Arbitration is an alternative means of settling a dispute by impartial persons without proceeding to a court trial. It is sometimes preferred as a means of settling a matter in order to avoid the expense, delay, and acrimony of litigation. There is no discovery and there are simplified rules of evidence in arbitration. The arbitrator or arbitrators are selected directly by the parties or are chosen in accordance with the terms of a contract in which the parties have agreed to use a court-ordered arbitrator or an arbitrator from the American Arbitration Association.
Courts have the inherent authority to supervise the charging of fees for legal services under their power to regulate the practice of law. A growing number of states, the courts and bar associations are seeking to encourage out-of-court resolution of fee disputes between attorneys and clients in alternative dispute resolution programs established and administered by bar associations. Typically these programs provide a client with the opportunity to voluntarily submit a fee dispute to either arbitration or mediation.
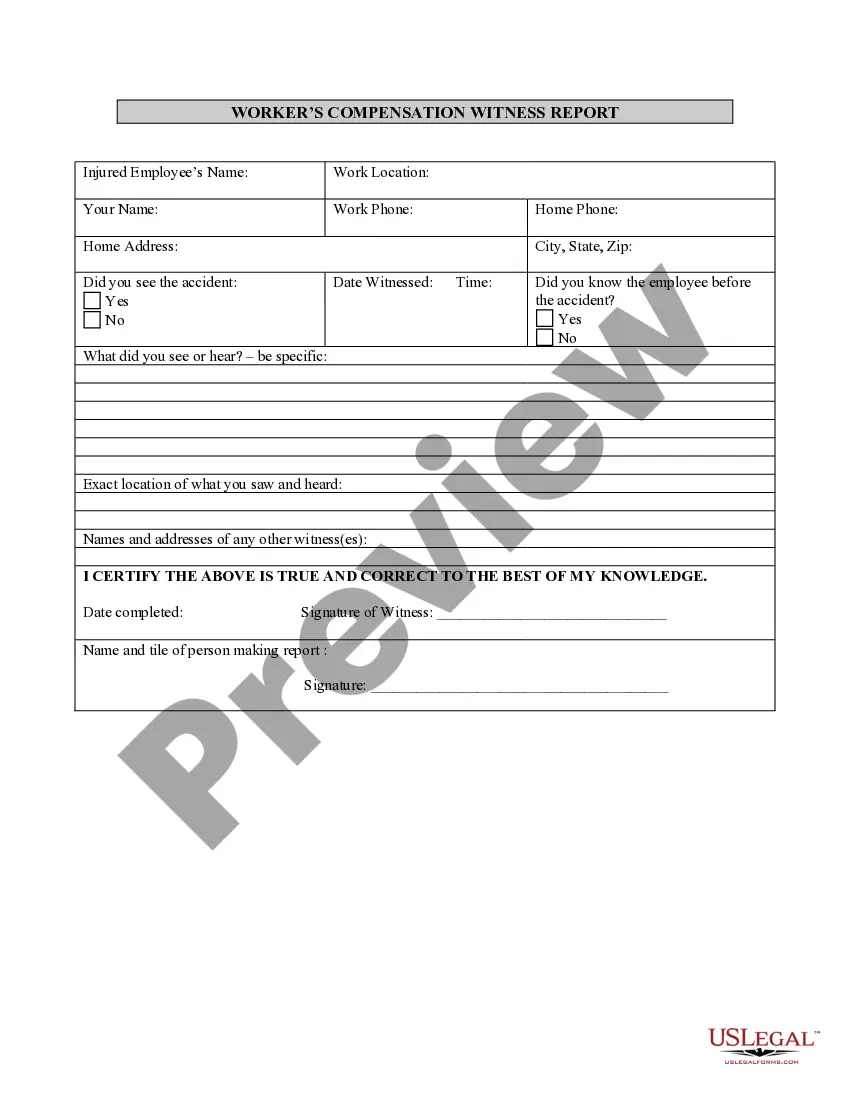
This form is a generic example that may be referred to when preparing such a form for your particular state. It is for illustrative purposes only. Local laws should be consulted to determine any specific requirements for such a form in a particular jurisdiction.