from each of the 47 legislative election districts. After every decennial census, legislative district boundaries are redrawn to conform to the principle of "one person/one vote".
Match Legislation is introduced. Bill is assigned a committee. Bill is placed on correct calendar. Bill goes to House or Senate floor to be voted on as passing or letting it die. Legislation is sent to the president.
Legislative Process Step 1: How Your Idea Becomes A Bill.Step 2: What To Do When Your Bill Goes To Policy Committee.Step 3: What If Your Bill Goes To A Fiscal Committee?Step 4: After Your Bill Passes The House Of Origin And Goes To The Second House.Step 5: You Can Still Act After Your Bill Goes To The Governor.