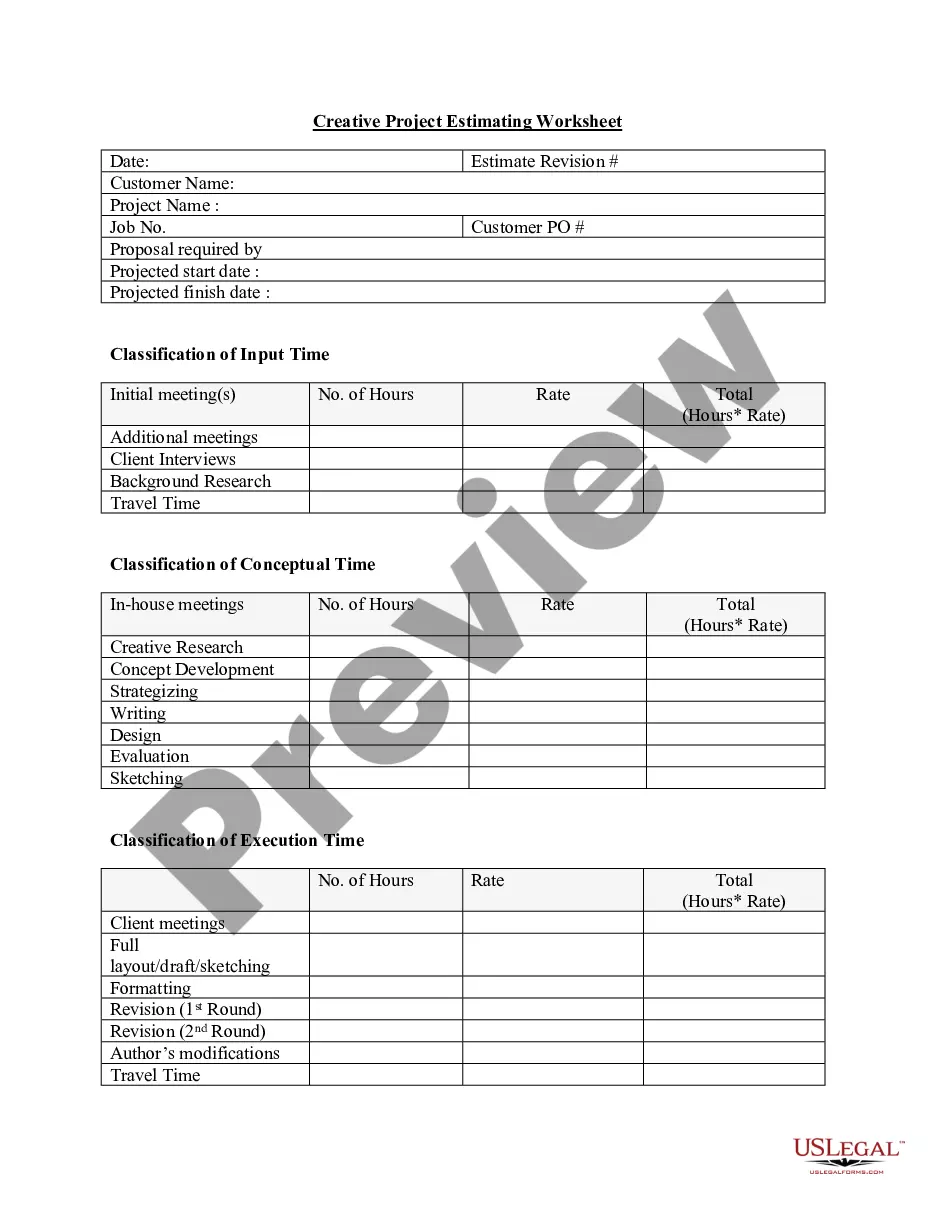
Wisconsin Classification of Employees for Personnel Manual or Employee Handbook regarding Full Time, Part Time, Temporary, Leased, Exempt, and Nonexempt Employees
Description
How to fill out Classification Of Employees For Personnel Manual Or Employee Handbook Regarding Full Time, Part Time, Temporary, Leased, Exempt, And Nonexempt Employees?
Are you currently in a situation where you frequently require documents for either professional or personal purposes? There are numerous legal document templates available online, but finding reliable ones can be challenging.
US Legal Forms offers thousands of document templates, such as the Wisconsin Classification of Employees for Personnel Manual or Employee Handbook related to Full Time, Part Time, Temporary, Leased, Exempt, and Nonexempt Employees, designed to meet both state and federal requirements.
If you are already familiar with the US Legal Forms website and possess an account, simply Log In. After that, you can download the Wisconsin Classification of Employees for Personnel Manual or Employee Handbook for Full Time, Part Time, Temporary, Leased, Exempt, and Nonexempt Employees template.
Choose a convenient file format and download your copy.
Access all the document templates you have purchased in the My documents section. You can download an additional copy of the Wisconsin Classification of Employees for Personnel Manual or Employee Handbook for Full Time, Part Time, Temporary, Leased, Exempt, and Nonexempt Employees anytime if needed. Just select the required form to download or print the template.
