Colorado Certificate of Trust - Indebtedness
Description
How to fill out Certificate Of Trust - Indebtedness?
If you need to comprehensive, download, or printing authorized papers web templates, use US Legal Forms, the greatest selection of authorized types, that can be found on-line. Make use of the site`s basic and convenient lookup to discover the papers you want. Different web templates for enterprise and specific uses are sorted by classes and says, or keywords. Use US Legal Forms to discover the Colorado Certificate of Trust for Property within a handful of clicks.
In case you are previously a US Legal Forms buyer, log in to the profile and then click the Obtain button to find the Colorado Certificate of Trust for Property. You can even accessibility types you formerly downloaded within the My Forms tab of the profile.
Should you use US Legal Forms initially, follow the instructions below:
- Step 1. Be sure you have selected the shape for the correct area/region.
- Step 2. Use the Preview method to examine the form`s information. Never forget about to see the explanation.
- Step 3. In case you are not happy together with the form, use the Search discipline at the top of the display to locate other versions from the authorized form design.
- Step 4. When you have located the shape you want, click the Purchase now button. Pick the prices plan you prefer and add your credentials to sign up to have an profile.
- Step 5. Method the transaction. You can utilize your Мisa or Ьastercard or PayPal profile to complete the transaction.
- Step 6. Pick the file format from the authorized form and download it in your device.
- Step 7. Comprehensive, revise and printing or signal the Colorado Certificate of Trust for Property.
Each authorized papers design you get is yours for a long time. You have acces to every form you downloaded inside your acccount. Select the My Forms section and pick a form to printing or download once again.
