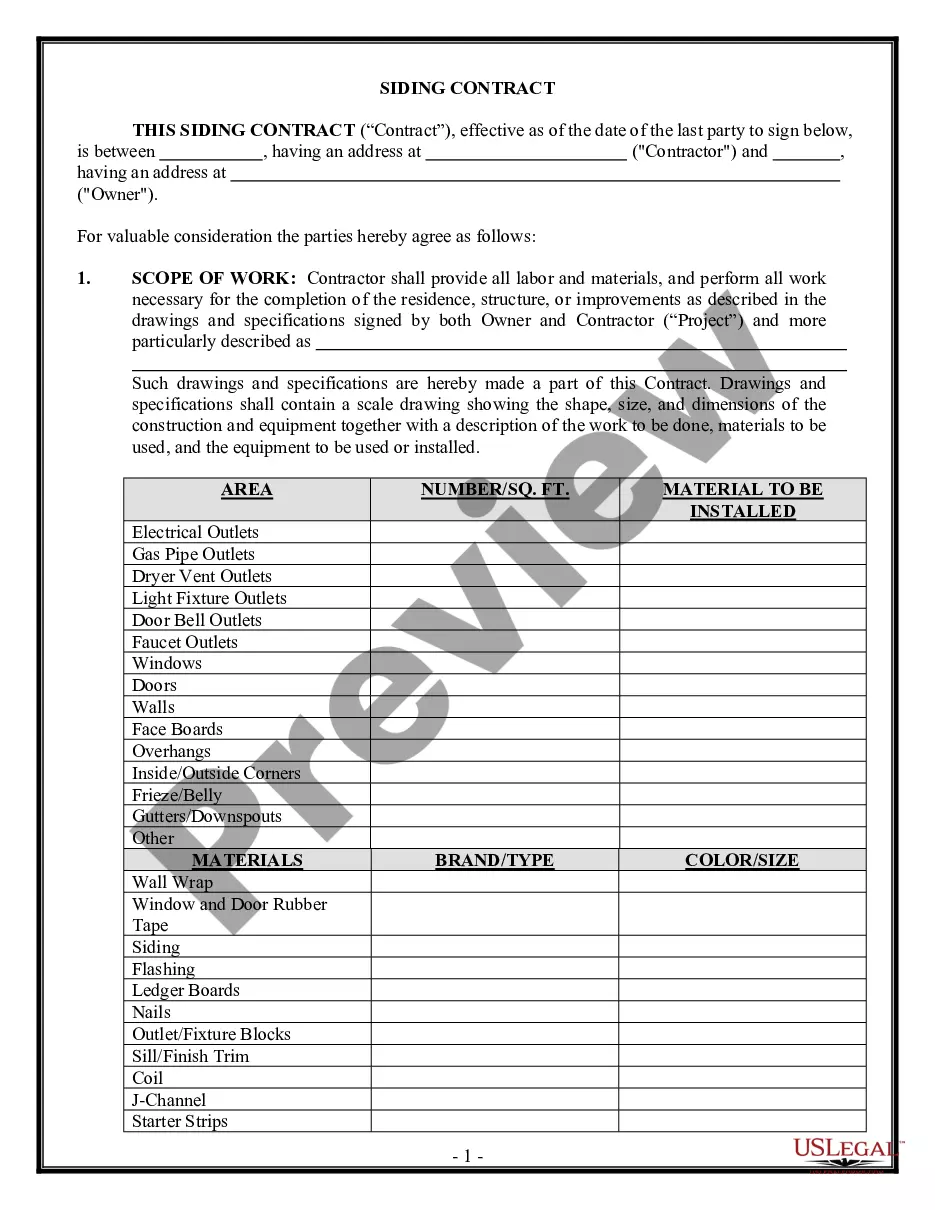
Petition for Removal of Minority - Emancipation
Description
Key Concepts & Definitions
Minority Emancipation: The legal process by which a minor (person under the age of 18 in most states) becomes an adult in the eyes of the law. This involves the rights to manage their own finances, make personal decisions, and live independently.
Petition for Removal of Minority Emancipation: A legal document submitted to a court to revoke the emancipated status of a minor, typically initiated by a guardian or parent.
