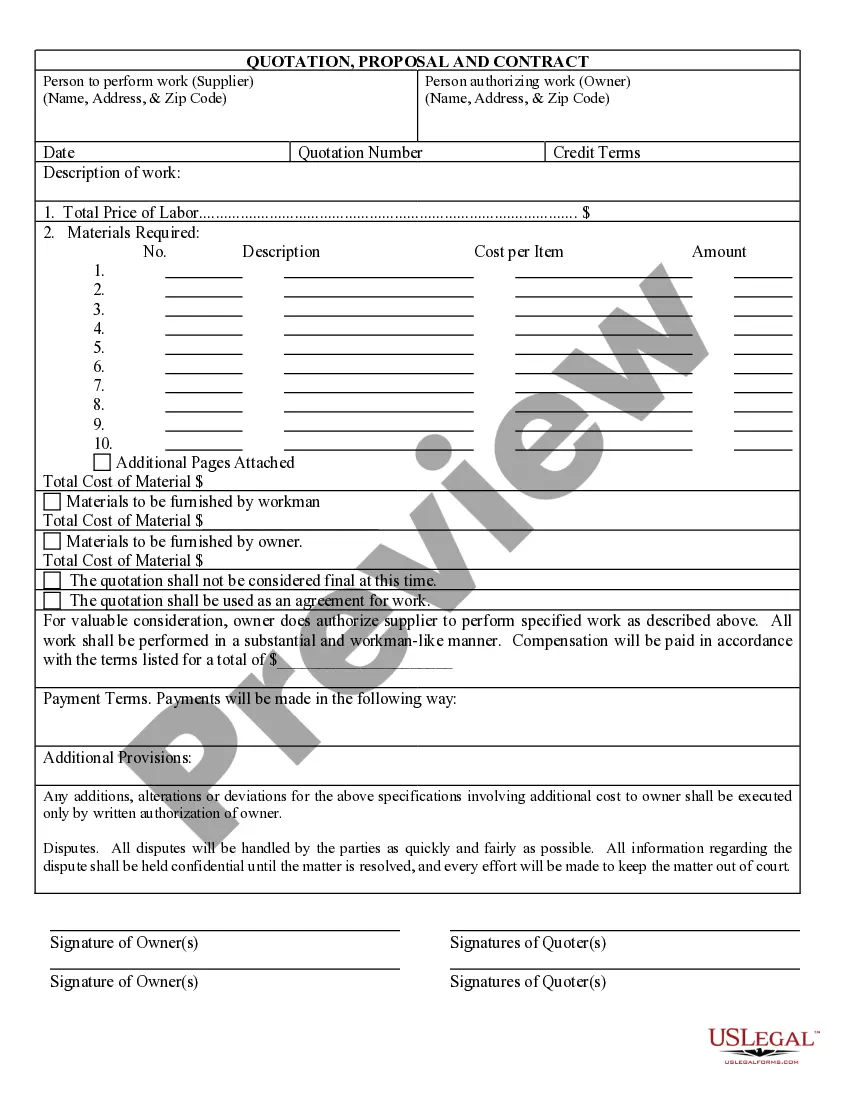
Sample Partition Agreement With Mexico In Minnesota
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
In short, to force the sale of jointly owned property, you must first confirm title, then attempt a voluntary sale or buyout, file and serve a partition lawsuit, get an appraisal, sell the property, and finally divide the sale proceeds fairly.
Typically, a partition action in Southern California can take anywhere from 6 to 12 months to complete. However, it's important to note that this is just an average, and your case could be resolved more quickly or take longer depending on various factors.
The actual time it takes from when a partition case is filed to when the land is partitioned physically, by sale, or by set-off varies from case to case. In general, partition cases can take several months or even years to resolve.
In California, the timeline of a partition lawsuit can range from several months to over a year. The duration is influenced by factors such as the number of parties involved, the nature of the property, and whether the case is contested.
Under Colorado law, a partition action is a legal proceeding used to divide or sell jointly owned real estate. When co-owners can't agree on how to manage, use, or sell their property, Colorado's partition statute provides a mechanism to separate their interests.
On the death of one of 2 joint tenants, the survivor becomes the sole owner; on the death of one of 3 or more joint tenants, the survivors are joint tenants of the entire interest.
Partition by Sale: Partition by sale occurs when the entire property is sold, and the proceeds of that sale are split between the owners ing to their proportional interest in the property. So, if co-owner A owns a 20% interest in the property, he or she should get 20% of the net proceeds.
In Wisconsin, every co-owner who no longer wishes to own their interest in the real estate has a right to partition their interest in the property, no matter what ownership percentage of the property they own. Chapter 842 of the Wisconsin Statutes governs the partition of real estate in Wisconsin.
If one owner wants to sell a jointly owned property but the other owner(s) refuse, the party seeking to sell can file a partition action. This legal procedure allows a court to intervene and force the sale of the property, dividing the proceeds among the owners ing to their ownership interests.