Compete and download, and printing the Colorado Certificate of Trust for Property with US Legal Forms. There are many expert and condition-particular types you can use for the enterprise or specific requirements.
Form popularity
FAQ
There are three ways to get a certificate of trust made: With a lawyer. An estate planning attorney can draft a certificate of trust for you to accompany your trust. With estate planning software. ... With a state-specific form from a financial institution or notary public.
A trust is different from other legal entities because it does not need approved by or registered with the government. Because no registration is required you may form an anonymous trust to protect your privacy.
A notary is not required in order for the trust agreement to be valid, although a preferred method to ensure the validity of the document in the event of a challenge.
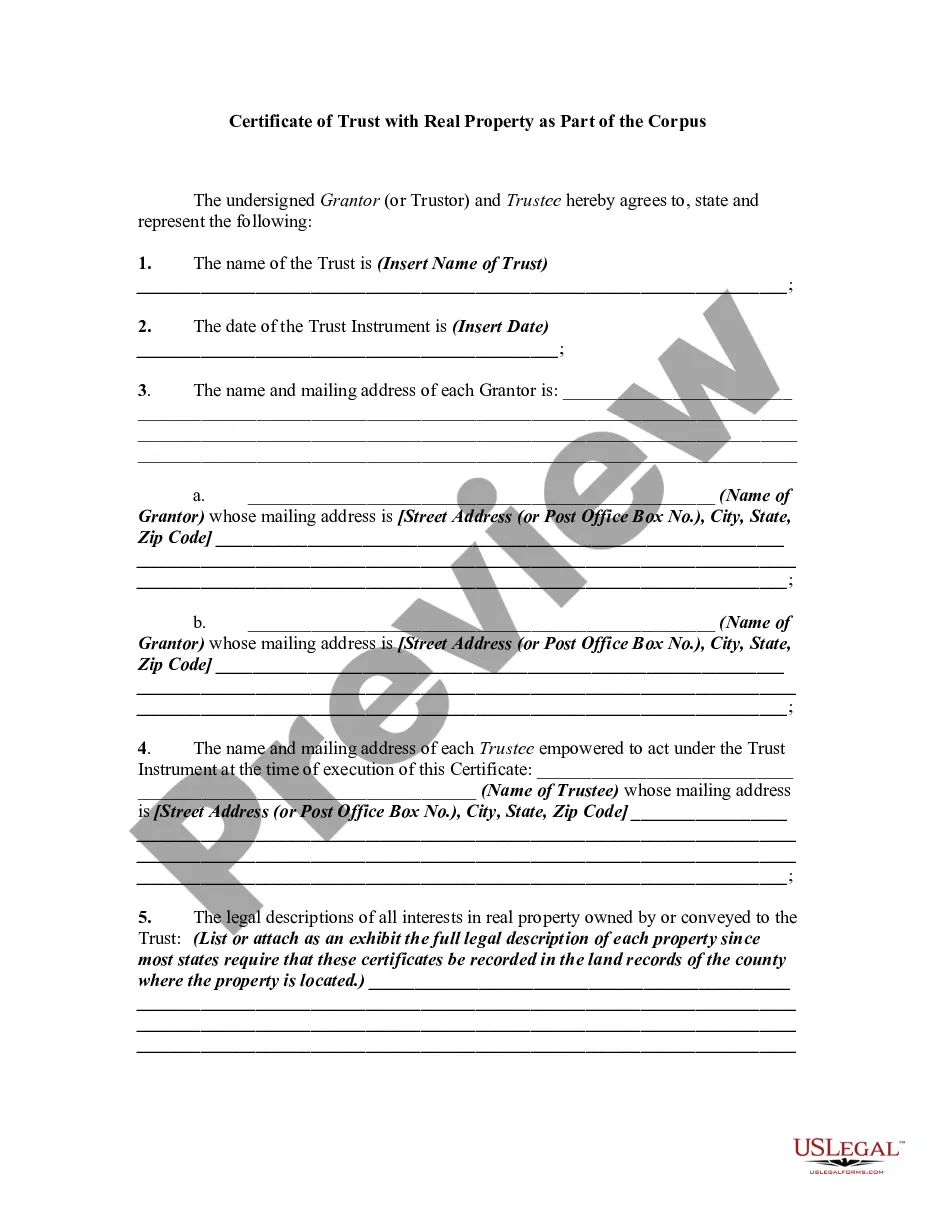
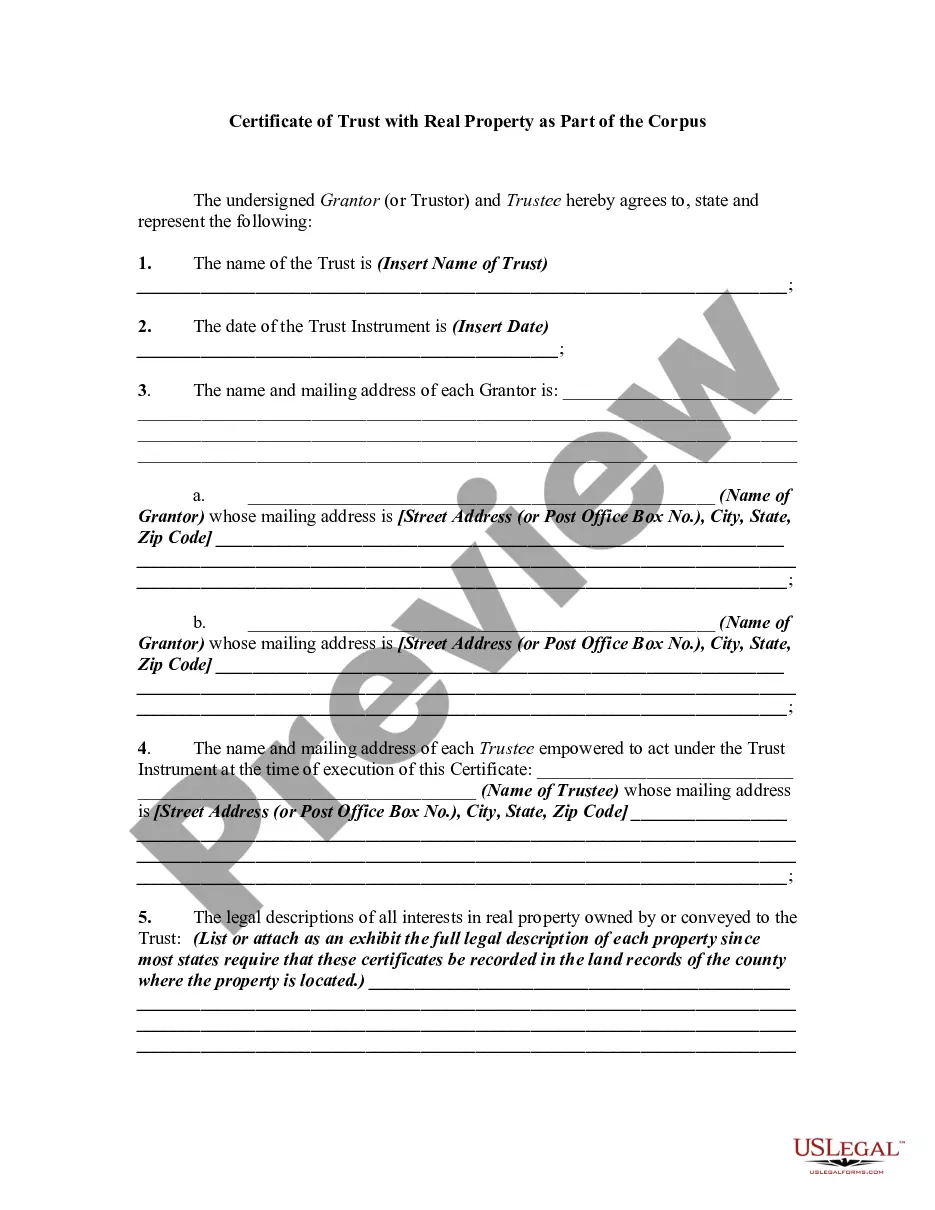
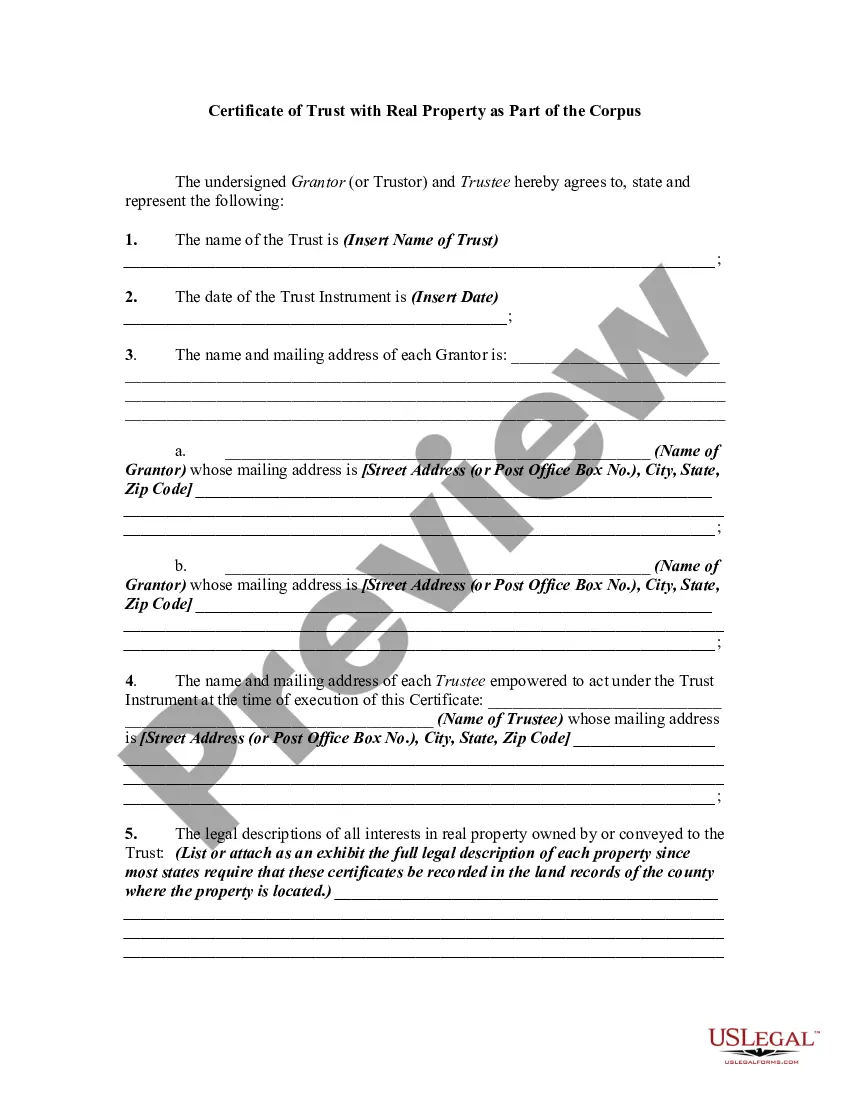
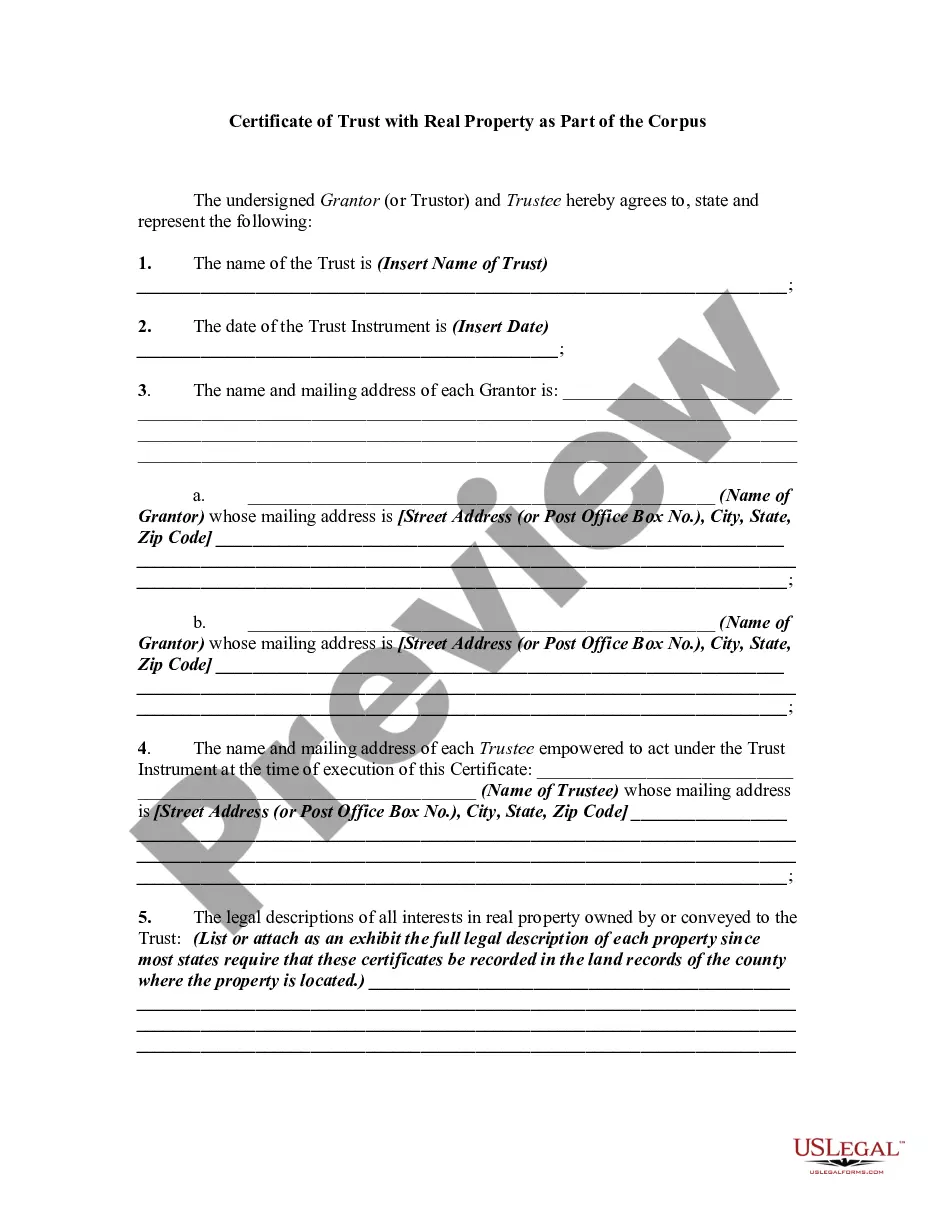
The certificate of trust must be a duly acknowledged affidavit or other written statement expressly made under penalty of perjury executed by any trustee and must include the following: (a) A statement that the trust exists and the date the trust instrument was executed; (b) The identity of the settlor; (c) The ...
Make a written demand for a copy of the Trust and its amendments, if any; Wait 60 days; and. If you do not receive a copy of the Trust within 60 days of making your written demand, file a petition with the probate court.
The trust agreement is the parent document that details anything and everything regarding the trust, including its agreements. Meanwhile, the certificate of trust is used in tandem to keep nonessential information confidential.
Make a written demand for a copy of the Trust and its amendments, if any; Wait 60 days; and. If you do not receive a copy of the Trust within 60 days of making your written demand, file a petition with the probate court.