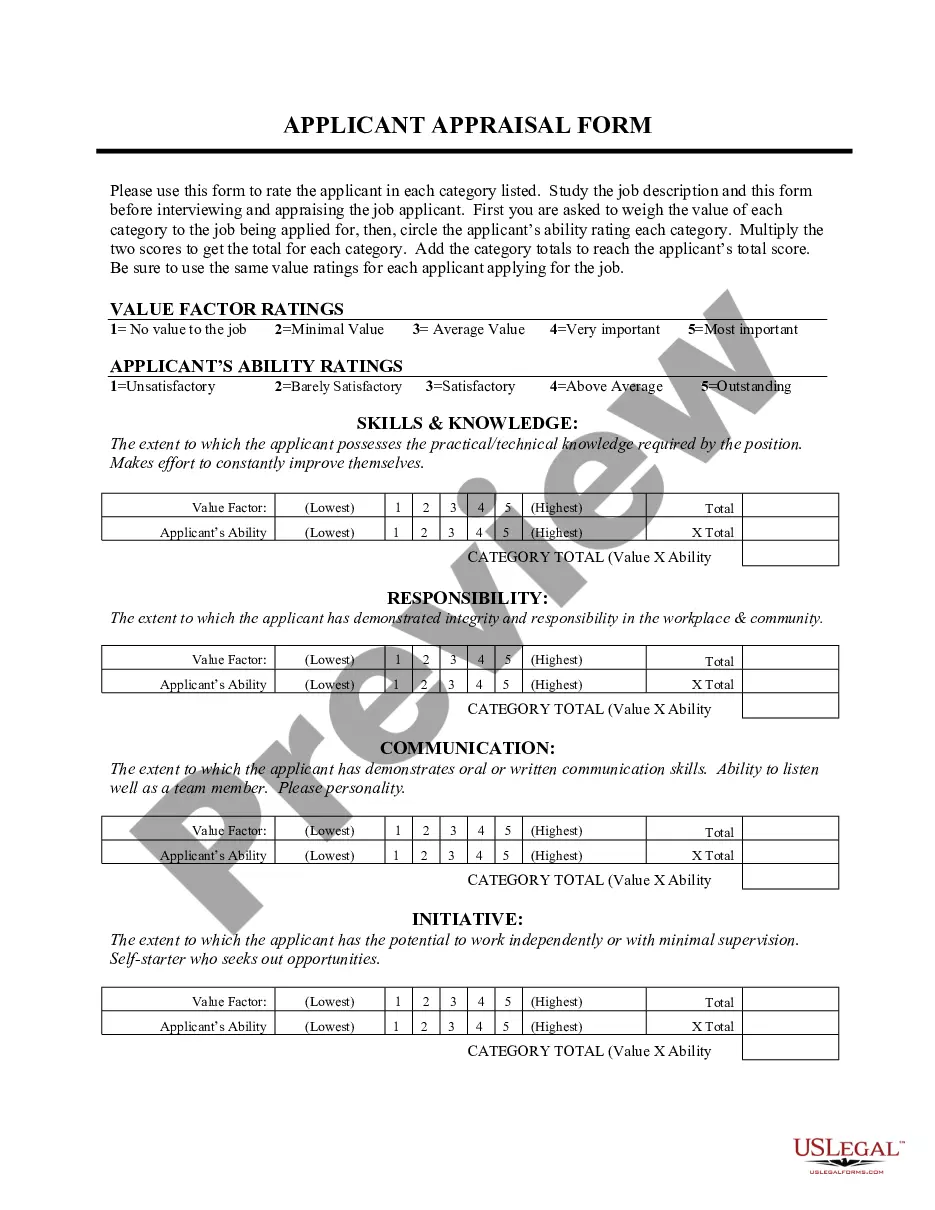
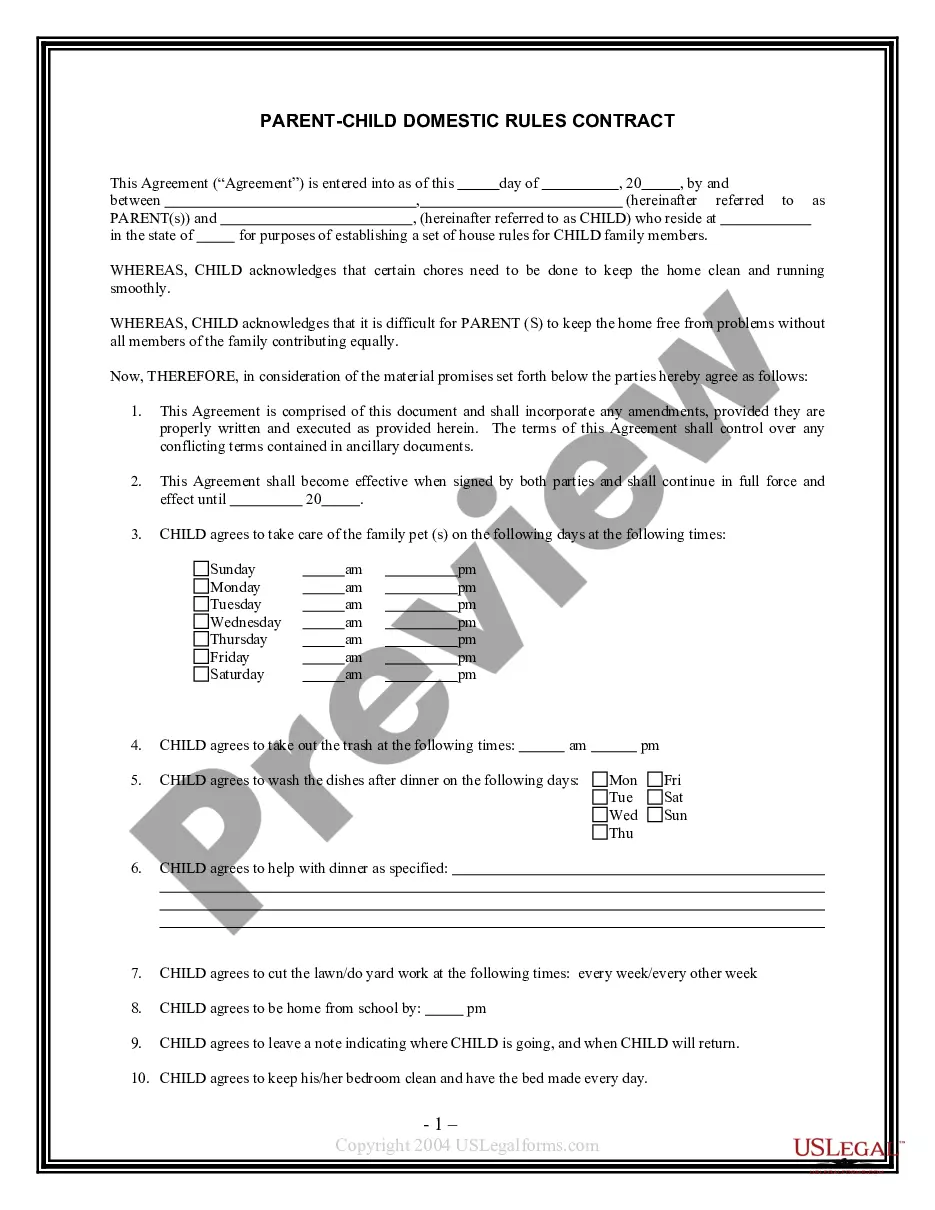
Principle With Law In Texas
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Instead of an affidavit that you must sign in front of a notary, Texas law lets you sign unsworn declarations in which you swear you are telling the truth, acknowledging that lying under oath is a crime.
After the House and Senate agree on the bill's language and both sides pass the bill, the Governor may: sign the bill into law; allow the bill to become law without signing; or veto the bill (A veto can be overridden if the bill received a 2/3 vote in the House and Senate).
On a separate page or pages, write a short and plain statement of the answer to the allegations in the complaint. Number the paragraphs. The answer should correspond to each paragraph in the complaint, with paragraph 1 of the answer corresponding to paragraph 1 of the complaint, etc.
Step 1: Fill out the Caption. Step 2: Check the Boxes for Your Defenses. Step 3: Enter any Additional Information. Step 4: You May Ask the Court for a Jury Trial. Step 5: Get Email Notifications. Step 6: Attachments. Step 7: Signature and Contact Information. Step 8: Certificate of Service Is Required.
To file online, go to E-File Texas ( ) 11 and follow the instructions. To file in person, take your answer (and copies) to the district clerk's office in the county where the plaintiff filed the case. At the clerk's office: Turn in your answer form (and copies).
Texas Rule of Civil Procedure 99(b) instructs, “The citation shall direct the defendant to file a written answer to the plaintiff's petition on or before a.m. on the Monday next after the expiration of twenty days after the date of service thereof.”
Examples of principles are, entropy in a number of fields, least action in physics, those in descriptive comprehensive and fundamental law: doctrines or assumptions forming normative rules of conduct, separation of church and state in statecraft, the central dogma of molecular biology, fairness in ethics, etc.
Rule of law is a principle under which all persons, institutions, and entities are accountable to laws that are: Publicly promulgated Equally enforced Independently adjudicated And consistent with international human rights principles.
The Texas Data Privacy and Security Act (TDPSA) was signed into law in June 2023 and will take effect on July 1, 2024. Texas became the sixth state to pass a major data privacy law in 2023. This comprehensive legislation aims to regulate how businesses collect, use and protect the personal data of Texas residents.
Examples of these general principles of law are laches, good faith, res judicata, and the impartiality of judges.