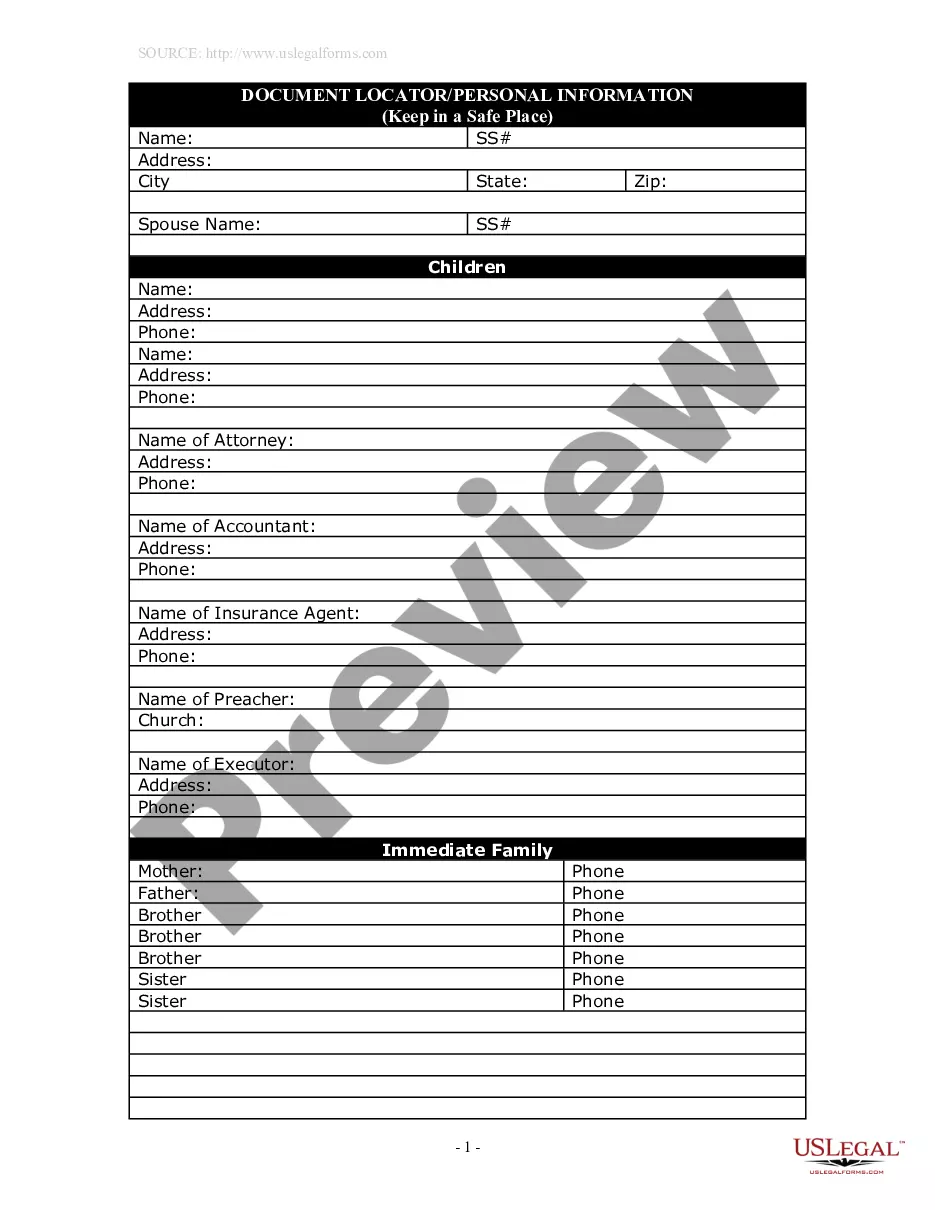
Work Labor Law For Breaks In Virginia
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Employers are not legally required to provide breaks for their employees in Virginia, except for minors aged 14-15 who are entitled to 30-minute meal breaks for every 5-hour shift. However, many employers voluntarily choose to offer rest and meal breaks as a means to enhance productivity.
Most places consider 9-5 to be 8 hours (lunch and coffee breaks count towards the total).
CA law specifically requires lunch breaks for employees that work over five hours on the shift. However, an employee and employer must agree to a waiver of the lunch break.
It is not legal in the US per OSHA regulations for an employer to work an employee 8 hours without a scheduled break. In fact, the OSHA rules are to be posted in every break room.
Work Hours in Virginia Thus, Virginia's employers must adhere to the guidelines set forth in the federal Fair Labor Standards Act, which state that employees must receive at least time-and-a-half for any hours that exceed 40 within a standard, seven-day workweek.
Employees must be allowed a meal period when they work more than five hours in a shift. A meal period must be at least 30 minutes long and start between the second and fifth hour of the shift.
Tennessee Law Requires Meal Breaks Tennessee law requires employers to provide a meal break, but no rest breaks. In Tennessee, employers must provide a 30-minute break to employees who are scheduled to work at least six consecutive hours. This break may be unpaid.
Virginia Labor Laws Guide Virginia Labor Laws FAQ Virginia minimum wage$11 Virginia overtime laws 1.5 times the minimum wage for any time worked over 40 hours/week ($16.5 for minimum wage workers) Virginia break laws Meal break for minors under 16 — 30 min per 5 hours
Yes. The Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) permits employers to require employees to obtain a completed certification from the worker's health care provider to substantiate the need for FMLA leave.