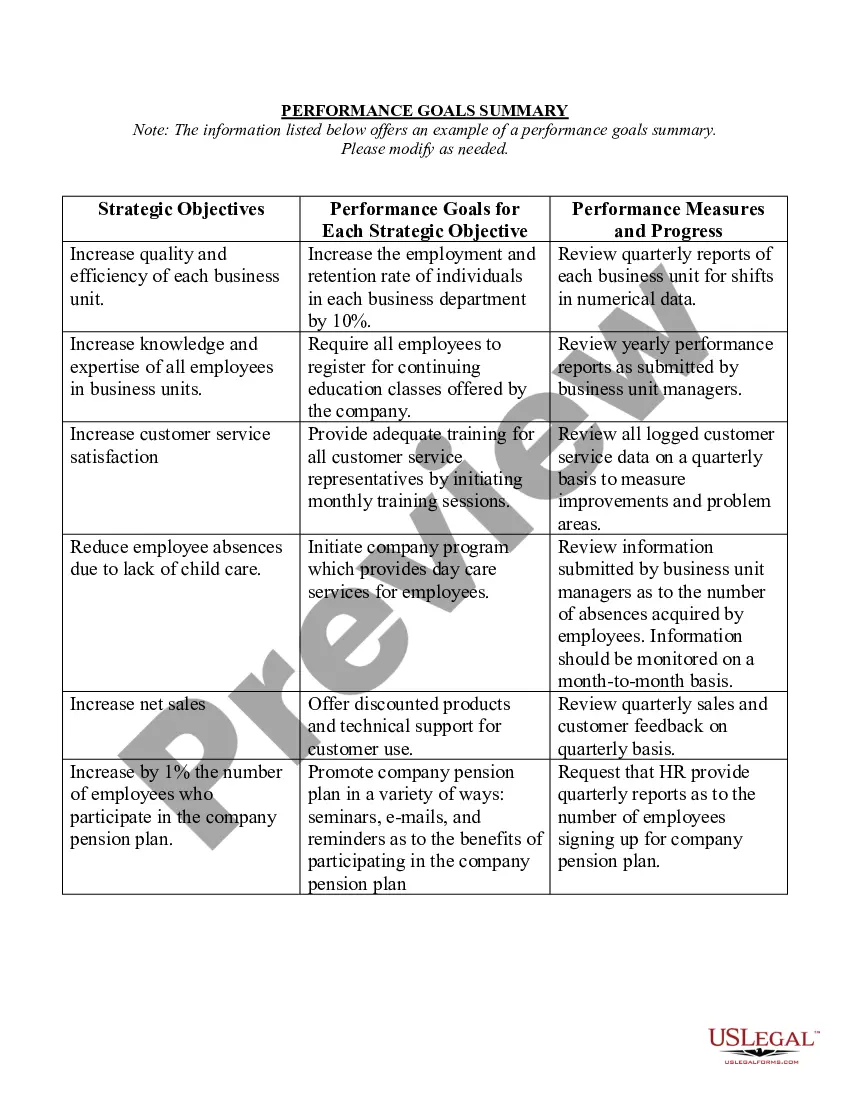
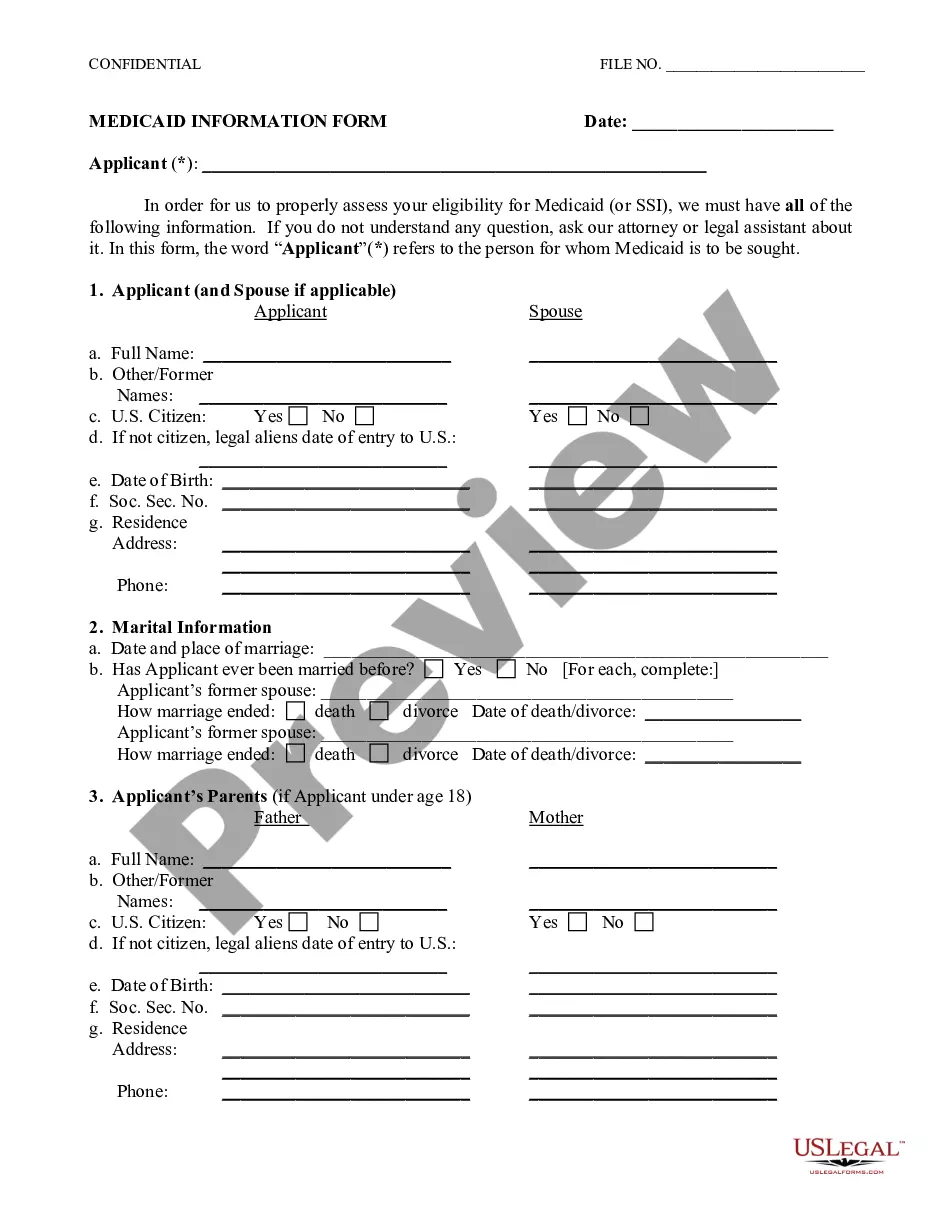
Deceptive Trade Forex In Allegheny
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
(These practices are commonly called misleading or unfair business practices.) They include false advertising, misrepresentation, tied selling, and failing to comply with regulations. Under consumer protection laws, they are illegal and can lead to compensatory or punitive damages.
Generally speaking, in Pennsylvania, there is a two-year statute of limitations that applies to any civil action in which an individual seeks to recover damages for personal injuries, or for the death of an individual, caused by the wrongful act or negligence of another person.
Section 201-2 prohibits false advertising.
First, the UTPCPL is not subject to the relatively short two-year statute of limitations applicable to common law fraud claims, thereby allowing a plaintiff to pursue what is in essence a claim for fraud so long as he files within the six-year limitations period applicable to UTPCPL claims.
The statute of limitations for a UTPCPL claim is six years, which means that a consumer must file a claim pursuant to the statute within six years from the date that an alleged wrongdoing occurred.
The UTPCPL also makes it an unfair or deceptive act or practice to engage in a “bait and switch” – advertising goods or services with intent not to sell them as advertised, or advertising them with intent not to supply the reasonably expectable public demand, unless the advertisement discloses a quantity limitation.
The Federal Trade Commission, as well as various state agencies, work to protect consumers from fraudulent, deceptive, and unfair business practices in the marketplace. To learn more or file a complaint about a bait-and-switch scam, visit .ftc.
Pennsylvania, unlike many states, does not have a “buyer's remorse” statute on the books, which means that consumers do not have legal grounds to return a vehicle unless they have a valid reason for doing so that is related to fraud, a serious defect, or misrepresentation.