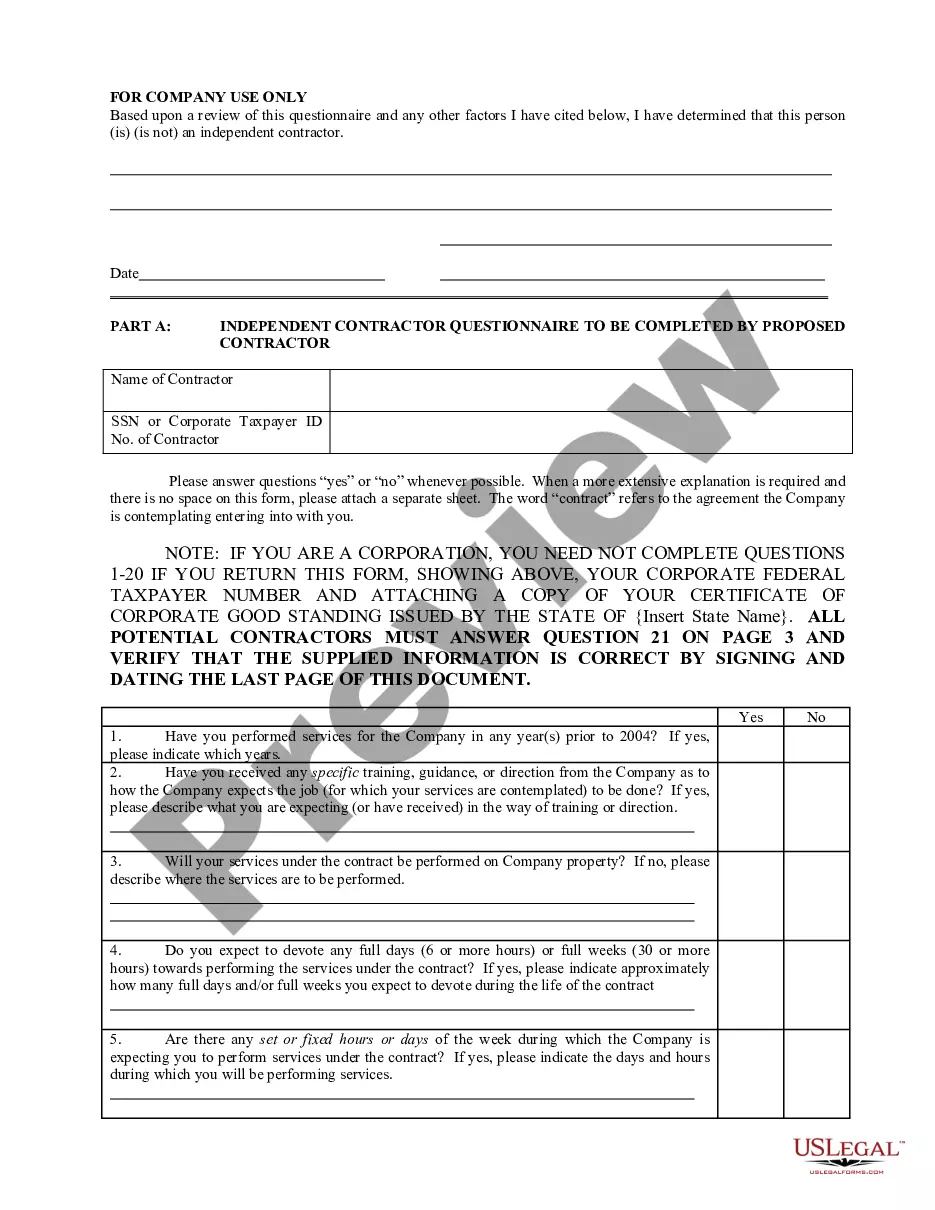
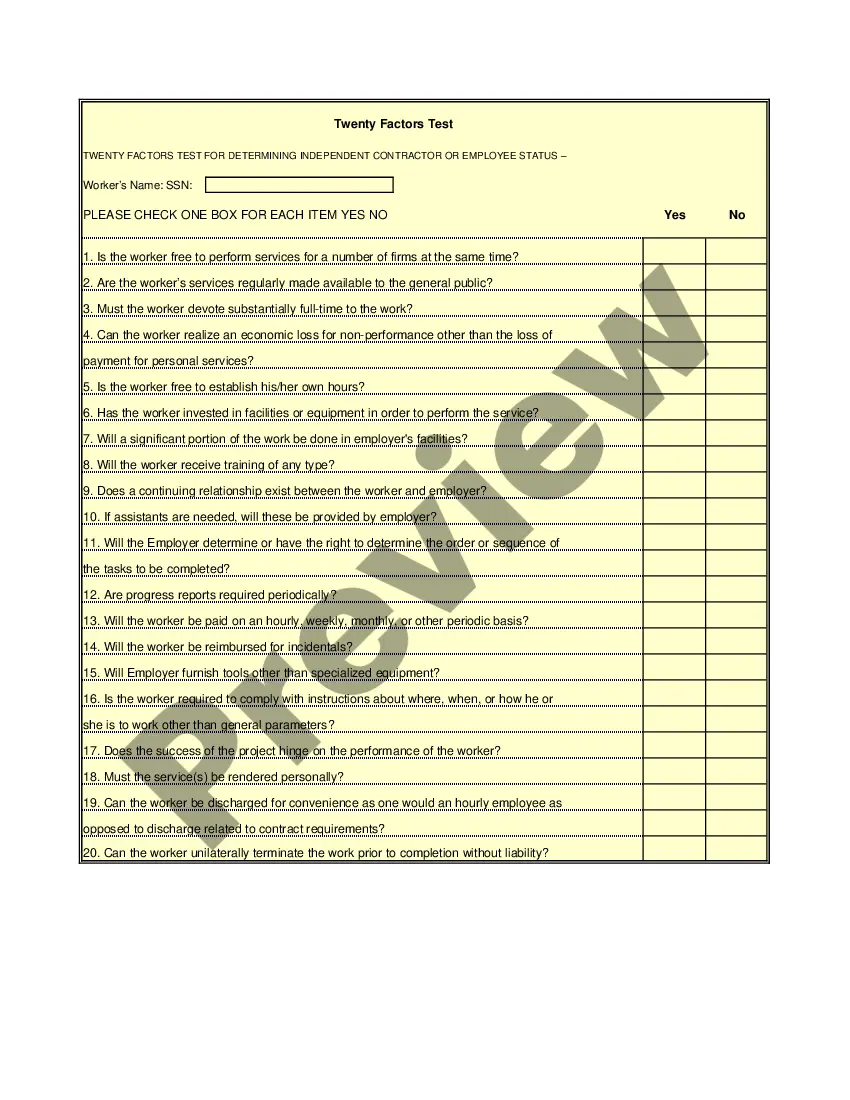
Vermont IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status
Description
How to fill out IRS 20 Quiz To Determine 1099 Vs Employee Status?
Are you currently in a situation where you require documents for either business or personal reasons almost all the time.
There are many authentic document templates available online, but finding forms you can rely on is challenging.
US Legal Forms offers a vast array of document templates, including the Vermont IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status, which are designed to meet state and federal requirements.
You can find all the document templates you have purchased in the My documents section. You can access an additional copy of the Vermont IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status anytime, if needed. Just click the necessary form to download or print the document template.
Utilize US Legal Forms, the most extensive collection of authentic forms, to save time and prevent mistakes. The service provides professionally crafted legal document templates that can be used for a variety of purposes. Create an account on US Legal Forms and start simplifying your life.
- If you are already familiar with the US Legal Forms website and have an account, simply Log In.
- Then, you can download the Vermont IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status template.
- If you do not have an account and want to start using US Legal Forms, follow these steps.
- Find the form you need and ensure it is for the correct city/county.
- Use the Review button to check the form.
- Read the description to ensure you have selected the right form.
- If the form is not what you’re looking for, use the Lookup field to find the document that suits your needs.
- When you find the right form, click Acquire now.
- Select the pricing plan you prefer, fill in the required information to create your account, and pay for the order using your PayPal or credit card.
- Choose a convenient document format and download your copy.
Form popularity
FAQ
To determine independent contractor status, you should assess control, relationship, and financial arrangements. Begin by asking how much control the worker has over their work schedule and methods. Then, consider the nature of the relationship; does the worker receive benefits typically given to employees, or do they manage their own business activities? Finally, evaluate if the individual has a significant investment in tools and materials, which often indicates independent contractor status. The Vermont IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status can help clarify these distinctions.
