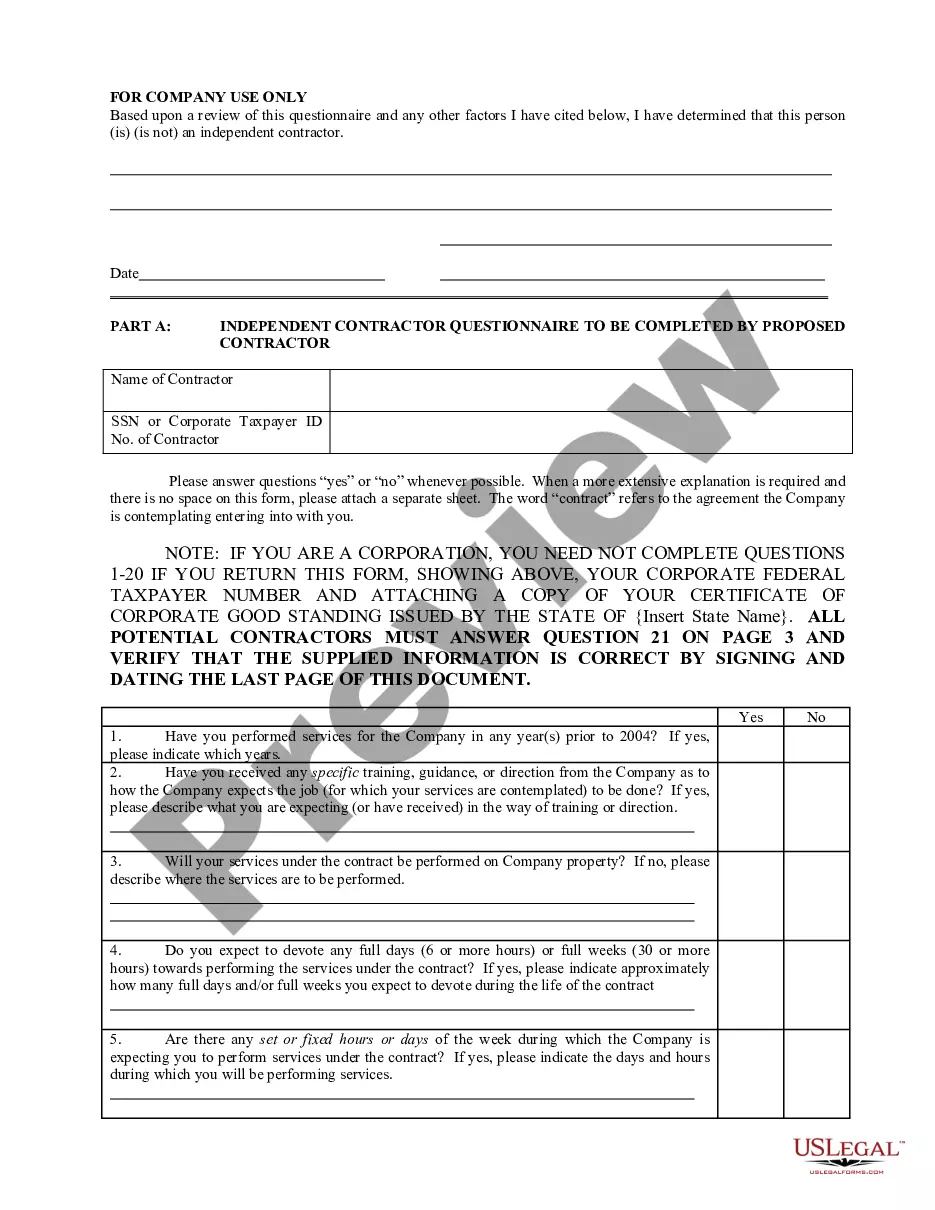
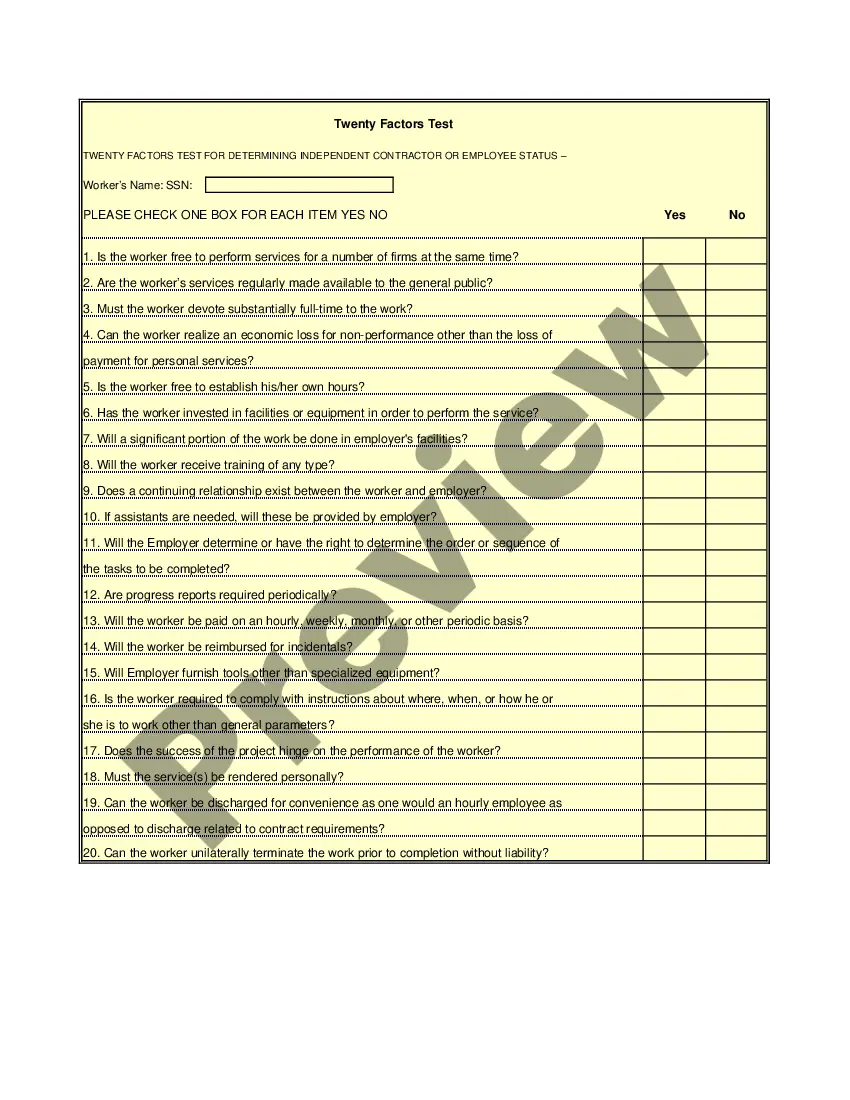
West Virginia IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status
Description
How to fill out IRS 20 Quiz To Determine 1099 Vs Employee Status?
If you need extensive, obtain, or producing legal document templates, use US Legal Forms, the largest selection of legal forms, which are available online.
Utilize the site’s straightforward and user-friendly search to locate the documents you require.
Numerous templates for business and personal purposes are organized by categories and states, or keywords.
Step 4. Once you have found the form you need, click on the Download now button. Choose the pricing plan you prefer and enter your details to register for an account.
Step 5. Complete the transaction. You can use your Visa or MasterCard or PayPal account to finalize the payment.
- Leverage US Legal Forms to find the West Virginia IRS 20 Questionnaire to Evaluate 1099 vs Employee Status with just a few clicks.
- If you are already a US Legal Forms user, sign in to your account and select the Download option to obtain the West Virginia IRS 20 Questionnaire to Evaluate 1099 vs Employee Status.
- You can also access forms you previously downloaded from the My documents section of your account.
- If this is your first time using US Legal Forms, follow the steps below.
- Step 1. Ensure you have selected the form for the correct city/state.
- Step 2. Utilize the Preview feature to review the content of the form. Don’t forget to check the description.
- Step 3. If you are not satisfied with the form, use the Search box at the top of the screen to find other variations of the legal form template.
Form popularity
FAQ
To successfully differentiate between a contractor and an employee, consider the nature of the work relationship and the level of independence. Employees typically work under an employer's direction and have fixed schedules, while contractors manage their own processes and work on a project basis. Utilizing the West Virginia IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status can help clarify this distinction. Furthermore, USLegalForms offers reliable resources to help you navigate these classifications.
The distinction between a 1099 worker and a W-2 employee primarily hinges on the degree of control and independence in the working relationship. The IRS uses specific criteria to make this determination, which you can review through the West Virginia IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status. Generally, W-2 employees tend to have employers dictating their work schedule and providing resources, whereas 1099 workers operate more independently in their business pursuits.
