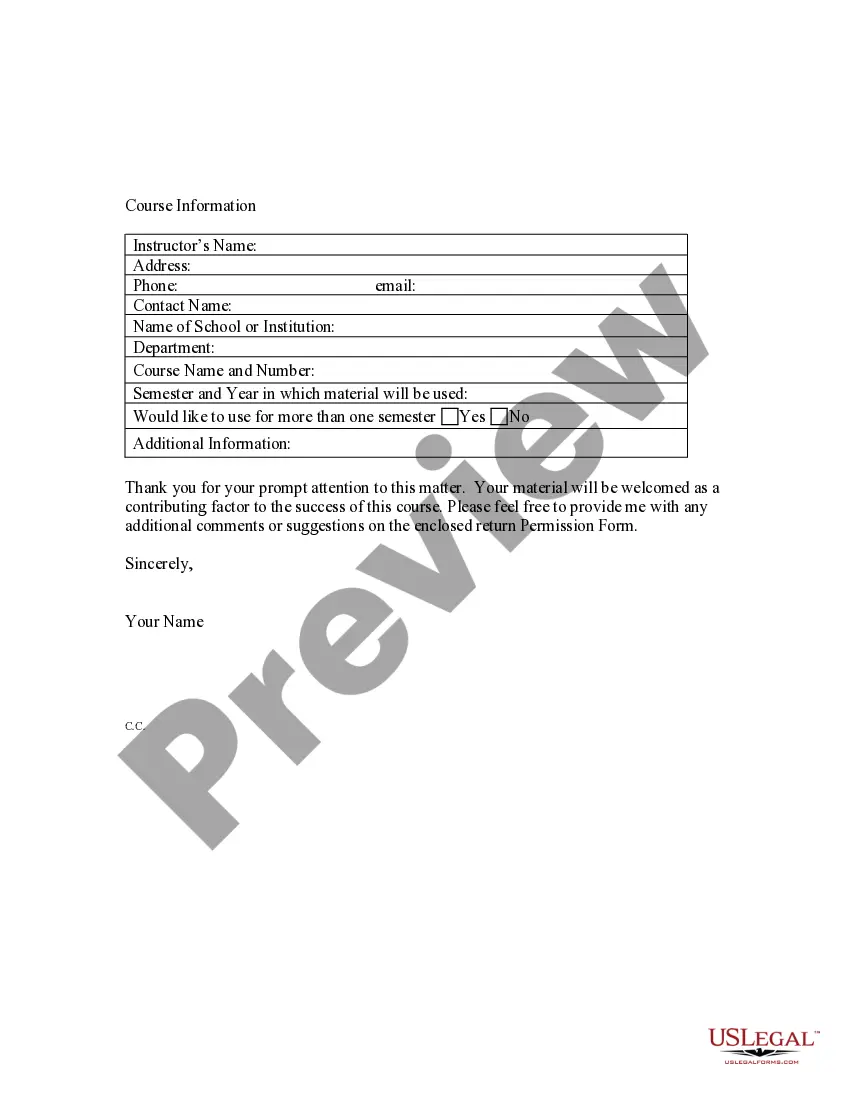
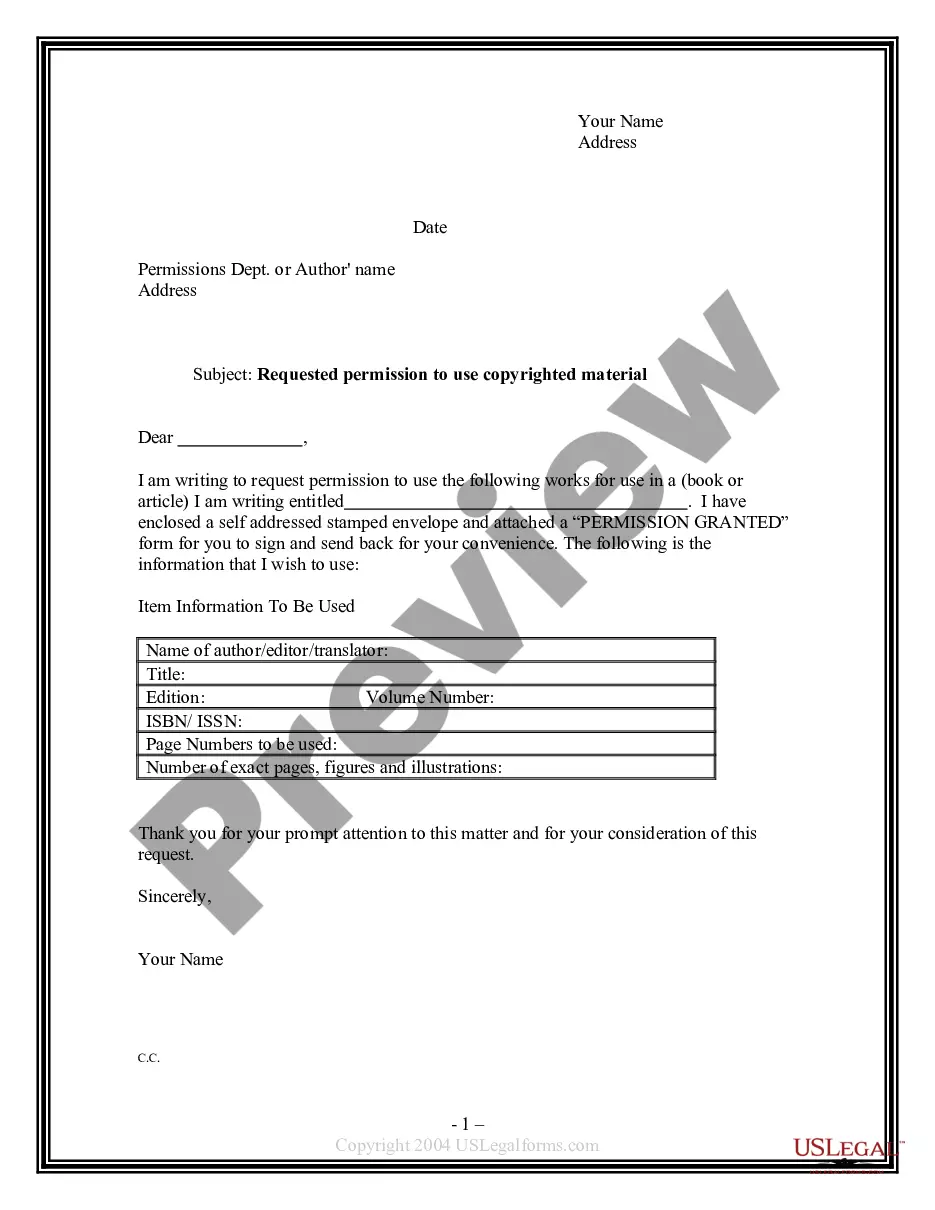
Vermont Permission Request to Use Copyrighted Material For Class
Description
How to fill out Permission Request To Use Copyrighted Material For Class?
