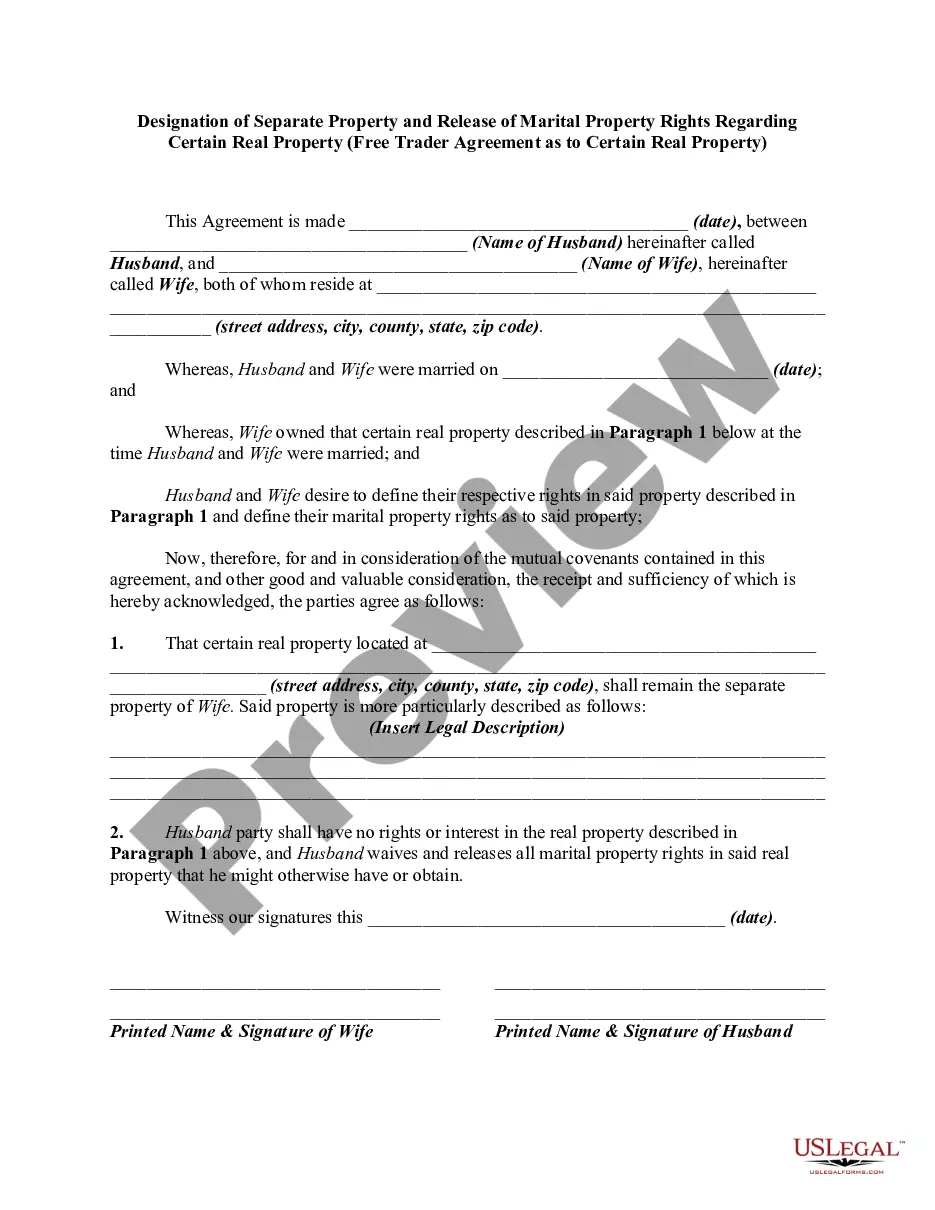
Wyoming FLSA Exempt / Nonexempt Compliance Form
Description
How to fill out FLSA Exempt / Nonexempt Compliance Form?
Selecting the finest sanctioned document format can be a challenge.
Of course, there are numerous templates available online, but how do you obtain the sanctioned type you desire.
Utilize the US Legal Forms website.
Firstly, confirm that you have selected the correct form for your city/region. You can explore the form using the Preview button and review the form outline to ensure it is the appropriate one for you.
- The service provides a vast array of templates, including the Wyoming FLSA Exempt / Nonexempt Compliance Form, suitable for both business and personal requirements.
- All the forms are reviewed by experts and meet state and federal regulations.
- If you are already registered, Log In to your account and click the Download button to retrieve the Wyoming FLSA Exempt / Nonexempt Compliance Form.
- Use your account to browse through the authorized forms you may have obtained previously.
- Visit the My documents tab in your account to download another copy of the document you need.
- If you are a new user of US Legal Forms, here are simple instructions to follow.
Form popularity
FAQ
An employee's FLSA status is whether that employee is classified as exempt or nonexempt according to the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). An employee who is nonexempt is entitled to receive overtime pay after they work a certain number of hours, while exempt employees are not eligible for overtime.
In fact, employees' right to discuss their salary is protected by law. While employers may restrict workers from discussing their salary in front of customers or during work, they cannot prohibit employees from talking about pay on their own time.
Nonexempt: An individual who is not exempt from the overtime provisions of the FLSA and is therefore entitled to overtime pay for all hours worked beyond 40 in a workweek (as well as any state overtime provisions). Nonexempt employees may be paid on a salary, hourly or other basis.
How to Make Sure You Stay Compliant with FLSA RequirementsAudit Jobs to Understand which are Exempt and Non-Exempt.Check the Minimum Wage Requirement in Your State.Pay for All Time Worked Even if it Is Unauthorized Overtime.Keep Detailed Documentation of All Non-Exempt Employees.
The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) establishes minimum wage, overtime pay, recordkeeping, and youth employment standards affecting employees in the private sector and in Federal, State, and local governments.
With few exceptions, to be exempt an employee must (a) be paid at least $23,600 per year ($455 per week), and (b) be paid on a salary basis, and also (c) perform exempt job duties. These requirements are outlined in the FLSA Regulations (promulgated by the U.S. Department of Labor).
The form of communicating a change in rate or manner of pay is not mandated by law, however, an employer and empoyee may agree to a wage payment arrangement that is other than semimonthly.
The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) establishes minimum wage, overtime pay, recordkeeping, and child labor standards affecting full-time and part-time workers in the private sector and in Federal, State, and local governments.
For the most part: no, employers may not prohibit employees from discussing compensation according to the National Labor Relations Board (NLRB) and an April 2014 Executive Order from former President Obama.
The FLSA also defines what kind of behavior can be considered working. For example, the FLSA is the reason you do not get paid for your commute to work, but you should get paid for any work you do, no matter what the time or place.