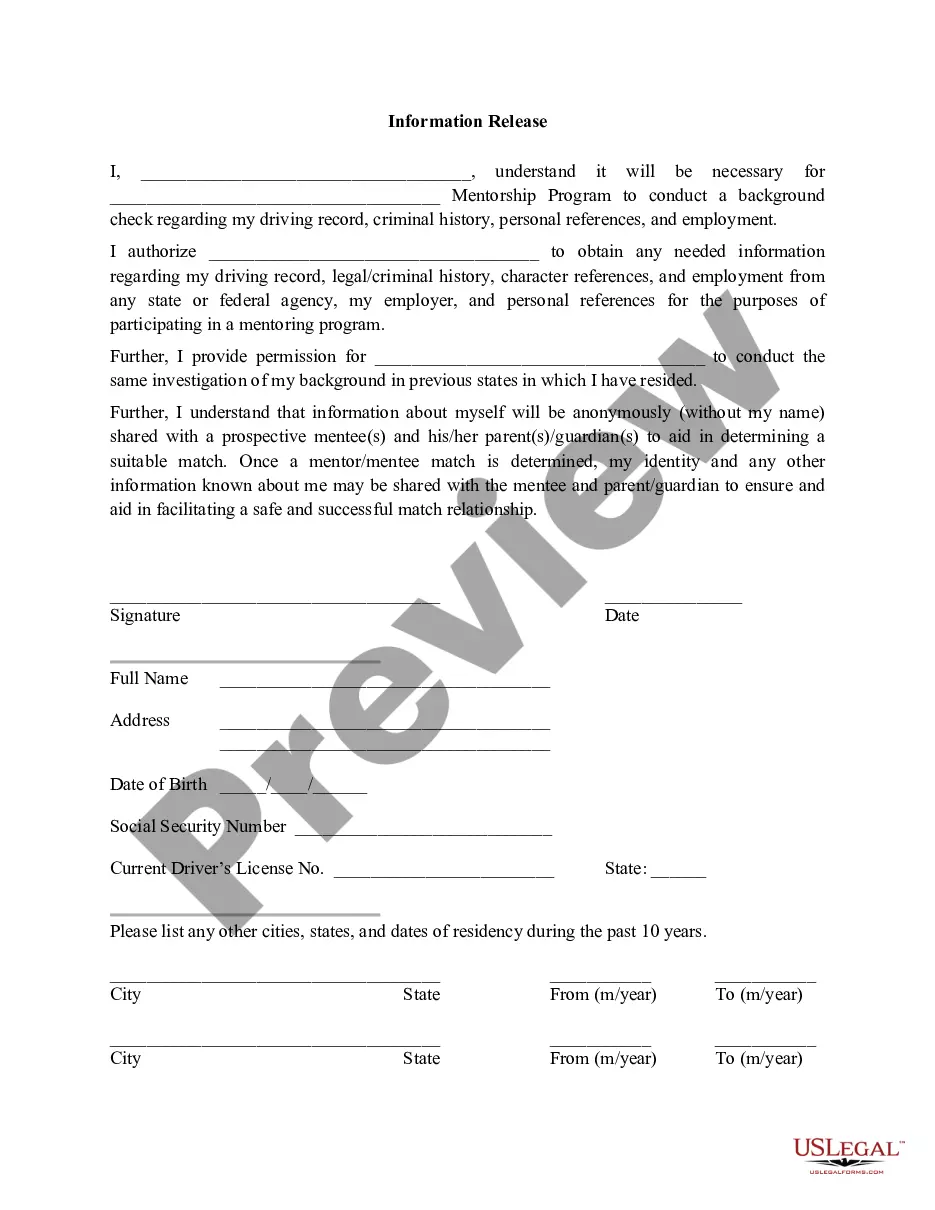
Wrongful Interference With A Business Relationship Example In Phoenix
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Tortious interference with prospective or anticipated contractual relations is defined in Section 766B of the Restatement (Second) of Torts as: “Inducing or otherwise causing a third person not to enter into or continue the prospective relation or (b) preventing the other from acquiring or continuing the relation.”
Examples of tortious interference include inducing a third party to breach a contract, spreading false information about a business or product, or stealing confidential business information.
As an example, someone could use blackmail to induce a contractor into breaking a contract; they could threaten a supplier to prevent them from supplying goods or services to another party; or they could obstruct someone's ability to honor a contract with a client by deliberately refusing to deliver necessary goods.
If a third party interferes with a contract or business relationship, it may be tortious interference in a business relationship. Some examples of actionable interference may include convincing a shared supplier to renege on a contract or a third party interrupting the sale of property to a business.
Tortious interference with business relationship is a similar claim that typically arises when no valid contract exists and a defendant intentionally interferes with the business relationship between a third party and the plaintiff, resulting in damages to the plaintiff.
For example, if a competitor spreads false rumors about a business to intentionally harm its reputation and steal customers, it could be considered wrongful interference with a business relationship.
Tortious interference with a business relationship An example is when a tortfeasor offers to sell a property to someone below market value knowing they were in the final stages of a sale with a third party pending the upcoming settlement date to formalize the sale writing.
A more thorough explanation: Interference with a business relationship is when someone intentionally disrupts or damages a business relationship between two parties. This can be done through various means, such as spreading false information, making threats, or offering bribes.