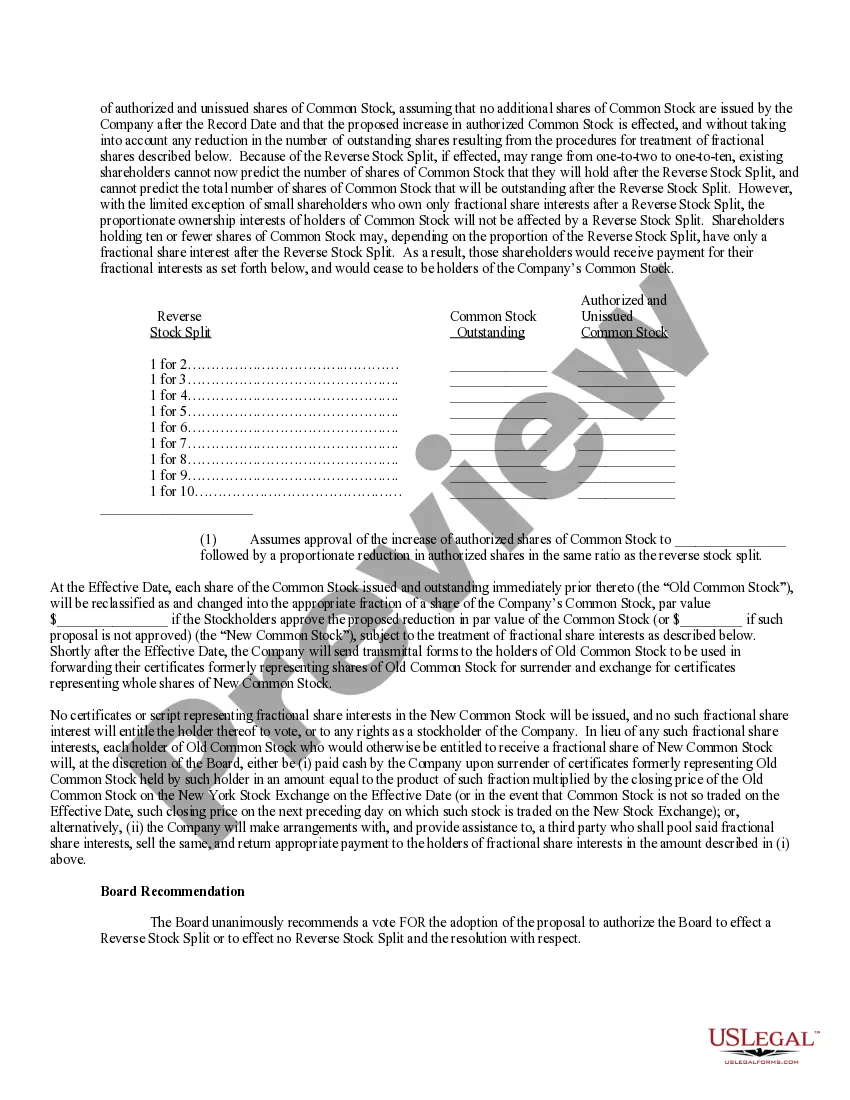
Par Value Formula
Description
How to fill out Proposal To Amend Certificate To Reduce Par Value, Increase Authorized Common Stock And Reverse Stock Split With Exhibit?
It’s clear that you cannot become a legal specialist instantly, nor can you swiftly learn how to draft the Par Value Formula without possessing a specialized skill set.
Generating legal documents is a lengthy endeavor that necessitates specific education and expertise. Therefore, why not leave the development of the Par Value Formula to the experts.
With US Legal Forms, one of the most extensive legal template collections, you can find everything from court documents to templates for in-office communication.
You can access your documents again from the My documents tab at any time. If you’re an existing customer, you can simply Log In and find and download the template from the same tab.
Regardless of the reason for your documentation—be it financial, legal, or personal—our platform is here to assist you. Explore US Legal Forms today!
- Identify the form you need by utilizing the search bar located at the top of the page.
- Preview it (if this option is available) and review the accompanying description to ascertain whether the Par Value Formula is what you seek.
- If you require another template, restart your search.
- Register for a no-cost account and select a subscription plan to acquire the template.
- Click Buy now. After your payment is processed, you can obtain the Par Value Formula, complete it, print it, and deliver it by mail or send it electronically to the relevant parties or organizations.
Form popularity
FAQ
To record par value stock, you first need to determine the par value set for each share. Then, when issuing stock, multiply the par value by the number of shares issued to calculate the total par value. You will make a journal entry that reflects this amount in the equity section of your balance sheet. Utilizing the par value formula helps ensure accurate financial reporting and compliance with legal requirements, which can be facilitated by platforms like US Legal Forms.
To calculate par value, you need to understand the par value formula. This formula typically involves dividing the total value of shares by the number of shares issued. For instance, if a company has issued 1,000 shares with a total value of $10,000, the par value would be $10 per share. By using this straightforward formula, you can easily determine the par value for any stock.
The par value formula determines the face value of a bond or stock, representing its nominal value at issuance. This formula is essential for investors as it helps assess the worth of their investments over time. Understanding the par value formula can simplify your investment decisions and clarify the financial health of the securities. If you seek more detailed guidance or resources, consider exploring USLegalForms to streamline your understanding of financial concepts.
A bond's par value is the face value of the bond plus coupon payments, annually or sem-annually, owed to the bondholders by the issuer of the debt. A bond with a par value of $1,000 and a coupon rate of 4% will have annual interest payments of 4% x $1,000 = $40.
Par value is the minimum share price, while market value is the current trading price. Par value is set in the certificate of incorporation. For most startups, the par value is set incredibly low, generally $0.0001 or $0.00001 per share.
?Par value? or ?face value? is the lowest price for which a company can sell stock. ?Fair Market Value? is the notional value of stock on the market at the time of sale. A reasonable par value for an early stage company can be as low as $0.00001. Setting a par value low can avoid tax liabilities later.
Par value should not be confused with other common stock values ? such as ?book value? and ?fair market value.? Thus, if a corporation's common stock has a par value of $0.01 per share, the corporation would be in violation of its charter if it sold any of its common stock for less than $0.01 per share.
For example, if a corporation issues 100 new shares of its common stock for a total of $2,000 and the stock's par value is $1 per share, the accounting entry is a debit to Cash for $2,000 and a credit to Common Stock?Par $100, and a credit to Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par for $1,900.