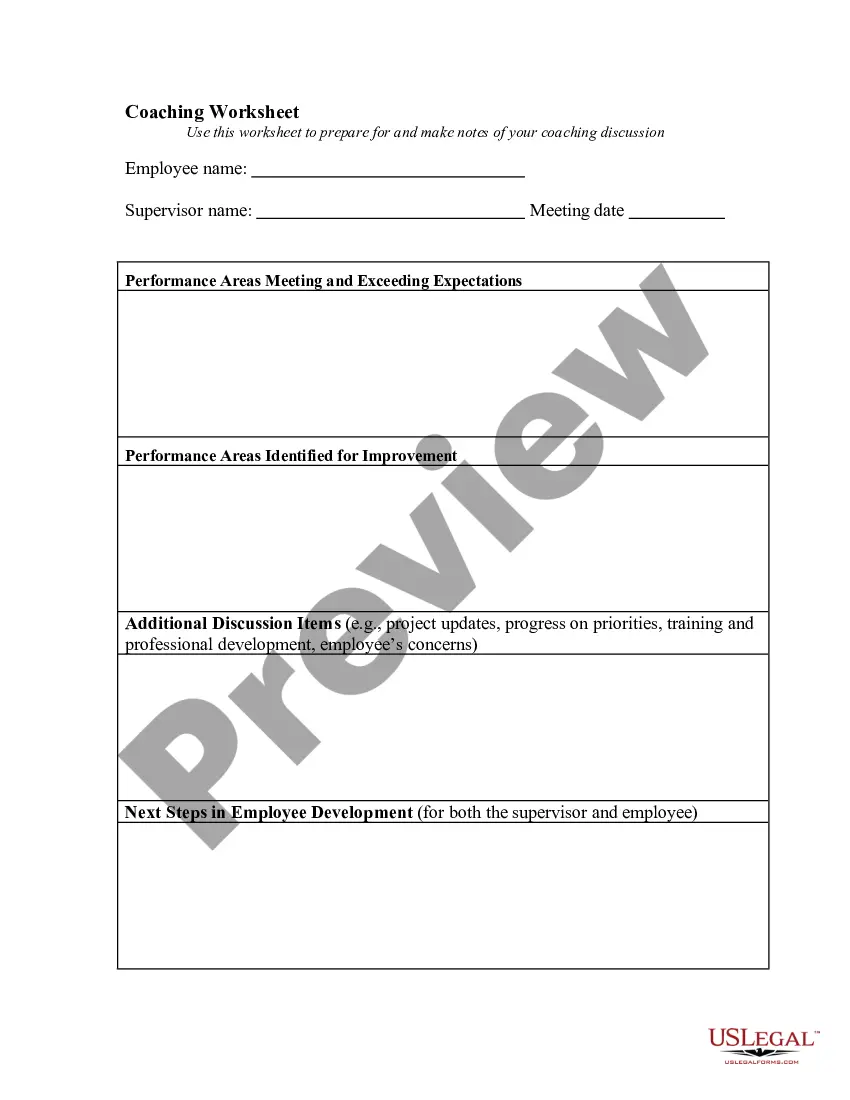
Shareholder Agreement Example In Wayne
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
We have 5 steps. Step 1: Decide on the issues the agreement should cover. Step 2: Identify the interests of shareholders. Step 3: Identify shareholder value. Step 4: Identify who will make decisions - shareholders or directors. Step 5: Decide how voting power of shareholders should add up.
In addition to requirements regarding quorum and voting, shareholders might include provisions around: certain decisions requiring unanimous shareholder consent (e.g. borrowing over a certain limit), certain shareholders having the right to appoint (more) directors, a requirement for shareholders to participate in ...
Our fees for preparing and drafting a shareholders' agreement start at £1,250 plus VAT. A Shareholders' Agreement helps protect the legal rights of all shareholders in a business and aims to ensure everyone is treated fairly.
What is included in a shareholder agreement? Decision making. The shareholder agreement states how business decisions are made. Joining the business. Provide for what happens in the event of death or incapacity. Settle internal disputes. Anticipating certain situations.
It should describe how the business will be run, how problems between shareholders will be handled, and clarify the responsibilities and benefits of each shareholder. A shareholder agreement outlines the details of a corporation so that there is no confusion as to the rights of each shareholder from the beginning.
The shareholders agreement should set out matters that are reserved for the board and those matters that will require shareholder approval. It will also set out the level of majority required to pass a particular resolution. Decisions reserved for the board typically relate to the day‑to‑day management of the company.
A shareholders agreement is a legally binding, private document that sets out further powers, rights and obligations that the owners have to each other and the company, beyond those that already exist under law or through the articles of association.
We have 5 steps. Step 1: Decide on the issues the agreement should cover. Step 2: Identify the interests of shareholders. Step 3: Identify shareholder value. Step 4: Identify who will make decisions - shareholders or directors. Step 5: Decide how voting power of shareholders should add up.