Labour Laws In Kenya In Fulton
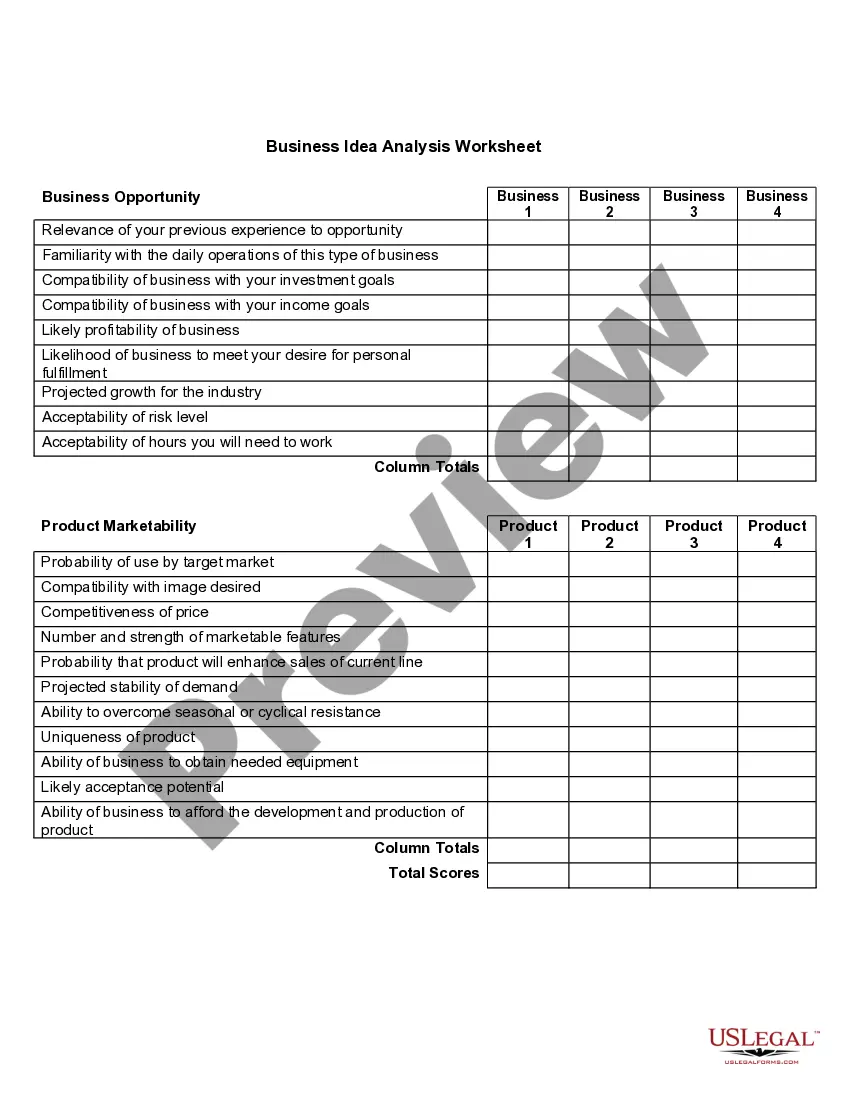
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Unfair Termination in Kenya When an employer terminates an employee's contract without proper cause, due process, and/or in contravention of the Kenya employment laws, it is considered unfair termination. The Court of Appeal in Civil Appeal No. 31 of 2015 between Kenfreight (E.A.) Limited versus Benson K.
Shift work is regulated, and regular workdays are Monday to Friday, 8 hours per day, with an additional 5 hours on Saturdays as specified by sector-specific orders under the Regulations of Wages and Conditions of Employment Act.
Minimum notice periods Period of continuous serviceMinimum notice period 1 year or less 1 week More than 1 year - 3 years 2 weeks More than 3 years - 5 years 3 weeks More than 5 years 4 weeks
Section 41 of the Employment Act, 2007 provides that “Subject to section 42 (1), an employer shall, before terminating the employment of an employee, on the grounds of misconduct, poor performance or physical incapacity explain to the employee, in a language the employee understands, the reason for which the employer ...
State Department for Labour and Skill Development. Bishops Road, Social Security House. ps@labour.go.ke. info@labour.go.ke. complaints@labour.go.ke.
Subject to Section 44 of the Employment Act of Kenya, an employer can summarily dismiss an employee. This basically means that an employer can terminate an employees employment without notice or with less notice than that to which the employee is entitled to on the contractual agreement or statutory provisions.
Labour law in Kenya is derived from several sources including the Constitution, Acts of Parliament and subsidiary legislation and International Conventions. This booklet will briefly highlight the significant laws as they relate to workers.
Individual labour disputes must go through mediation with labour mediators before any request is made for resolution by the Labour Arbitration Council or the Court. Upon consensus, the disputing parties may request labour dispute resolution by the Labour Arbitration Council.
Process: Employment litigation typically follows a defined procedure: Filing a Claim: The aggrieved employee files a formal complaint with the relevant authority, often the Employment and Labour Relations Court (ELRC) in Kenya. Defense: The employer responds to the claim, outlining their position on the matter.