Contingent Contract With Example In Chicago
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
A contingency is a potentially negative event that may occur in the future, such as an economic recession, natural disaster, or fraudulent activity. Companies and investors plan for various contingencies through analysis and implementing protective measures.
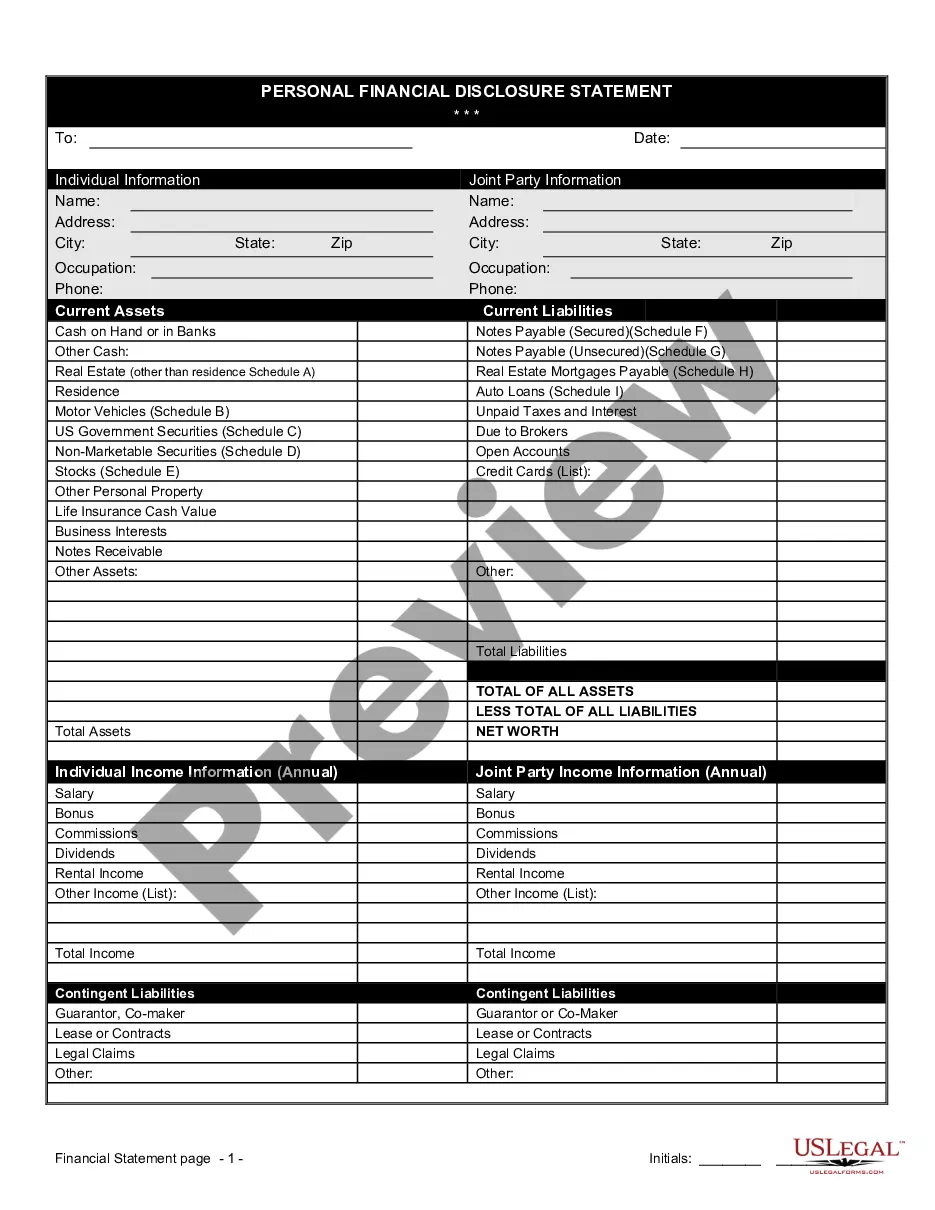
An example of a contingent liability that a company should record is possible product warranty costs. This refers to the potential expense a company may incur if they need to repair or replace a product that is covered under warranty. Another example is the threat of a lawsuit by a competitor.
With a contingent offer, you have stated that a certain condition must be met before the sale moves forward. If it doesn't, the contract is void, and the seller can move on to a backup offer received while the sale was contingent.
When an event or situation is contingent, it means that it depends on some other event or fact. For example, sometimes buying a new house has to be contingent upon someone else buying your old house first.
Your parents might have had one more child than they actually did, and so you could have had another sibling. This sibling that does not exist but could have is also considered a contingent thing. Contingent things are often contrasted with necessary things.
Example of a Contingency Contract One straightforward example might be a child who agrees with their parent that if they get an A in a particular class, they will get a new bicycle. Of course, the contract may be verbal, and it may be between family members.
In a contingency contract, the task defines exactly what behavior a person must engage in to access the reward. It should include what needs to be done, who must do it, when it must be done and details with how it must be done. It should be very clear and specific for all parties.
There must be a valid contract to do or not to do something. The performance of the contract must be conditional. The said event must be collateral to such contracts and the event should not be at the discretion of the promisor. These are some rules that have to be followed for a contingent contract to be enforceable.
In the case of conditional contracts, conditions that need to be fulfilled are certain, i.e., bound to happen, which is not the case with contingent contracts, as such conditions may or may not happen.