Depreciation Excel Sheet Format In Philadelphia
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
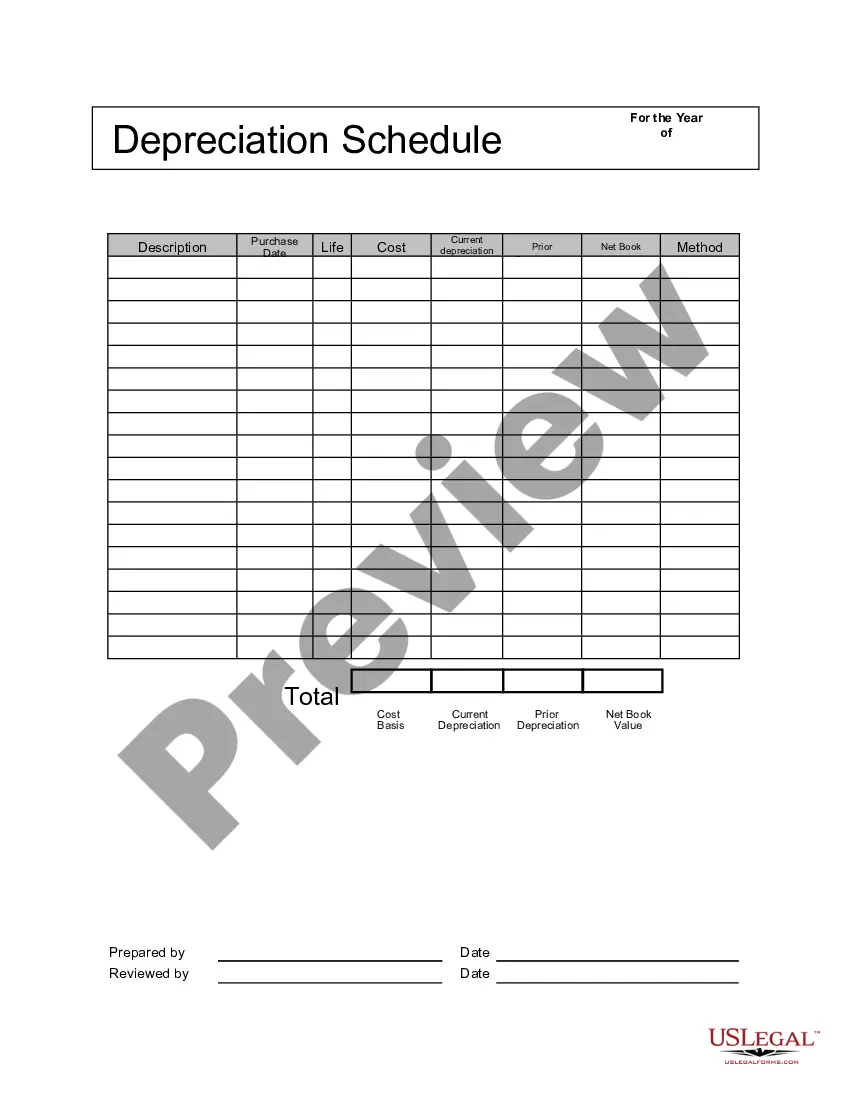
You'll need three columns: The first column registers the depreciation deduction (aka depreciation expense) you plan to take each year. The second column shows the depreciation that has accumulated at the end of each year. The third column logs the book value of the asset at the end of each year.
The equation of a straight line is y = mx + b. Once you know the values of m and b, you can calculate any point on the line by plugging the y- or x-value into that equation. You can also use the TREND function. where x and y are sample means; that is, x = AVERAGE(known x's) and y = AVERAGE(known_y's).
Value this is the salvage value making f4 absolute. And what's the life. This is c5 you make itMoreValue this is the salvage value making f4 absolute. And what's the life. This is c5 you make it absolute. And you close it. So this is the amount will the the assets will be depreciated.
Step 1: Assemble the Column Headers in Row 1 of the Spreadsheet. Create a new Excel spreadsheet file and assemble the following information in Row 1 of the spreadsheet. Step 2: Enter the Depreciation Expense Formulas. Step 3: Enter the Accumulated Depreciation Formulas.
Value this is the salvage value making f4 absolute. And what's the life. This is c5 you make itMoreValue this is the salvage value making f4 absolute. And what's the life. This is c5 you make it absolute. And you close it. So this is the amount will the the assets will be depreciated.
Microsoft Excel has built-in depreciation functions for multiple depreciation methods including the straight-line method, the sum of the years' digits method, the declining balance method (the DB function), the double-declining balance accelerated method (the DDB function), the variable declining balance method (VDB ...
In MACRS straight line, LN calculates the percentage for a year by dividing one depreciation period by the remaining life of the asset, and then applying this amount with the averaging convention to determine the depreciation amount for that year.
The annual depreciation of assets by using the straight-line method is calculated by dividing the depreciable amount by the total number of years. In this case, it amounts to INR 1600 per year (8,000 / 5). It results in a depreciation rate of 20% (INR 1600 / INR 8,000).