- If you do not have an account and want to start using US Legal Forms, follow these steps.
- Find the form you need and ensure it is suitable for your state/region.
- Use the Review option to evaluate the form.
- Read the information to ensure you have selected the correct form.
- If the form does not meet your requirements, use the Research field to find the form that fits your needs.
- Once you find the appropriate form, click Acquire now.
- Select the pricing plan you prefer, fill out the necessary information to create your account, and pay for the transaction using your PayPal or credit card.
Form popularity
FAQ
A company might decide to change a position from exempt to non-exempt for various reasons, primarily related to compliance with labor laws or budgetary constraints. This shift can help the company ensure it meets legal standards for employee classifications under the Wisconsin Classification of Employees for Personnel Manual or Employee Handbook regarding Full Time, Part Time, Temporary, Leased, Exempt, and Nonexempt Employees, which can minimize legal risks. Additionally, changing classifications may help firms manage labor costs more effectively, especially in industries where overtime demands fluctuate. Being transparent with employees during this transition will maintain trust and clear communication.
The classification of a position as exempt or non-exempt under Wisconsin law hinges on specific criteria set forth in the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). This includes considerations of job duties, salary level, and salary basis. Generally, jobs that involve managerial responsibilities, specialized expertise, or sales outside of a fixed location tend to fall under the exempt category. Understanding these distinctions can aid employers in accurately aligning roles with the Wisconsin Classification of Employees for Personnel Manual or Employee Handbook regarding Full Time, Part Time, Temporary, Leased, Exempt, and Nonexempt Employees, enhancing compliance and job satisfaction.
Employment on an at-will basis means that the employment relationship can end at any time, by either the employer or employee, without prior notice or reason. This concept is crucial for understanding the Wisconsin Classification of Employees for Personnel Manual or Employee Handbook regarding Full Time, Part Time, Temporary, Leased, Exempt, and Nonexempt Employees. Both parties should embrace this flexibility while considering the implications for job security and employment stability.
Yes, a statement in the employee handbook can be considered a term of the employment contract if it establishes expectations or obligations that are reasonable and clear. In light of the Wisconsin Classification of Employees for Personnel Manual or Employee Handbook regarding Full Time, Part Time, Temporary, Leased, Exempt, and Nonexempt Employees, it is vital for both parties to recognize these terms. However, they should not conflict with state or federal laws to ensure enforceability.
When an employment-at-will statement is present in a personnel policy, it signifies that the employment relationship can be terminated spontaneously, without a requirement for cause. This stipulation is crucial in the Wisconsin Classification of Employees for Personnel Manual or Employee Handbook regarding Full Time, Part Time, Temporary, Leased, Exempt, and Nonexempt Employees, as it sets the groundwork for flexible employment arrangements. Therefore, employees understand that while they can leave at will, employers retain the same right.
The at-will statement in the employee handbook clarifies the employment relationship and outlines the mutual understanding that either party can end the employment at any time. This statement is essential within the framework of the Wisconsin Classification of Employees for Personnel Manual or Employee Handbook regarding Full Time, Part Time, Temporary, Leased, Exempt, and Nonexempt Employees. It helps prevent misunderstandings regarding job security and long-term commitments.
Employment-at-will is a legal doctrine that allows either the employer or the employee to terminate the employment relationship at any time, for any reason that is not illegal. In the context of the Wisconsin Classification of Employees for Personnel Manual or Employee Handbook regarding Full Time, Part Time, Temporary, Leased, Exempt, and Nonexempt Employees, this means that unless explicitly stated otherwise, employment is not guaranteed for a certain duration. This flexibility benefits staffing needs while granting employees the freedom to seek better opportunities.
Salaried exempt employees in Wisconsin often work well beyond the standard 40 hours a week. While there are no legal caps on working hours, employers should ensure that workloads remain manageable to avoid exhaustion and maintain productivity. Detailing these expectations in your employee handbook can align your company’s practices with employee well-being. This consideration is essential within the Wisconsin Classification of Employees for Personnel Manual or Employee Handbook regarding Full Time, Part Time, Temporary, Leased, Exempt, and Nonexempt Employees.
In Wisconsin, full-time employment typically refers to positions that require employees to work at least 30 hours per week. Employers have some discretion in defining what 'full-time' means in their personnel manuals. However, it is best practice to be consistent and clearly communicate the criteria to avoid confusion. This clarity supports accurate Wisconsin Classification of Employees for Personnel Manual or Employee Handbook regarding Full Time, Part Time, Temporary, Leased, Exempt, and Nonexempt Employees.
In Wisconsin, salaried employees cannot be 'forced' to work a specific number of hours, but employers must ensure that work demands are reasonable. While many salaried positions expect full-time commitments, overworking employees can lead to burnout and legal issues. Clearly defined limits in your employee handbook can promote a healthy work environment and clarify expectations regarding employee duties. This guidance is essential for the Wisconsin Classification of Employees for Personnel Manual or Employee Handbook regarding Full Time, Part Time, Temporary, Leased, Exempt, and Nonexempt Employees.