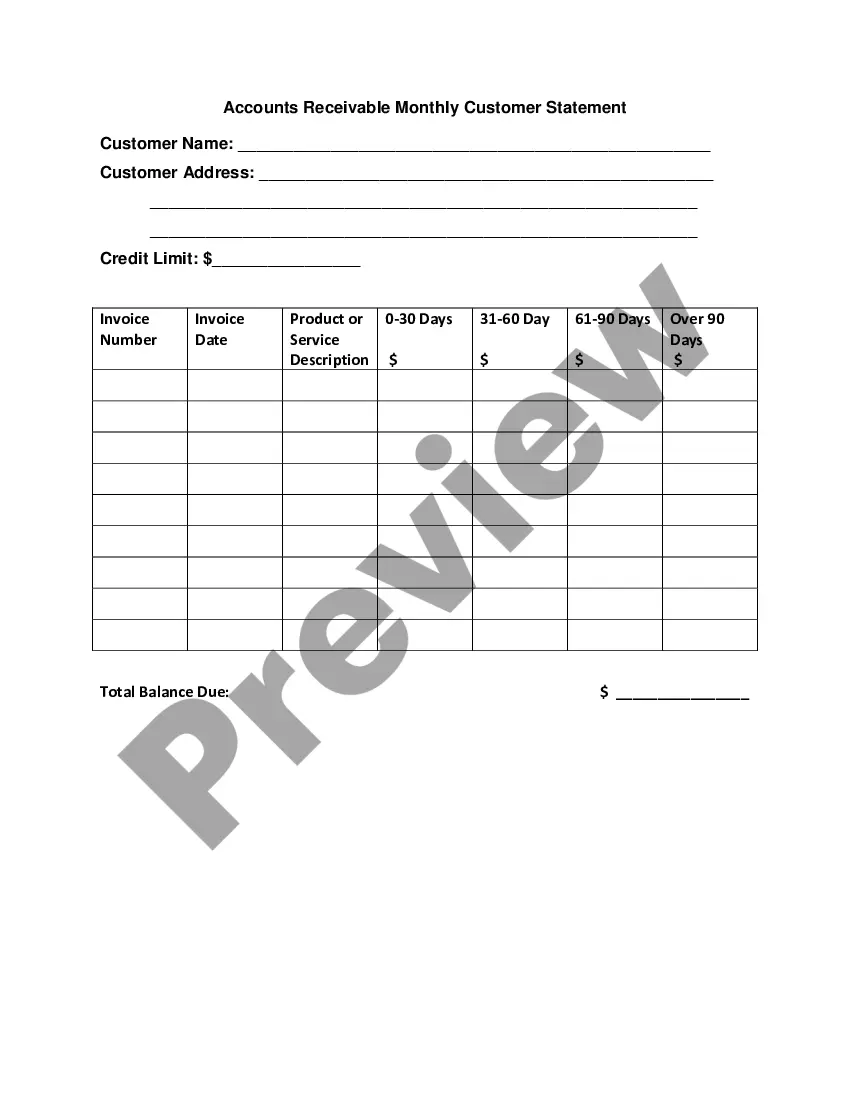
Contingency Agreement Sample For Drrm In Phoenix
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
A management process that analyses disaster risks and establishes arrangements in advance to enable timely, effective and appropriate responses.
A contingency is a potentially negative future event or circumstance, such as a global pandemic, natural disaster, or terrorist attack. By designing plans that take contingencies into account, companies, governments, and individuals are able to limit the damage done by such events.
How to create a contingency plan Map out essential processes. Create a list of risks for each process. Evaluate the potential impact and likelihood of each risk. Calculate costs and contingency reserves, and identify issues to mitigate. Create a response plan for prioritized events. Test the contingency plan.
Emergency Contingency Plan Template Define clear examples of your focus areas. Think about the objectives that could fall under that focus area. Set measurable targets (KPIs) to tackle the objective. Implement related projects to achieve the KPIs.
They include: Develop the contingency planning policy statement. Conduct the business impact analysis (BIA). Identify preventive controls. Create contingency strategies. Develop an information system contingency plan. Ensure plan testing, training, and exercises. Ensure plan maintenance.
3.5. Contingency Planning Contingency plan is a preparation plan for immediate response or determined the safety standard requirement to disaster. In contingency plan, we define the scenario of possible disaster; possible resources for immediate response; and actions plan for effective immediate response.
How to write a contingency plan Make a list of risks. Weigh risks based on severity and likelihood. Identify important risks. Conduct a business impact analysis. Create contingency plans for the biggest risks. Get approval for contingency plans. Share your contingency plans. Monitor contingency plans.
RA 10121 is the legal basis for creating the NDRRMC. The NDRRMC operates on four thematic areas or pillars: (1) Prevention and Mitigation, (2) Preparedness, (3) Response and Early Recovery, and (4) Recovery and Rehabilitation.
The CDRA uses a six-step process. It involves organizing climate change and hazard information; scoping of potential spatial or areal, and sectoral impacts; developing an exposure database; conducting a climate change vulnerability assessment; conducting a disaster risk assessment; and summarizing findings.