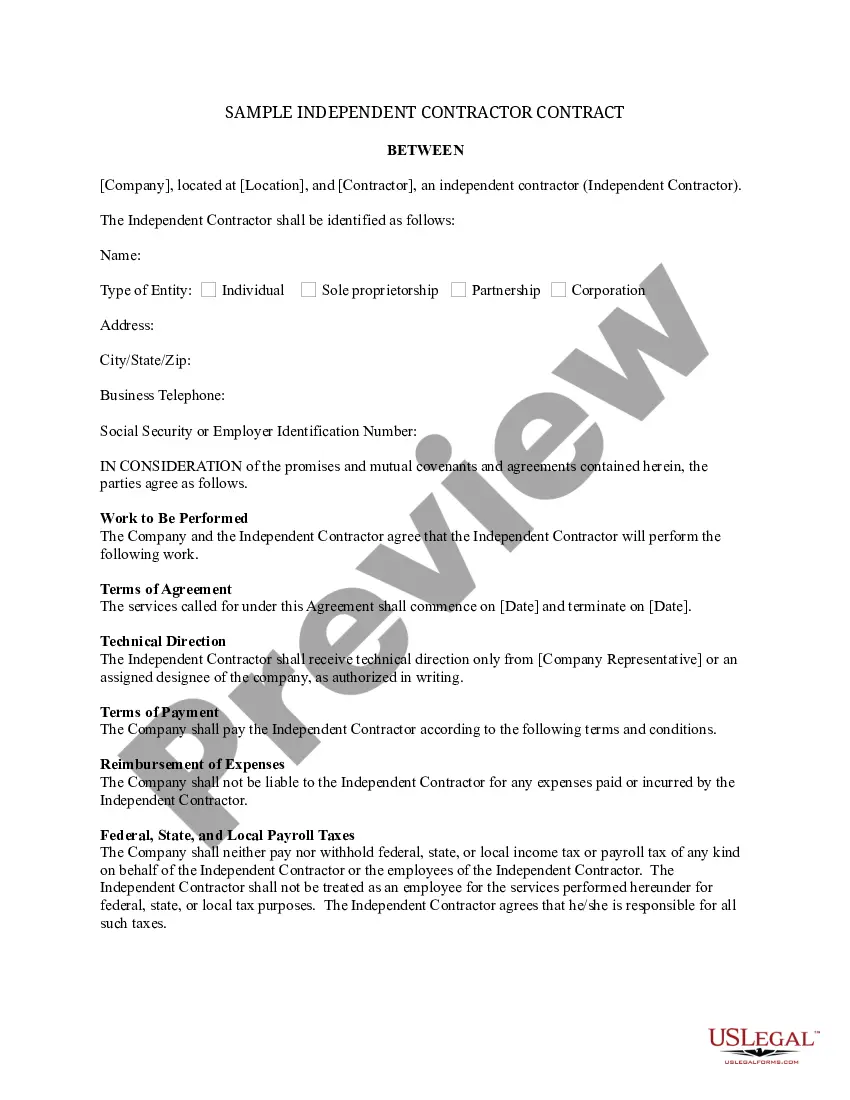
Arkansas Ratification of Acts
Description
How to fill out Ratification Of Acts?
Choosing the best legitimate document web template might be a have difficulties. Obviously, there are plenty of themes available on the net, but how do you get the legitimate kind you will need? Use the US Legal Forms web site. The service offers thousands of themes, like the Arkansas Ratification of Acts, which can be used for business and personal requires. All of the varieties are checked out by specialists and satisfy federal and state needs.
Should you be already listed, log in in your accounts and click on the Acquire switch to find the Arkansas Ratification of Acts. Utilize your accounts to check through the legitimate varieties you might have ordered formerly. Proceed to the My Forms tab of your accounts and acquire yet another backup of your document you will need.
Should you be a fresh user of US Legal Forms, here are simple guidelines that you can adhere to:
- Initially, make sure you have selected the appropriate kind to your metropolis/area. You may examine the shape using the Preview switch and look at the shape outline to make sure this is basically the right one for you.
- In case the kind will not satisfy your preferences, use the Seach area to get the correct kind.
- When you are certain the shape would work, go through the Purchase now switch to find the kind.
- Opt for the rates strategy you want and type in the required info. Create your accounts and pay money for an order using your PayPal accounts or Visa or Mastercard.
- Choose the file structure and obtain the legitimate document web template in your system.
- Complete, edit and printing and indication the acquired Arkansas Ratification of Acts.
US Legal Forms may be the biggest collection of legitimate varieties that you can discover various document themes. Use the service to obtain skillfully-produced files that adhere to status needs.
Form popularity
FAQ
1874 Arkansas Constitution The fifth and current Constitution of the State of Arkansas, framed and adopted by the convention which assembled at Little Rock, July 14th, 1874, and ratified by the people of the state, at the election held Oct. 13th, 1874.
The Third Arkansas Constitution (1864) The 1864 constitution abolished slavery and repudiated secession but did not define the rights former slaves would enjoy. Also, this constitution, unlike that of 1836, provided for the popular election of secretary of state, auditor, treasurer, and judges.
The earliest state-mandated segregation in Arkansas occurred with the passage of Act 52 of 1868, which established segregated education for black and white students. The quandary in which most black citizens found themselves required them to consider which would be the lesser of two evils: exclusion or segregation.
1874 Arkansas Constitution The fifth and current Constitution of the State of Arkansas, framed and adopted by the convention which assembled at Little Rock, July 14th, 1874, and ratified by the people of the state, at the election held Oct. 13th, 1874.
Passed by the Senate on June 8, 1866, and ratified two years later, on July 9, 1868, the Fourteenth Amendment granted citizenship to all persons "born or naturalized in the United States," including formerly enslaved people, and provided all citizens with ?equal protection under the laws,? extending the provisions of ...
The 1836 Arkansas Constitution was the first of Arkansas's constitutions, created during the push for Arkansas's statehood. It is written on four pages, front and back. It outlines the basic laws of state government and defines the rights of Arkansas citizens.
While the state's first three constitutions varied little, the new document imposed several major changes. The 1868 Constitution continued a four-year term for the governor, added the office of lieutenant governor, and established greater power within the executive branch, weakening local control.