Consignment Note For Scheduled Waste Malaysia In Suffolk
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
F waste codes are the most common waste codes. They include spent solvents, like those that are dirty from cleaning or dissolving something. "F" codes also include several process wastes, like the wastes generated from cyanide-based electroplating.
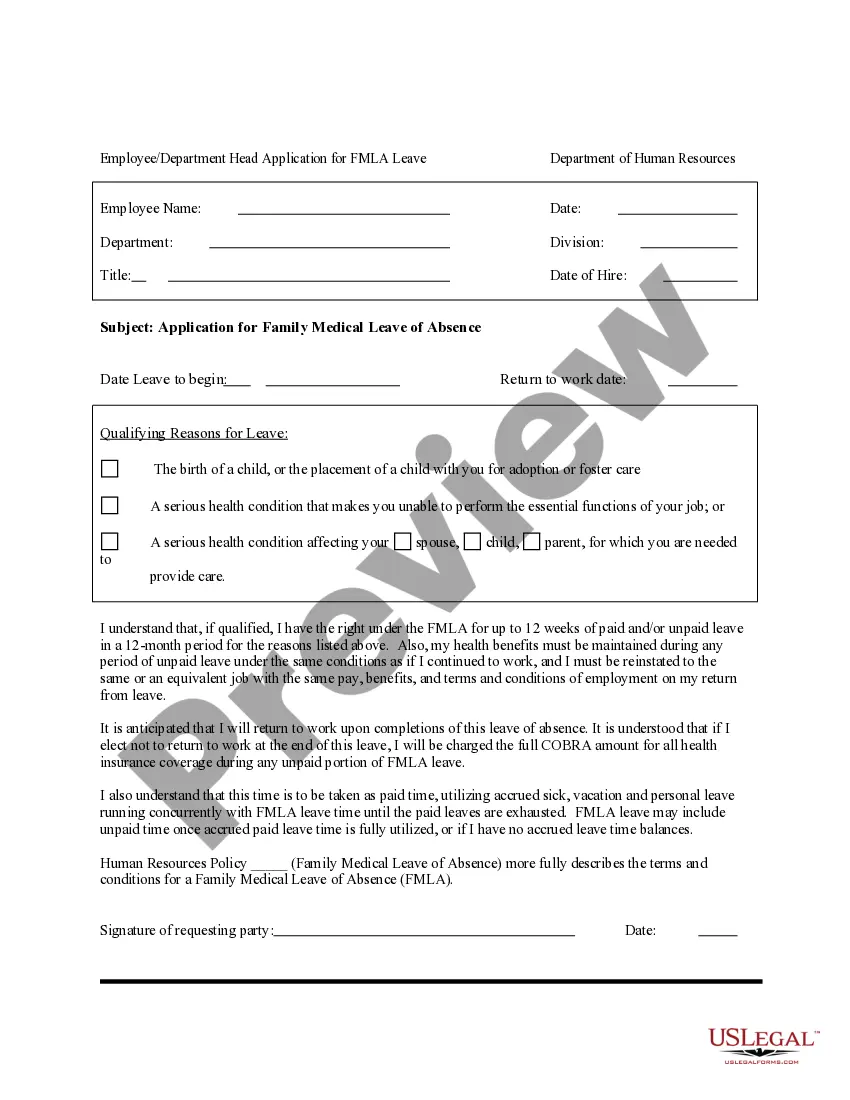
In order to dispose the scheduled waste, the waste generator should fill in and submit the disposal form to PTJ appointed officer. The appointed officer will then make an application to CMU for SW disposal. Download the disposal form here.
SW 204. Sludges containing one or several metals including chromium, copper, nickel, zinc, lead, cadmium, aluminium, tin, vanadium and beryllium.
SW102. Waste of lead acid batteries in whole or crushed form. SW103. Waste of batteries containing cadmium and nickel or mercury or lithium.
The SW 110 wastes are defined as wastes from the electrical and electronic assemblies containing components such as accumulators, mercury-switches, glass from cathode-ray tubes and other activated glass or polychlorinated biphenyl-capasitors, or contaminated with cadmium, mercury, lead, nickel, chromium, copper, ...
Ministry of Housing and Local Government (MHLG) committed in ensuring every planning in waste management system will be implemented holistically to create a clean, quality and sustainable environment.
Contaminated Carbon Filters Handling (SW 410) ing to DOE – Environmental Quality (Scheduled Waste) Regulations 2005.
SW 501. Any residues from treatment or recovery of scheduled wastes.
● Hazardous waste is defined as any. waste falling within the categories of. waste listed in the First Schedule of the Environment Quality (Scheduled Wastes) Regulations 2005. Hazardous Substances Division. Department of Environment Malaysia.
Electronic Scheduled Waste Information Systems (eSWIS)