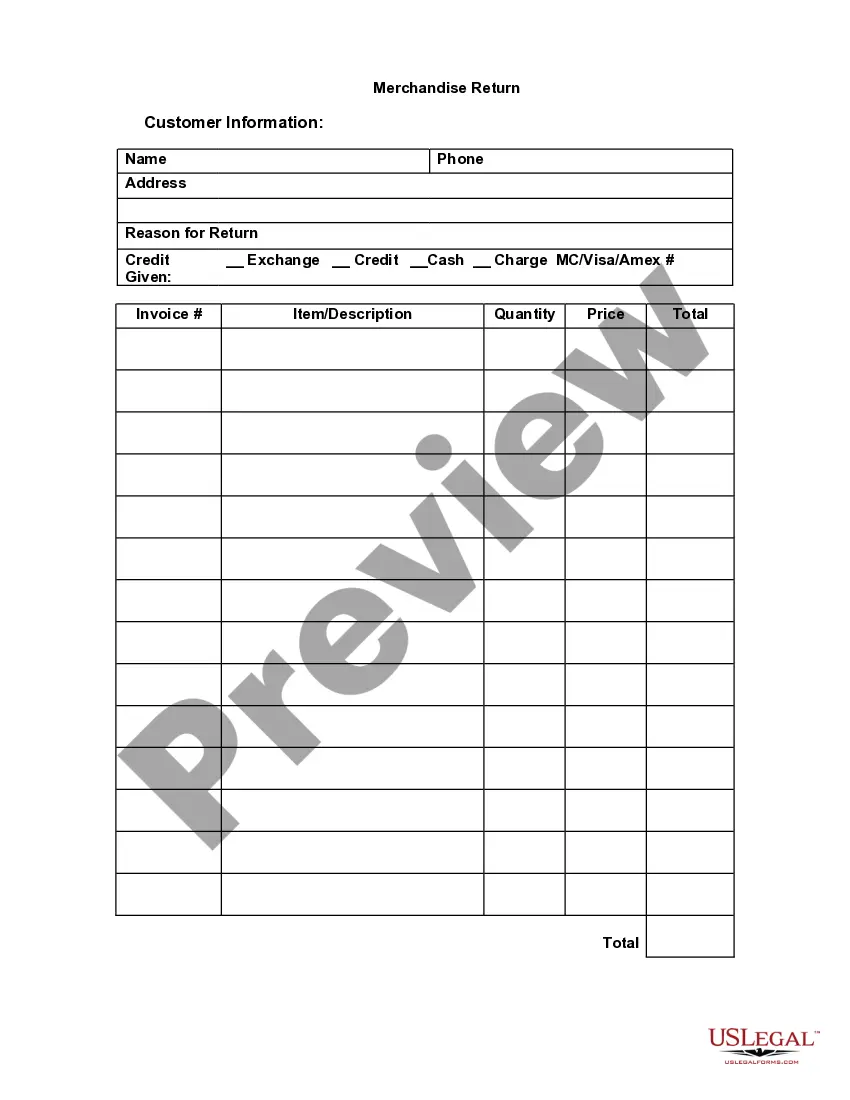
Factoring Agreement File Format Canada In Fulton
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Algebra II/Factoring Rules 1 1. GCF. 2 2. Difference of two squares: a2 - b2 = (a+b)(a-b) 3 3. Trinomial whose leading coefficient is one. 4 4. Sum of two cubes: a3 + b3 = (a+b)(a2 - ab + b2) 5 5. Perfect Square Trinomials: a2 + 2ab + b2 = (a+b)2 6 6. Factor by Grouping.
Factor analysis is a statistical technique that reduces a set of variables by extracting all their commonalities into a smaller number of factors. It can also be called data reduction. When observing vast numbers of variables, some common patterns emerge, which are known as factors.
Factor, in mathematics, a number or algebraic expression that divides another number or expression evenly—i.e., with no remainder. For example, 3 and 6 are factors of 12 because 12 ÷ 3 = 4 exactly and 12 ÷ 6 = 2 exactly.
In mathematics, factorization (or factorisation, see English spelling differences) or factoring consists of writing a number or another mathematical object as a product of several factors, usually smaller or simpler objects of the same kind.
The basic elements required for the agreement to be a legally enforceable contract are: mutual assent , expressed by a valid offer and acceptance ; adequate consideration ; capacity ; and legality .
A note outlining the rules that may make a contract void or unenforceable, on grounds such as illegality or public policy (ex turpi causa), or voidable for duress or undue influence.