Several factors determine if a person is an employee or an independent contractor, including the level of control, the financial relationship, and the ongoing relationship between the worker and the employer. The IRS deeply investigates these areas to classify the worker accurately. To navigate this complexity, consider using the West Virginia IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status, which simplifies this process.
To determine whether a person is an employee or an independent contractor, look at the relationship dynamics, control factors, and financial considerations. Analyze how much independence the worker has, how they receive compensation, and the nature of the work. The West Virginia IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status can provide a structured approach to make an informed decision.
The IRS places the most weight on behavioral control when determining whether a person is an employee or an independent contractor. This aspect examines how much control the employer has over how work gets done. It’s essential to understand this criterion thoroughly. The West Virginia IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status can assist you in assessing behavioral control effectively.
The IRS employs three tests to evaluate employment status: the behavioral test, the financial test, and the relationship test. The behavioral test assesses whether the employer controls how work is performed. The financial test looks at how payments are made and whether the worker has a significant investment in their work. Lastly, the relationship test considers any agreements and the nature of benefits provided. The West Virginia IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status can help you apply these tests.
To distinguish between a W-2 employee and a 1099 independent contractor, assess the level of control and independence in the working relationship. Employees typically follow a set schedule, receive benefits, and perform work under direct supervision. In contrast, independent contractors usually operate with greater autonomy. The West Virginia IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status provides valuable insights for making this determination.
The IRS uses the West Virginia IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status to assess whether a worker is an independent contractor or employee. This quiz evaluates the degree of control a business has over the worker and the nature of the working relationship. Key factors include the level of instruction, the integration into the business, and whether the worker provides their tools. Understanding these criteria can help you classify workers correctly and ensure compliance with tax regulations.