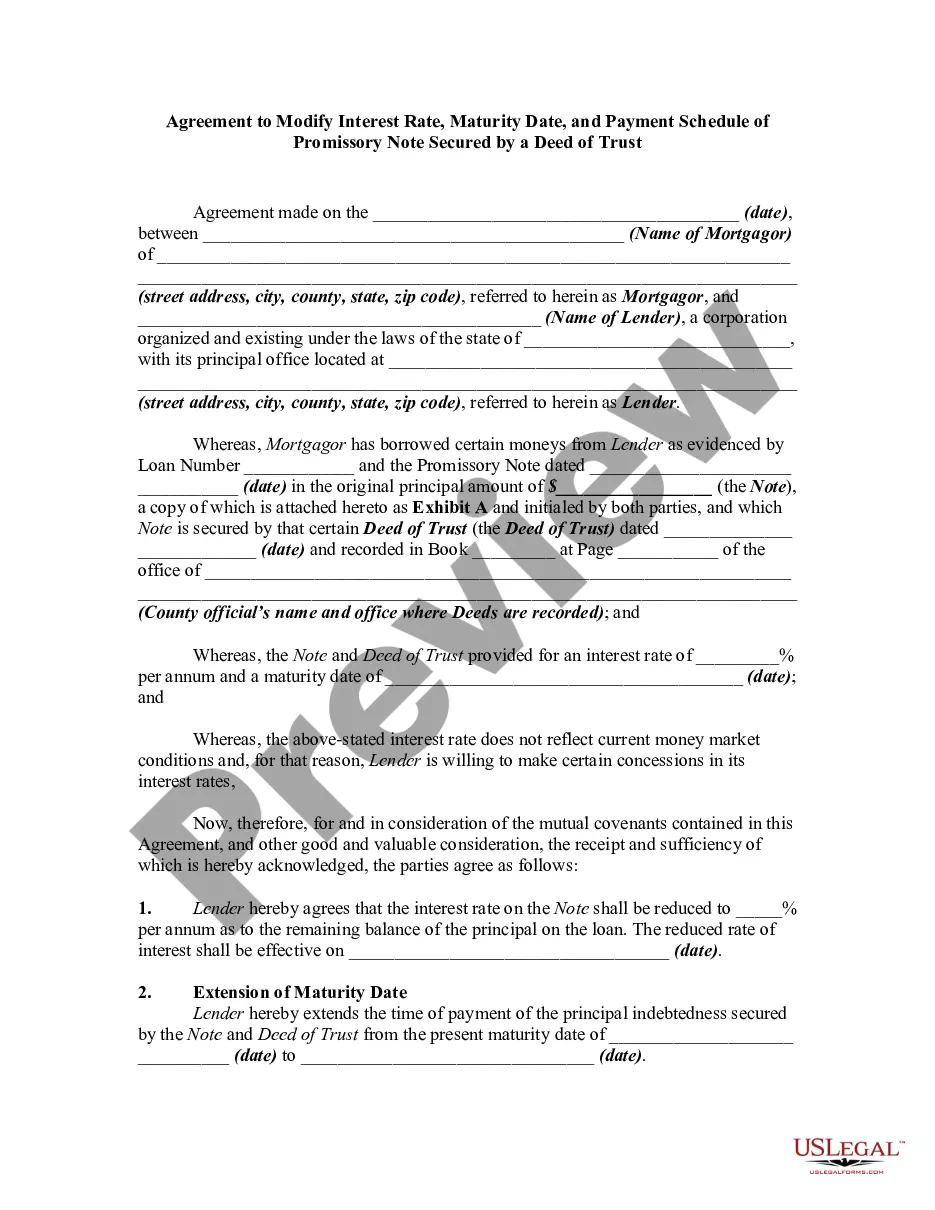
US Legal Forms - one of several greatest libraries of legal varieties in the USA - provides a variety of legal papers templates you are able to download or printing. Using the web site, you may get a huge number of varieties for organization and specific functions, sorted by groups, claims, or keywords and phrases.You can get the most recent types of varieties such as the Kentucky Agreement to Change or Modify Interest Rate, Maturity Date, and Payment Schedule of Promissory Note Secured by a Deed of Trust within minutes.
If you already have a membership, log in and download Kentucky Agreement to Change or Modify Interest Rate, Maturity Date, and Payment Schedule of Promissory Note Secured by a Deed of Trust in the US Legal Forms catalogue. The Obtain option will show up on each develop you perspective. You get access to all earlier downloaded varieties inside the My Forms tab of your own bank account.
If you wish to use US Legal Forms for the first time, listed below are easy recommendations to obtain began:
- Be sure you have picked out the right develop for the city/area. Select the Preview option to review the form`s content. Browse the develop information to actually have chosen the correct develop.
- When the develop does not fit your specifications, take advantage of the Search field near the top of the screen to discover the the one that does.
- Should you be pleased with the form, validate your selection by clicking on the Get now option. Then, select the prices plan you favor and offer your qualifications to sign up on an bank account.
- Process the purchase. Make use of bank card or PayPal bank account to perform the purchase.
- Choose the formatting and download the form in your gadget.
- Make alterations. Complete, change and printing and sign the downloaded Kentucky Agreement to Change or Modify Interest Rate, Maturity Date, and Payment Schedule of Promissory Note Secured by a Deed of Trust.
Every single web template you put into your account lacks an expiry day and it is the one you have forever. So, if you wish to download or printing an additional backup, just visit the My Forms portion and click on around the develop you need.
Get access to the Kentucky Agreement to Change or Modify Interest Rate, Maturity Date, and Payment Schedule of Promissory Note Secured by a Deed of Trust with US Legal Forms, the most comprehensive catalogue of legal papers templates. Use a huge number of specialist and condition-particular templates that fulfill your business or specific requirements and specifications.