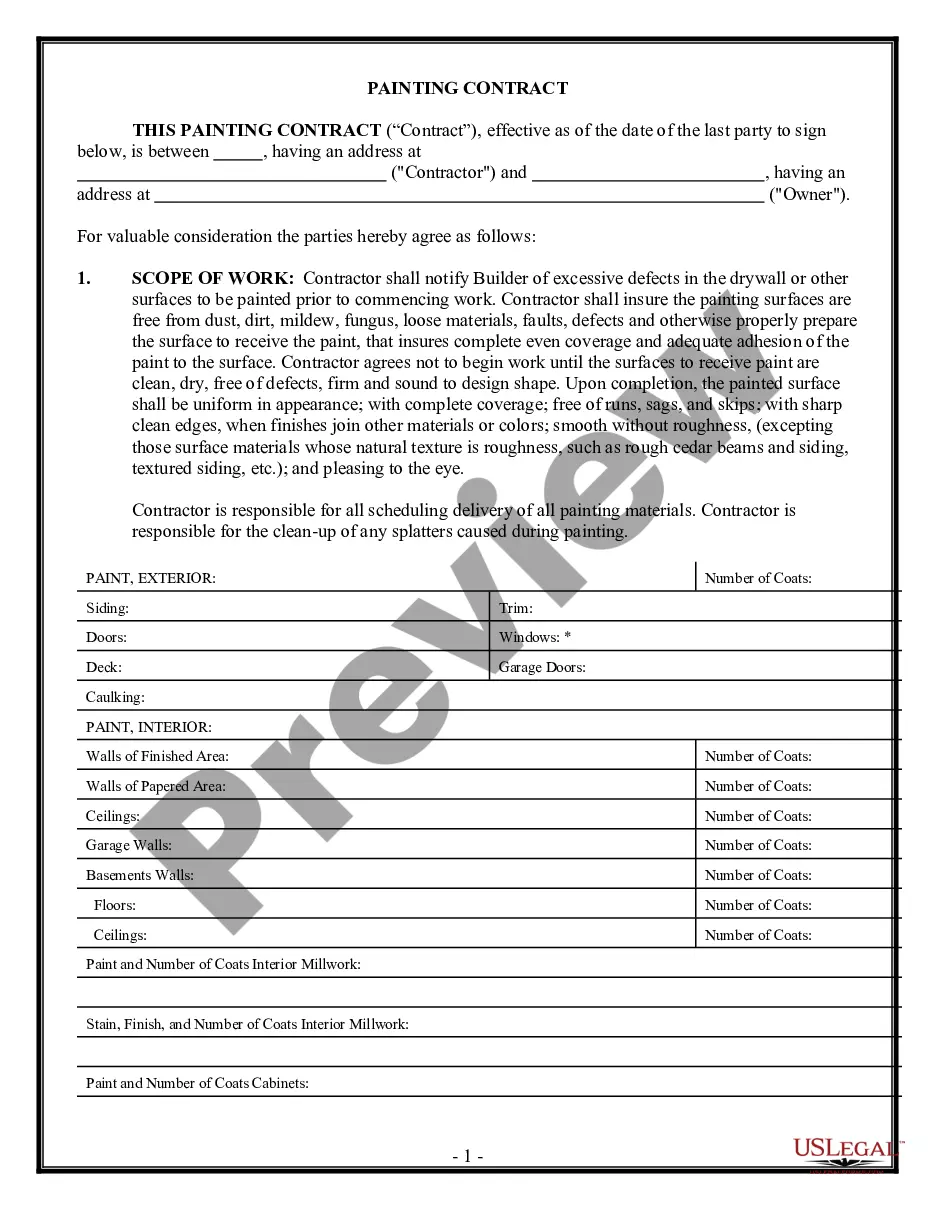
International Sales Contract Sample For Real Estate In San Bernardino
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Types of Sales Contracts Sales agreements. Order forms. Change order forms. Master service agreements. Statements of work. Terms of service. Renewal and upsell agreements.
Special Sales Contract. used for foreclosures/short sales. including riders, addendum, and amendments, is the complete agreement between a buyer and a seller.
Answer. The Special Sales Contract is used to put in an offer on a home that is being SOLD As-Is.
Typically, a sales contract offers more details about the terms of the transaction than a bill of sale. It includes things like warranty information and delivery arrangements, and is drafted before any goods are exchanged.
International sale contracts refer to contracts for the sale of goods involving sea transit and various forms of contractual documents common in the import and export trades.
In an international business contract, it's essential to define the jurisdiction that will govern the contract and the laws that will apply in the event of a dispute. Your dispute resolution section should also detail the agreed-upon dispute resolution mechanism.
Top ten tips in drafting and negotiating an international contract Avoiding retaliation claims. The language of the contract. Clear contract prose. Common law versus civil law. Jurisdictional issues. Terms of art. Personnel. In negotiations, expect the unexpected.
So, the names and addresses of the buyer and seller, as well as the date of the agreement. Description of goods or services sold. Clearly describe what the customer is buying, including quantity, brand, model, specifications, and any other relevant details. Descriptions of warranties or guarantees.
Contracts for the International Sale of Goods (Vienna, 1980) The United Nations Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL) drafted the CISG. Currently the CISG has seventy-six parties. The CISG aims to provide an internationally recognizable body of law governing the sale of goods across international borders.
Top ten tips in drafting and negotiating an international contract Avoiding retaliation claims. The language of the contract. Clear contract prose. Common law versus civil law. Jurisdictional issues. Terms of art. Personnel. In negotiations, expect the unexpected.