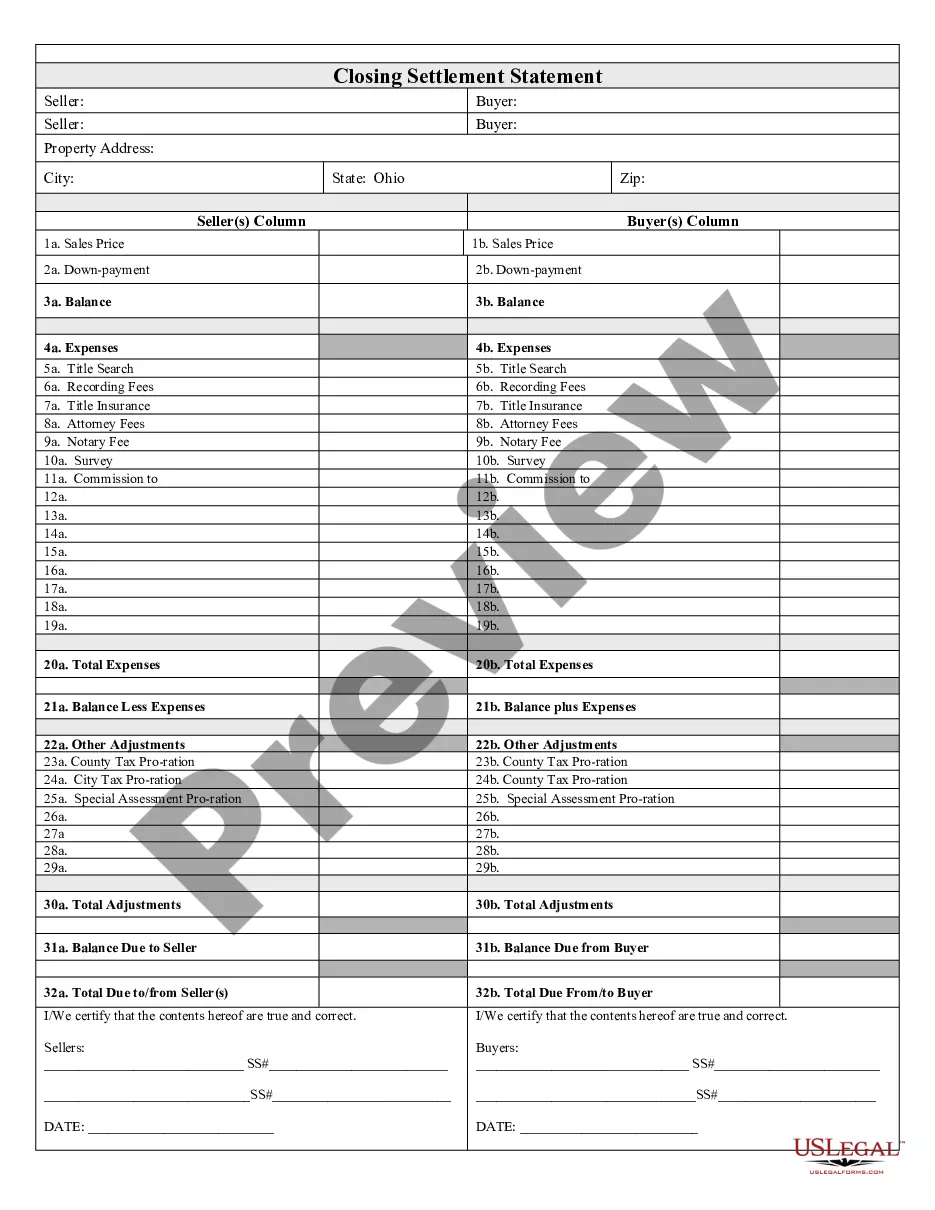
Texas Deceptive Trade Practices Act Statute Of Limitations In Cook
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Statute of Limitations Criminal Charges in Texas OffenseLimitationStatute Theft by a Public Servant of Government Property 10 Years 12.01(2) Forgery or passing a forged instrument 10 Years 12.01(2) Injury to Elderly or Disabled (First Degree) 10 Years 12.01(2) Sexual Assault 10 Years 12.01(2)37 more rows •
Don't let your claim to business debt grow stale. Remember, there is a statute of limitation for commercial debt in Texas. You have four years to take legal action to collect on business debt.
A statute of limitation usually starts counting down on the date of the alleged crime. Exceptions include certain crimes against children, which start when the child turns 18. Also, the statute of limitation for lying about the identity of an egg or donor starts at the time the crime is discovered.
Exemptions to The Texas Deceptive Trade Practices Act (the “DTPA”) Attorneys (or other similar professionals), Real Estate brokers & Realtors are oftentimes exempt from DTPA claims. This exemption, however, will not apply in cases of fraud or misrepresentation.
Texas law gives someone 4 years to bring a lawsuit for unpaid debt. This time period is commonly referred to as the statute of limitations. Once the time period is up, a person is prohibited from filing suit to recover the debt. This means the debt is time-barred.
The statute of limitations on debt in Texas is four years.
The Statute of Limitations for DTPA Claims Specifically, any action under the act must be initiated within two years after the occurrence of the false, misleading, or deceptive act or practice, or after the consumer becomes aware or should have been aware of it.
The primary tool the Office of the Attorney General uses to protect Texas consumers is the Deceptive Trade Practices Act (DTPA). This law lists many practices that are false, deceptive, or misleading. When you fall victim to illegal practices covered by the DTPA, you may have the right to sue for damages under the act.