To determine if a person is an employee or an independent contractor, consider evaluating control, payment structure, and the contextual relationship. This process may seem daunting; however, using tools like the Vermont IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status can help clarify these distinctions and guide you toward a correct classification.
Determining whether someone is a W-2 employee or a 1099 independent contractor can be streamlined by assessing the degree of control over the work performed. Generally, W-2 employees have more significant oversight than 1099 contractors. The Vermont IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status can assist individuals and businesses in making this distinction clearer.
The designation of an individual as either an employee or an independent contractor is determined by various factors, including control, relationship, and job responsibilities. The IRS sets forth specific criteria, which can be complex. To simplify this understanding, the Vermont IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status can be a valuable resource.
When assessing independent contractor status, several key questions arise. Questions may focus on control, payment methods, and the nature of the work relationship. Exploring the Vermont IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status can guide your understanding of these essential inquiries.
The IRS utilizes specific guidelines to determine if a worker qualifies as an independent contractor. They examine the degree of control the employer has over how the work is performed, along with other relevant factors. The Vermont IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status offers clarity in these determinations, ensuring you understand the differences.
The three primary tests used to determine if someone is an employee include the behavioral test, the financial test, and the relationship test. These tests assess who controls how and when the work is done, how payment is made, and how the worker perceives their relationship with the employer. Utilizing the Vermont IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status can simplify evaluating these aspects.
Determining whether a person is an employee or an independent contractor largely depends on the nature of the relationship between the worker and the employer. The Vermont IRS 20 Quiz to Determine 1099 vs Employee Status is a helpful tool in this area. It considers factors like behavioral control, financial control, and the relationship between the parties to classify the worker correctly.