Step-by-Step Guide to Petition for Removal of Minority Emancipation
- Gather Necessary Documentation: Collect relevant documents such as the original minority emancipation form, real estate documents if applicable, and name change paperwork.
- Consult a Lawyer: Seek free legal consultation to understand the implications and process. This step is crucial for navigating state-specific laws effectively.
- File the Petition: Complete the required forms with guidance from legal counsel and submit them to the appropriate family court.
- Parental Consent: If needed, obtain consent from both parents, adhering to the parental consent age requirements set by state law.
- Use Technology: Utilize esignature device compatibility through platforms like airslate signnow for submitting documents, ensuring compatibility with your devices.
- Attend the Hearing: Both the minor and the petitioner must be present at the court hearing to discuss the reasons for the revocation of emancipation.
Risk Analysis
Petitioning for the removal of minority emancipation involves risks such as legal repercussions for the minor, potential strain on family relationships, and the uncertainty of court decisions, which may not always favor the petitioner. Furthermore, the court might investigate the reasons behind the petition, requiring thorough justification.
Pros & Cons
- Pros: Revoking emancipation can protect minors from financial mismanagement and poor decision-making.
- Cons: The legal process can be lengthy and emotionally taxing for all parties involved.
Best Practices
When petitioning for the removal of minority emancipation, it's recommended to maintain clear and open communication with all involved parties, ensure all documents are meticulously prepared, and engage a skilled attorney who specializes in family law.
How to fill out Petition For Removal Of Minority - Emancipation?
When it comes to drafting a legal document, it is easier to delegate it to the experts. Nevertheless, that doesn't mean you yourself cannot get a sample to use. That doesn't mean you yourself cannot find a template to use, however. Download Petition for Removal of Minority - Emancipation straight from the US Legal Forms site. It provides a wide variety of professionally drafted and lawyer-approved forms and templates.
For full access to 85,000 legal and tax forms, users simply have to sign up and select a subscription. After you are signed up with an account, log in, find a particular document template, and save it to My Forms or download it to your device.
To make things easier, we have included an 8-step how-to guide for finding and downloading Petition for Removal of Minority - Emancipation fast:
- Make sure the form meets all the necessary state requirements.
- If available preview it and read the description before buying it.
- Click Buy Now.
- Select the suitable subscription for your needs.
- Make your account.
- Pay via PayPal or by credit/visa or mastercard.
- Choose a needed format if several options are available (e.g., PDF or Word).
- Download the file.
After the Petition for Removal of Minority - Emancipation is downloaded it is possible to fill out, print and sign it in any editor or by hand. Get professionally drafted state-relevant documents within a matter of seconds in a preferable format with US Legal Forms!
Form popularity
FAQ
How can a minor become legally emancipated in Texas? A minor who wishes to have the legal capacity of an adult can petition a Texas court for the removal of disabilities of minority. This process is also known as emancipation.
Once a child is emancipated, his or her parents do not have custody or control of him or her anymore. Emancipation is usually forever. But the court can cancel the emancipation if the minor asking for the emancipation lies to the court or is no longer able to support himself or herself.
Your parents or legal guardian must have consented or acquiesced to your living away from them. Parental consent is generally required for a teen to become emancipated.
If you will be 18 in six months or less, there isn't time to complete the court process which takes four to six months. If you decide emancipation is the right option for you, you must go through some specific court procedures.
Additionally, emancipation can be revoked or canceled by court order. For example, emancipation may be revoked when the minor is convicted of a crime or is revealed to have lied to the court during their emancipation hearing.
If you will be 18 in six months or less, there isn't time to complete the court process which takes four to six months. If you decide emancipation is the right option for you, you must go through some specific court procedures.
To pursue emancipation through court decree, you can file for a declaration of emancipation without your parent's permission. If you need assistance with the process, you can contact a local or state legal aid organization.
In California, for example, minors as young as 14 may become emancipated. States that allow for judicial emancipation will consider whether it serves the minor's best interests.
Once you reach 16, although you cannot do everything that an adult can do, there are decisions you can make that your parents cannot object to, as well as certain things that you can only do with parental consent. You can leave home with or without your parents' consent as long as your welfare is not at risk.