It is feasible to spend numerous hours online attempting to locate the legal document template that satisfies the federal and state stipulations you need.
US Legal Forms offers thousands of legal forms that are assessed by professionals.
It is easy to acquire or create the Vermont Permission Request to Use Copyrighted Material for Class from the service.
If available, use the Preview button to review the document template as well. If you wish to find another version of the form, use the Search field to locate the template that meets your needs and criteria. Once you have found the template you require, click Get now to proceed. Select the pricing plan you desire, enter your details, and register for an account on US Legal Forms. Complete the transaction. You can use your credit card or PayPal account to pay for the legal form. Choose the format of the document and download it to your device. Make adjustments to your document if needed. You can fill out, modify, sign, and print the Vermont Permission Request to Use Copyrighted Material for Class. Download and print thousands of document templates using the US Legal Forms Website, which provides the largest collection of legal forms. Utilize professional and state-specific templates to address your business or personal needs.
- If you already possess a US Legal Forms account, you can Log In and click the Download button.
- After that, you can fill out, modify, print, or sign the Vermont Permission Request to Use Copyrighted Material for Class.
- Every legal document template you purchase is your property forever.
- To obtain another copy of the purchased form, go to the My documents section and click the corresponding button.
- If you are using the US Legal Forms website for the first time, follow the simple instructions below.
- First, ensure you have selected the correct document template for your state/city of your choice.
- Check the form description to confirm you have chosen the appropriate form.
Form popularity
FAQ
To ask for permission to use copyrighted material, you should start by identifying the copyright owner. Once you know who holds the rights, draft a clear Vermont Permission Request to Use Copyrighted Material For Class. This request should include details about how you plan to use the material, such as the purpose, duration, and distribution. Don't forget to provide your contact information, so the owner can easily respond to your request.
When writing a letter to request permission to use copyrighted material, start with a polite introduction that states your purpose. Clearly identify the material you wish to use and describe how you plan to use it in your project. Include a Vermont Permission Request to Use Copyrighted Material for Class to ensure clarity and completeness. Platforms like USLegalForms provide templates that can guide you in creating a professional and effective request.
Requesting permission to use copyrighted material involves contacting the copyright holder to explain your intended use. You should clearly outline how the material will be used, the context, and the duration of use. Submitting a Vermont Permission Request to Use Copyrighted Material for Class is essential to ensure you have legal clearance. Tools like USLegalForms can assist you in crafting a formal request that includes all necessary details.
To legally use copyrighted material in a school project, you must first assess whether your use qualifies as fair use. Fair use allows for limited use of copyrighted material without permission, but it depends on factors like purpose, nature, amount used, and market impact. If your use does not meet fair use criteria, you should submit a Vermont Permission Request to Use Copyrighted Material for Class to the copyright holder for approval. Utilizing platforms like USLegalForms can help streamline this process.
The Fair Use Doctrine and Education That section of the Copyright Act says that there's no copyright infringement if the use of the material is fair, in other words "for purposes such as criticism, comment, news reporting, teaching (including multiple copies for classroom use), scholarship, or research."
Yes, You Can Use Copyrighted Material in the Classroom.
The four factors of fair use:The purpose and character of the use, including whether such use is of commercial nature or is for nonprofit educational purposes.The nature of the copyrighted work.The amount and substantiality of the portion used in relation to the copyrighted work as a whole.More items...
Fair use permits a party to use a copyrighted work without the copyright owner's permission for purposes such as criticism, comment, news reporting, teaching, scholarship, or research.
Rights in your copyrighted works: assignments, projects, papers, and theses. When a student creates an original and creative assignment, project, paper, or thesis, the student holds copyright in that work, automatically, without any need to register the work to obtain a copyright.
Section 107 of the Copyright Act gives examples of purposes that are favored by fair use: criticism, comment, news reporting, teaching (including multiple copies for classroom use), scholarship, and research. Use for one of these illustrative purposes is not automatically fair, and uses for other purposes can be